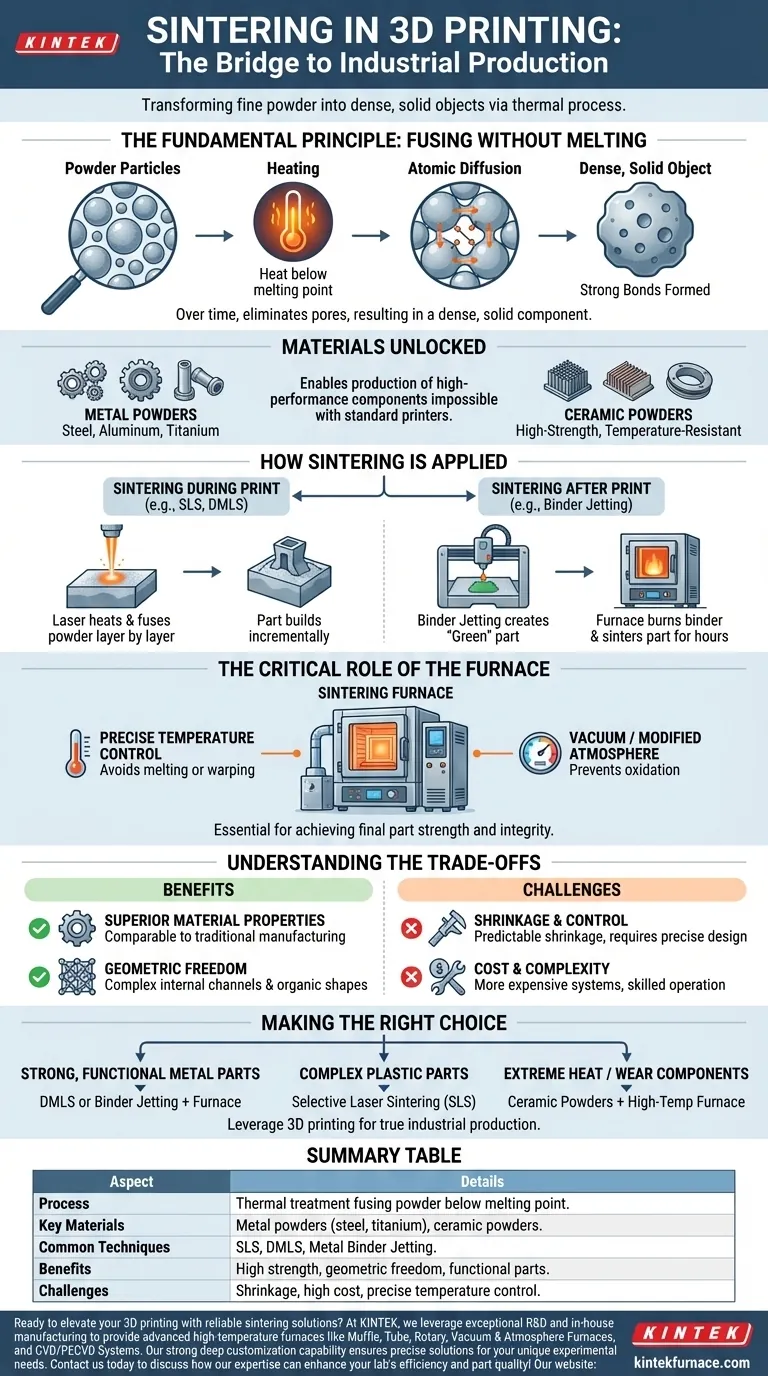
In the world of advanced manufacturing, sintering is the thermal process that transforms fine powder into a dense, solid object. In 3D printing, this technique is used to create highly complex parts from materials like metal and ceramic by heating them to a point where the powder particles fuse together, but do not fully melt.
Sintering is the critical bridge between 3D printing simple plastic models and manufacturing industrial-grade, functional parts. It unlocks the ability to print with high-performance materials like metals and ceramics, but it requires a deep understanding of process control to achieve the desired results.

The Fundamental Principle: Fusing Without Melting
What Sintering Really Is
Sintering is a process of atomic diffusion. When a compacted mass of powder is heated to a high temperature—below its melting point—the atoms on the surfaces of individual particles become agitated.
This energy allows them to migrate across the boundaries of adjacent particles, forming strong chemical bonds. Over time, this process eliminates the pores between particles, resulting in a dense, solid component.
The Materials It Unlocks
This technique is the key to working with materials that are difficult or impossible to process with conventional extrusion-based 3D printers.
Sintering is primarily used for metal powders (such as steel, aluminum, or titanium) and ceramic powders. This enables the production of high-strength, wear-resistant, and temperature-resistant components.
How Sintering Is Applied in 3D Printing
Sintering During the Print
In processes like Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) or Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), sintering happens layer by layer. A high-powered laser traces the part's cross-section onto a thin bed of powder.
The laser's energy instantly heats and fuses the powder particles in that specific area. A new layer of powder is then spread, and the process repeats until the object is complete.
Sintering After the Print
In other technologies, like Metal Binder Jetting, the "printing" step and the "sintering" step are separate. The printer deposits a binding agent onto a powder bed to create a fragile, preliminary part known as a "green" part.
This green part is then carefully moved to a high-temperature sintering furnace. Inside the furnace, the binder is burned away, and the part is heated for many hours, allowing the metal particles to sinter into a fully dense, solid metal object.
The Critical Role of the Furnace
A sintering furnace is a piece of precision equipment. It must provide extremely precise temperature control to avoid melting or warping the part.
It also often creates a vacuum or modified atmosphere to prevent the metal from oxidizing at high temperatures, which would compromise the final part's strength and integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Benefit: Superior Material Properties
The primary advantage of sintering-based 3D printing is the ability to produce parts with mechanical properties comparable to those made with traditional manufacturing. The final components are dense, strong, and functional.
Benefit: Geometric Freedom
Because the object is supported by a bed of unfused powder during the printing process, these methods can create incredibly complex internal channels, lattices, and organic shapes that would be impossible to machine.
Challenge: Shrinkage and Control
During the sintering process, as the gaps between powder particles close, the part shrinks. This shrinkage is predictable but must be precisely accounted for in the initial design to achieve accurate final dimensions.
Challenge: Cost and Complexity
Sintering-based systems, whether involving lasers or separate furnaces, are significantly more expensive and complex to operate than standard 3D printers. They require skilled technicians and controlled environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Whether sintering is the right approach depends entirely on your final application.
- If your primary focus is creating strong, functional metal parts: You will be using a process like Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) or a two-step binder jetting and furnace sintering workflow.
- If your primary focus is producing complex plastic parts with good mechanical properties: Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is the relevant technology, which sinters polymer powders instead of metal.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing components that must withstand extreme heat or wear: You will need a process specifically for ceramic powders, which are sintered in a high-temperature furnace after printing.
Understanding the principles of sintering empowers you to leverage 3D printing for true industrial production.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Process | Thermal treatment fusing powder particles below melting point via atomic diffusion |
| Key Materials | Metal powders (e.g., steel, titanium), ceramic powders |
| Common Techniques | Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), Metal Binder Jetting |
| Benefits | High strength, geometric freedom, functional parts comparable to traditional methods |
| Challenges | Predictable shrinkage, high cost, need for precise temperature control and skilled operation |
Ready to elevate your 3D printing with reliable sintering solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, whether you're working with metals, ceramics, or other materials. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your lab's efficiency and part quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- What is an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments



















