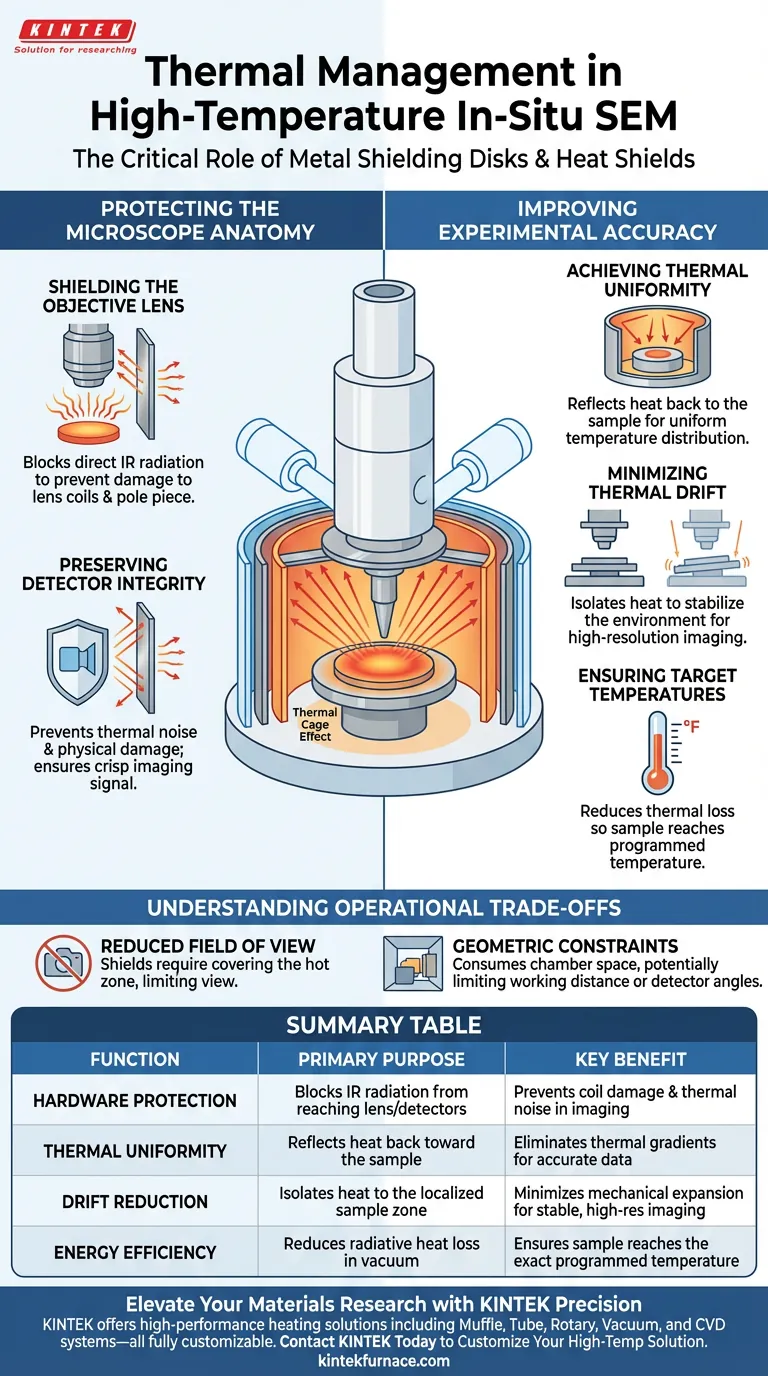
Metal shielding disks and heat shields are essential thermal management components in high-temperature in-situ Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). They serve a dual purpose: protecting the microscope's sensitive hardware from destructive heat and creating a stable thermal environment for the sample. By containing thermal radiation, these barriers ensure accurate experimentation and prevent image artifacts caused by thermal drift.
High-temperature SEM requires a delicate balance between heating the sample and keeping the microscope cool. Shielding components bridge this gap, preventing radiation damage to the column while ensuring the sample actually reaches the programmed temperature.
Protecting the Microscope Anatomy
The environment inside an SEM column is highly sensitive. Introducing a heat source poses significant risks to the precision instruments located millimeters away from the sample.
Shielding the Objective Lens
The objective lens is often located very close to the sample to achieve high resolution.
Without shielding, the intense heat radiating from the sample stage can damage the lens coils or pole piece. Metal disks act as a physical barrier, blocking this direct line-of-sight radiation.
