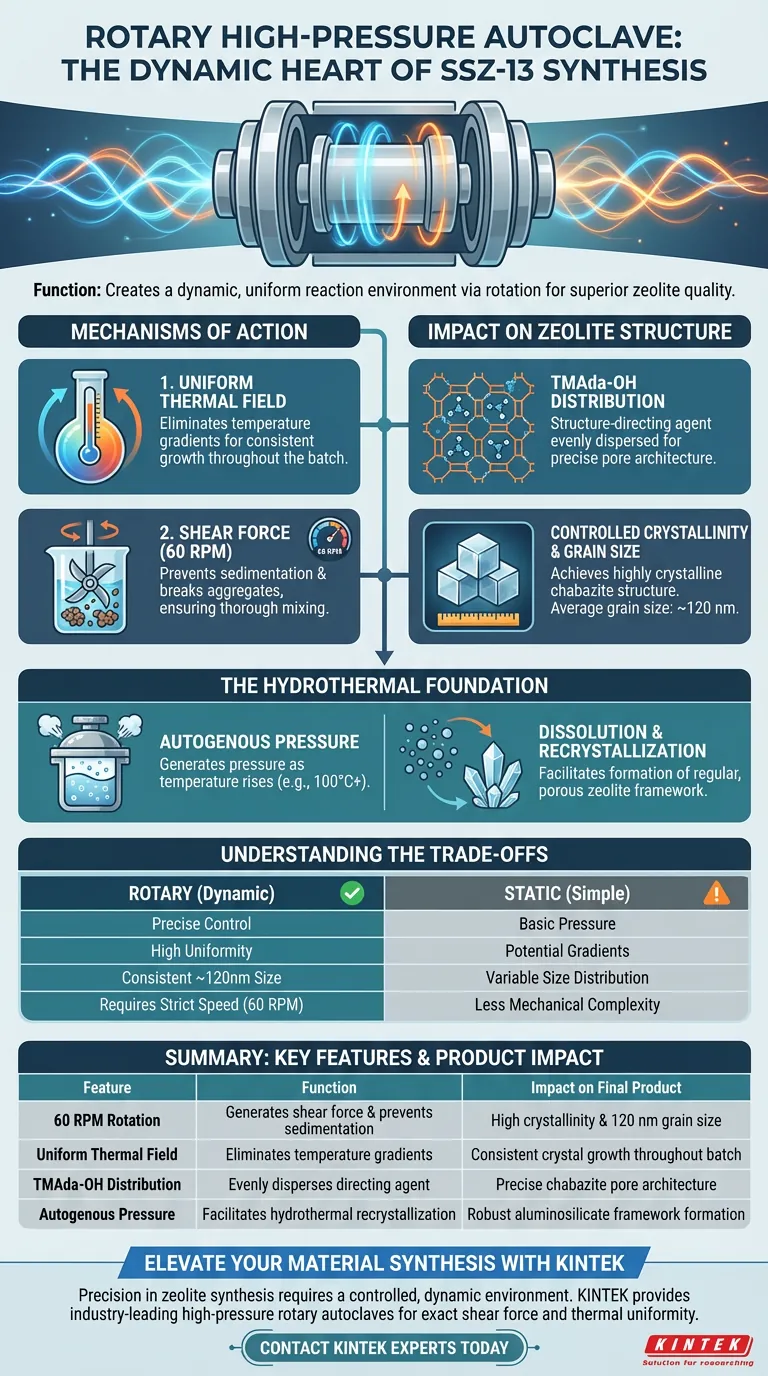
The primary function of a rotary high-pressure autoclave in SSZ-13 synthesis is to create a dynamic reaction environment through the generation of a uniform thermal field and shear force. Typically operating at a rotation speed of 60 rpm, this equipment facilitates the thorough mixing of the synthesis gel components. This mechanical action ensures the structure-directing agent (TMAda-OH) is evenly distributed throughout the aluminosilicate framework, which is essential for achieving a specific grain size and high crystallinity.
The rotary autoclave goes beyond simple containment by introducing kinetic energy into the synthesis. It ensures that the chemical interaction between the gel and the directing agent is uniform, directly resulting in a highly crystalline chabazite structure with controlled particle dimensions.
Mechanisms of Action
Creating a Uniform Thermal Field
In static synthesis, temperature gradients can occur within the reactor, leading to inconsistent crystal growth. A rotary autoclave eliminates this issue by continuously moving the mixture.
This rotation creates a uniform thermal field, ensuring that every part of the synthesis gel is exposed to the exact same temperature profile simultaneously.
