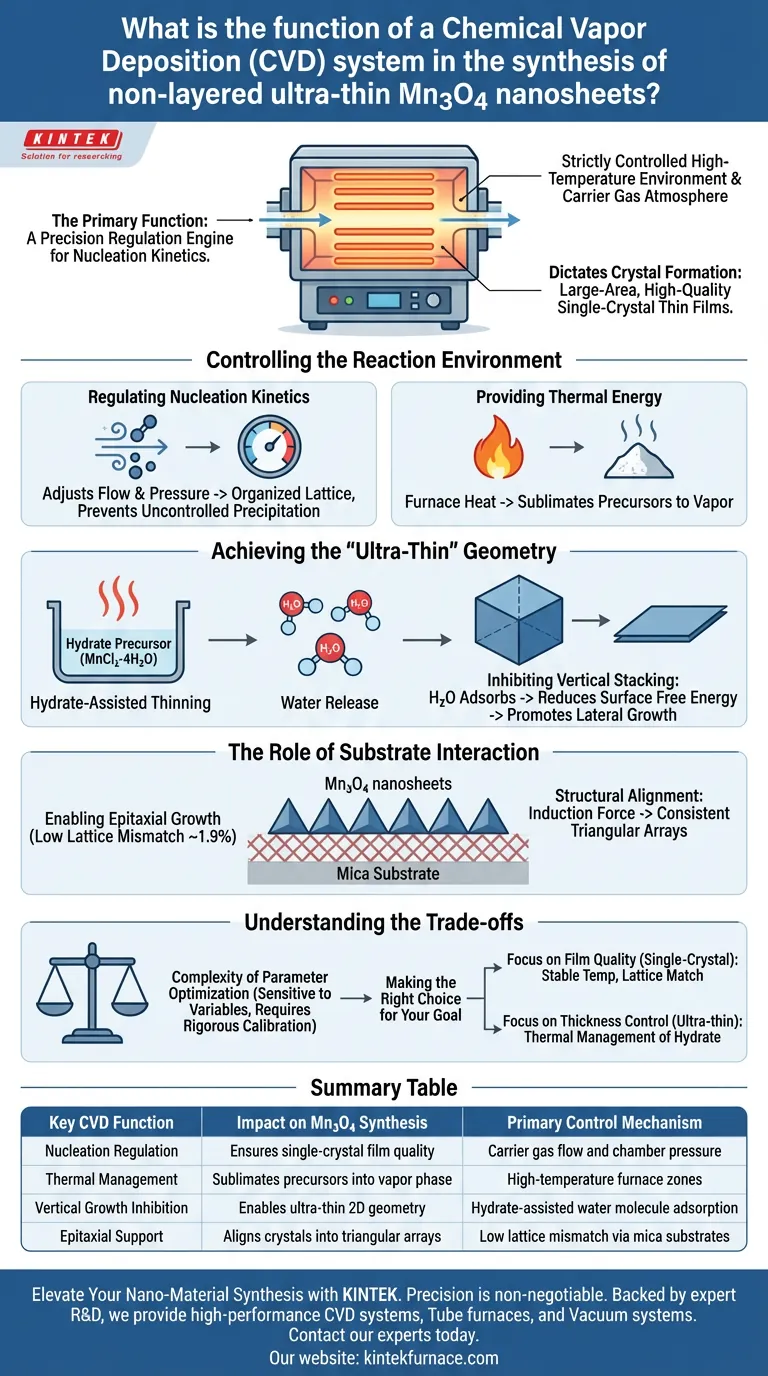
The primary function of a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) system is to act as a precision regulation engine for nucleation kinetics. It establishes a strictly controlled high-temperature environment and carrier gas atmosphere required to grow Mn3O4. By rigorously managing furnace temperature, internal pressure, and precursor gas flow, the system dictates how crystals form, enabling the synthesis of large-area, high-quality single-crystal thin films.
The CVD system effectively orchestrates the competition between vertical and lateral crystal growth. By maintaining specific environmental conditions, it forces non-layered materials like Mn3O4 to form atomically thin sheets rather than bulk structures.

Controlling the Reaction Environment
To achieve high-quality synthesis, the CVD system must maintain stability across several critical variables.
Regulating Nucleation Kinetics
The core function of the system is the management of nucleation kinetics. By adjusting the flow rate of the carrier gas and the pressure within the chamber, the system controls how fast reactive species reach the substrate.
This precise regulation prevents uncontrolled precipitation. Instead, it fosters an environment where atoms settle in an organized lattice structure, resulting in single-crystal films.