Preserving Detector Integrity
Detectors, such as Secondary Electron (SE) or Backscattered Electron (BSE) detectors, are vulnerable to thermal noise and physical damage.
Heat shields prevent infrared radiation from flooding these detectors. This protection preserves the signal-to-noise ratio, ensuring that the image remains crisp rather than washed out by thermal interference.
Improving Experimental Accuracy
Beyond protection, shielding plays a critical scientific role. It ensures that the data collected reflects the true behavior of the material at the intended temperature.
Achieving Thermal Uniformity
In a vacuum, heat is lost primarily through radiation. Without shields, the sample surface radiates heat away faster than the heater can supply it.
This leads to significant thermal gradients. Shielding reflects this radiation back toward the sample, creating a "thermal cage" that improves temperature uniformity across the heating zone.
Minimizing Thermal Drift
Temperature fluctuations cause mechanical expansion and contraction in the microscope stage, known as thermal drift.
Drift causes the image to move across the screen, making it impossible to focus or capture high-resolution video of dynamic processes. By isolating the heat, shields stabilize the local environment and significantly reduce this movement.
Ensuring Target Temperatures
A common failure in high-temp SEM is a mismatch between the programmed temperature and the actual sample temperature.
Shields reduce thermal loss, ensuring the sample actually reaches the temperature set by the controller. This validates that your experimental results correlate accurately with the specific thermal conditions you intended to test.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
While shielding is vital, it introduces physical constraints to the experiment that must be managed.
Reduced Field of View
Effective shielding requires covering as much of the hot zone as possible.
Geometric Constraints
The addition of disks and shields consumes valuable space within the chamber.
This can limit the working distance or restrict the angles available for specific detectors, potentially requiring a compromise between thermal stability and imaging geometry.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the success of your in-situ experiment, prioritize the function of the shield based on your specific data requirements.
- If your primary focus is Equipment Safety: Prioritize thick, multi-layered metal shields that completely block the line of sight to the pole piece and detectors.
- If your primary focus is Temperature Accuracy: Ensure the shielding creates a near-enclosed environment to minimize radiative loss and maximize thermal uniformity.
- If your primary focus is Image Stability: Focus on lightweight shielding designs that isolate the heating element to prevent thermal expansion in the surrounding stage components.
Ultimately, proper shielding transforms high-temperature microscopy from a hazardous variable into a controlled, precise analytical technique.
Summary Table:
| Function | Primary Purpose | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware Protection | Blocks IR radiation from reaching lens/detectors | Prevents coil damage and thermal noise in imaging |
| Thermal Uniformity | Reflects heat back toward the sample | Eliminates thermal gradients for accurate data |
| Drift Reduction | Isolates heat to the localized sample zone | Minimizes mechanical expansion for stable, high-res imaging |
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces radiative heat loss in vacuum | Ensures sample reaches the exact programmed temperature |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK Precision
Thermal management is the difference between a successful experiment and costly equipment failure. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance heating solutions including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique lab requirements.
Whether you are performing sensitive in-situ SEM or large-scale material synthesis, our thermal experts are here to help you achieve perfect temperature uniformity and equipment longevity.
Contact KINTEK Today to Customize Your High-Temp Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Jérôme Mendonça, Renaud Podor. Development of a microfurnace dedicated to <i>in situ</i> scanning electron microscope observation up to 1300 °C. III. <i>In situ</i> high temperature experiments. DOI: 10.1063/5.0207477
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is the use of high-vacuum pump groups critical for photothermal catalytic chamber pre-treatment?
- What is the significance of using a quartz boat as a catalyst carrier? Optimize Purity and Kinetics in CCVD
- Why is a vacuum drying oven necessary for Al2O3/TiC ceramic powders? Ensure Purity and Prevent Agglomeration
- What happens during the 180-degree rotation of the impeller in a water circulating vacuum pump? Uncover the Suction Mechanism
- What is the purpose of waveguide-to-coax adapters? Key Roles in High-Temperature Measurement Chains
- Why is the integration of a K-type thermocouple and a data logger necessary for Vanadis 60 steel? Unlock Precision.
- What are the specific functions of high-purity graphite molds in SPS? Optimize Your Sintering Process
- Why is a Pt5%Au crucible required for S53P4 bioactive glass? Ensure Purity at 1400°C