Application of Shear Force
The rotation, specifically at 60 rpm, introduces necessary shear force to the mixture. This physical agitation prevents the sedimentation of heavier components and breaks up gel aggregates.
This dynamic environment promotes the thorough mixing of reactants, preventing localized concentrations that could lead to impurities or irregular structures.
Impact on Zeolite Structure
Distribution of the Structure-Directing Agent
The critical chemical interaction in this process involves TMAda-OH, the structure-directing agent. The rotary action ensures this agent is uniformly distributed within the aluminosilicate framework.
Without this uniform distribution, the template cannot effectively guide the formation of the desired pore architecture throughout the entire batch.
Control of Grain Size and Crystallinity
The combination of uniform heat and shear force directly dictates the physical properties of the final product.
The process ensures the formation of a highly crystalline chabazite structure. Furthermore, it allows for precise control over the crystal dimensions, yielding an average grain size of approximately 120 nm.
The Hydrothermal Foundation
Generating Autogenous Pressure
While rotation provides mixing, the "high-pressure" aspect of the autoclave remains fundamental to zeolite synthesis. The sealed vessel allows for the generation of autogenous pressure as temperatures rise (e.g., to 100 °C or higher).
Dissolution and Recrystallization
This pressurized hydrothermal environment facilitates the dissolution of silicate and aluminate gels. It creates the necessary physical conditions for these dissolved components to recrystallize into a highly regular, porous zeolite structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Mechanical Complexity vs. Static Simplicity
Using a rotary autoclave introduces mechanical variables that must be precisely controlled. Unlike static autoclaves, where temperature is the primary variable, rotary systems require strict adherence to rotation speeds (e.g., 60 rpm) to replicate results.
The Risk of Inadequate Mixing
If the rotation speed is too low or the mechanism fails, the system reverts to a quasi-static state. This leads to a loss of the uniform thermal field, potentially resulting in a wider distribution of grain sizes and lower overall crystallinity compared to the target 120 nm.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your SSZ-13 zeolite synthesis, align your equipment choice with your specific structural requirements.
- If your primary focus is Uniformity and Crystallinity: Utilize a rotary autoclave set to 60 rpm to ensure equal distribution of TMAda-OH and consistent grain sizes around 120 nm.
- If your primary focus is Basic Phase Formation: A standard static high-pressure autoclave may suffice for generating the necessary autogenous pressure, though crystal size distribution may be less controlled.
By leveraging the shear force and thermal uniformity of a rotary autoclave, you transform a chaotic chemical mixture into a precise, high-performance molecular sieve.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in SSZ-13 Synthesis | Impact on Final Product |
|---|---|---|
| 60 RPM Rotation | Generates shear force & prevents sedimentation | High crystallinity & 120 nm grain size |
| Uniform Thermal Field | Eliminates temperature gradients | Consistent crystal growth throughout batch |
| TMAda-OH Distribution | Evenly disperses structure-directing agent | Precise chabazite pore architecture |
| Autogenous Pressure | Facilitates hydrothermal recrystallization | Robust aluminosilicate framework formation |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision in zeolite synthesis requires more than just heat—it requires a controlled, dynamic environment. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-pressure rotary autoclaves designed to deliver the exact shear force and thermal uniformity your research demands.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of lab equipment including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your unique hydrothermal specifications.
Ready to achieve superior crystallinity and precise grain size control?
Contact KINTEK Experts Today to find the perfect high-temp solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
References
- Konstantin Khivantsev, János Szanyi. Increasing Al-Pair Abundance in SSZ-13 Zeolite via Zeolite Synthesis in the Presence of Alkaline Earth Metal Hydroxide Produces Hydrothermally Stable Co-, Cu- and Pd-SSZ-13 Materials. DOI: 10.3390/catal14010056
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the objective of GC-MS analysis on bio-oil? Unlock Chemical Value and Industrial Utility
- What is sintering in the context of 3D printing? Unlock Dense, Functional Parts with Precision
- Why is an industrial-grade forced air drying oven required for Ca2.5Ag0.3Sm0.2Co4O9 ceramic? Precision Pre-Treatment
- How is the problem of surface oxidation and decarburization addressed in conventional heat treatment? Learn the Machining Allowance Method
- Why is an industrial-grade drying oven necessary for biomass activation? Ensure Structural Integrity & Yield
- What role does a high-temperature sintering furnace play in lead-free piezoelectric ceramics? Optimizing Performance
- What is the impact of microwave power on the synthesis of 2D metal oxides? Master High-Speed Material Production
- What are the methods of heat transfer in furnaces? Master Heat Control for Better Results



