Providing Thermal Energy
The CVD system, specifically the furnace component, provides the high thermal energy needed to sublimate precursors. This transforms solid source materials into the vapor phase, which is essential for transport to the deposition zone.
Achieving the "Ultra-Thin" Geometry
Synthesizing non-layered materials as nanosheets is inherently difficult because they naturally tend to grow into three-dimensional bulk crystals. The CVD system facilitates a specific chemical strategy to overcome this.
Hydrate-Assisted Thinning
The system is used to heat hydrate precursors, such as MnCl2·4H2O. Under controlled heating, these precursors release water molecules.
Inhibiting Vertical Stacking
The released water molecules adsorb onto the surface of the growing material. This process significantly reduces the surface free energy associated with vertical growth.
Consequently, the system creates an environment where vertical stacking is inhibited and lateral (sideways) growth is promoted. This is the key mechanism that allows non-layered Mn3O4 to form nanosheets with atomic-level thickness.
The Role of Substrate Interaction
The CVD system does not operate in isolation; it functions in tandem with the substrate to guide crystal alignment.
Enabling Epitaxial Growth
The system creates the conditions necessary for epitaxial growth on substrates like mica. Mica is utilized because it has a very low lattice mismatch (approximately 1.9%) with Mn3O4.
Structural Alignment
Because of the high structural compatibility maintained within the CVD environment, the substrate provides a strong induction force. This ensures the nanosheets align in specific directions, forming consistent triangular arrays.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While CVD is powerful, it is highly sensitive to process variables.
Complexity of Parameter Optimization
The primary challenge is the interdependence of variables. A slight fluctuation in carrier gas flow or a minor deviation in the temperature zone can disrupt the nucleation kinetics.
This sensitivity means that while the system offers precise control, achieving that control requires rigorous calibration. If the specific "hydrate-assisted" conditions are not perfectly maintained, the material will revert to its natural tendency to grow as a 3D bulk crystal rather than an ultra-thin sheet.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Success in synthesizing Mn3O4 nanosheets depends on how you utilize the CVD system's capabilities.
- If your primary focus is Film Quality (Single-Crystal): Prioritize the stability of the furnace temperature and the precision of the lattice match with the mica substrate to ensure strong epitaxial alignment.
- If your primary focus is Thickness Control (Ultra-thin): Focus on the thermal management of the hydrate precursor to ensure the consistent release of water molecules, which effectively blocks vertical growth.
The CVD system is not just a furnace; it is a kinetic control tool that forces non-layered materials to adopt a two-dimensional form through precise environmental regulation.
Summary Table:
| Key CVD Function | Impact on Mn3O4 Synthesis | Primary Control Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleation Regulation | Ensures single-crystal film quality | Carrier gas flow and chamber pressure |
| Thermal Management | Sublimates precursors into vapor phase | High-temperature furnace zones |
| Vertical Growth Inhibition | Enables ultra-thin 2D geometry | Hydrate-assisted water molecule adsorption |
| Epitaxial Support | Aligns crystals into triangular arrays | Low lattice mismatch via mica substrates |
Elevate Your Nano-Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable when synthesizing non-layered materials like Mn3O4. At KINTEK, we understand that a CVD system is more than just a furnace—it is a high-stakes kinetic engine. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-performance CVD systems, Tube furnaces, and Vacuum systems specifically engineered for the rigorous demands of material science.
Whether you need to master hydrate-assisted thinning or achieve perfect epitaxial growth, our customizable lab high-temperature solutions provide the stability and control your research deserves.
Ready to achieve atomic-level precision? Contact our technical experts today to discuss your unique project requirements and discover how KINTEK can empower your next breakthrough.
Visual Guide
References
- Jiashuai Yuan, Wei Liu. Controllable synthesis of nonlayered high-κ Mn3O4 single-crystal thin films for 2D electronics. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-56386-9
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why use Argon and Hydrogen for MnS Nanosheet CVD? Achieve High-Purity Synthesis Results
- How is CVD applied in advanced materials and nanotechnology? Unlock Atomic Precision for Next-Gen Innovations
- Why is a vacuum deposition chamber an essential hardware environment? Unlock High-Performance Thermal Power Coatings
- What role does CVD play in semiconductor manufacturing? Enable Precise Thin Film Deposition for Microchips
- What are the four main stages of the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process? Master Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What are the limitations of CVD? Balancing Cost, Safety, and Temperature for Optimal Results
- What are the general reactions for metal and ceramic deposition in CVD? Master Key Processes for Superior Thin Films
- What is the working principle of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? Master Thin Film Growth for Superior Coatings



















