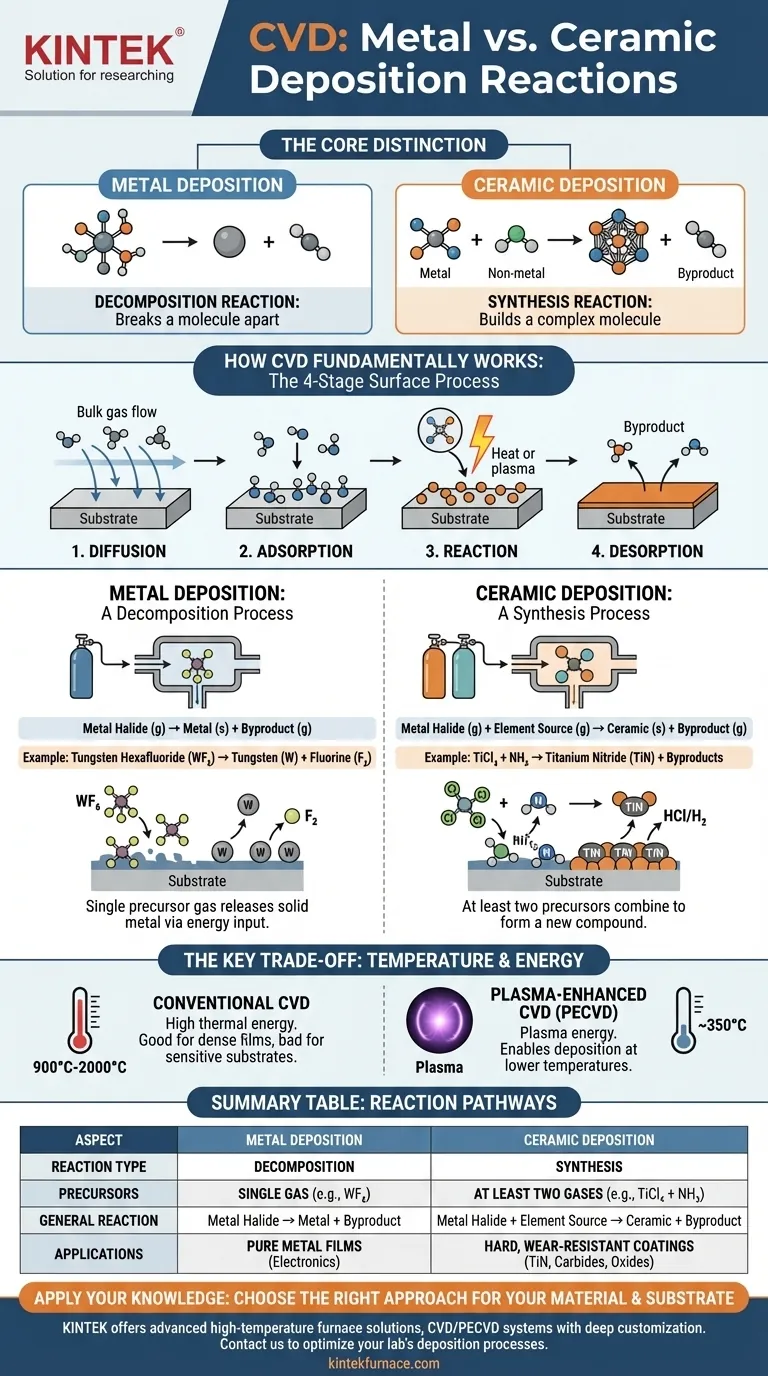
In Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), the fundamental difference between depositing a pure metal and a ceramic lies in the type of reaction and the number of reactive gases required. Metal deposition is typically a decomposition reaction from a single gas source, while ceramic deposition is a synthesis reaction requiring at least two different precursor gases to combine and form the new material on the substrate.
The core distinction is simple: metal deposition breaks a molecule apart, while ceramic deposition builds a new, more complex molecule. This determines the precursors you need and the conditions required to create the final thin film.
How CVD Fundamentally Works
Before examining the specific reactions, it's crucial to understand the universal mechanism of CVD. The entire process unfolds in four distinct stages on the surface of the component being coated.
Stage 1: Diffusion to the Surface
Reactive precursor gases are introduced into a chamber and must first travel from the bulk gas flow to the substrate's surface.
Stage 2: Adsorption onto the Surface
Once at the substrate, the gas molecules physically adsorb, or "stick," to the surface, making them available for a chemical reaction.
Stage 3: Reaction on the Surface
This is the critical stage where the intended chemistry occurs. High temperatures (or plasma energy) provide the activation energy for the adsorbed molecules to react, forming the solid film material.
Stage 4: Desorption of Byproducts
The chemical reaction creates the desired solid film but also produces gaseous byproducts. These byproducts must detach, or "desorb," from the surface and diffuse away so that new reactants can take their place.
Metal vs. Ceramic: A Tale of Two Reactions
The specific reaction in Stage 3 defines whether you deposit a metal or a ceramic. The difference is whether you are simply isolating a metal or synthesizing a new compound.
Metal Deposition: A Decomposition Process
To deposit a pure metal, a single precursor gas containing that metal is used. The energy in the chamber breaks this molecule down, leaving the solid metal on the surface.
The general reaction is: Metal Halide (g) → Metal (s) + Byproduct (g)
Here, a gas like Tungsten Hexafluoride (WF₆) is heated, causing it to decompose and deposit a solid tungsten film (W), releasing fluorine gas as a byproduct.
Ceramic Deposition: A Synthesis Process
To deposit a ceramic, you must combine a metal with a non-metal element. This requires introducing at least two separate precursor gases into the chamber simultaneously.
The general reaction is: Metal Halide (g) + Element Source (g) → Ceramic (s) + Byproduct (g)
For example, to create Titanium Nitride (TiN), you would co-react a titanium source gas like Titanium Tetrachloride (TiCl₄) with a nitrogen source gas like Ammonia (NH₃). The reaction forms solid TiN on the substrate. The same principle applies to forming carbides (using a carbon source like methane), oxides (using an oxygen source), or borides (using a boron source).
Understanding the Key Trade-off: Temperature
The primary challenge in CVD is managing the immense energy required to drive these surface reactions. This creates a significant trade-off between process capability and substrate compatibility.
The High Heat of Conventional CVD
Traditional, thermally driven CVD processes operate at extremely high temperatures, often between 900 °C and 2000 °C.
This high heat is effective at producing high-quality, dense films. However, it severely limits the types of materials you can coat, as many substrates will warp, deform, or suffer metallurgical changes that degrade their mechanical properties.
The Alternative: Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD)
To overcome temperature limitations, Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) uses an electrical field to generate a plasma within the reaction chamber.
This highly energetic plasma provides the activation energy for the reaction to occur, rather than relying solely on thermal energy. This allows for deposition at much lower temperatures, typically around 350 °C, making it possible to coat temperature-sensitive materials without damaging them.
Applying This to Your Deposition Goal
Understanding these reaction pathways allows you to select the right approach for your specific material and substrate.
- If your primary focus is depositing a pure metal film: Your process will center on the thermal decomposition of a single precursor gas containing the desired metal.
- If your primary focus is creating a hard, wear-resistant ceramic coating: You must design a process that effectively co-reacts a metal source gas with a non-metal source gas (e.g., nitrogen, oxygen, or carbon).
- If your substrate is temperature-sensitive (e.g., aluminum, polymers, or certain steel alloys): Conventional high-temperature CVD is not viable, and you must use a lower-temperature process like PECVD.
Mastering CVD begins with recognizing that you are orchestrating a precise chemical reaction on a surface.

Summary Table:
| Aspect | Metal Deposition | Ceramic Deposition |
|---|---|---|
| Reaction Type | Decomposition | Synthesis |
| Precursor Gases | Single gas (e.g., WF₆) | At least two gases (e.g., TiCl₄ + NH₃) |
| General Reaction | Metal Halide (g) → Metal (s) + Byproduct (g) | Metal Halide (g) + Element Source (g) → Ceramic (s) + Byproduct (g) |
| Temperature Range | High (900-2000°C) or lower with PECVD (~350°C) | High (900-2000°C) or lower with PECVD (~350°C) |
| Key Applications | Pure metal films for electronics, coatings | Hard, wear-resistant coatings like TiN, carbides, oxides |
Ready to optimize your CVD processes for high-quality metal and ceramic films? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're working with temperature-sensitive substrates or need robust coatings, contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results! Contact us now
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- How is silicon dioxide deposited from tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) in PECVD? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality SiO2 Films
- What are the classifications of CVD based on vapor characteristics? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition Process
- What are the drawbacks of CVD compared to PECVD? Key Limitations for Your Lab
- What is plasma-deposited silicon nitride, and what are its properties? Discover Its Role in Solar Cell Efficiency
- What parameters control the quality of PECVD-deposited films? Master Key Variables for Superior Film Properties



















