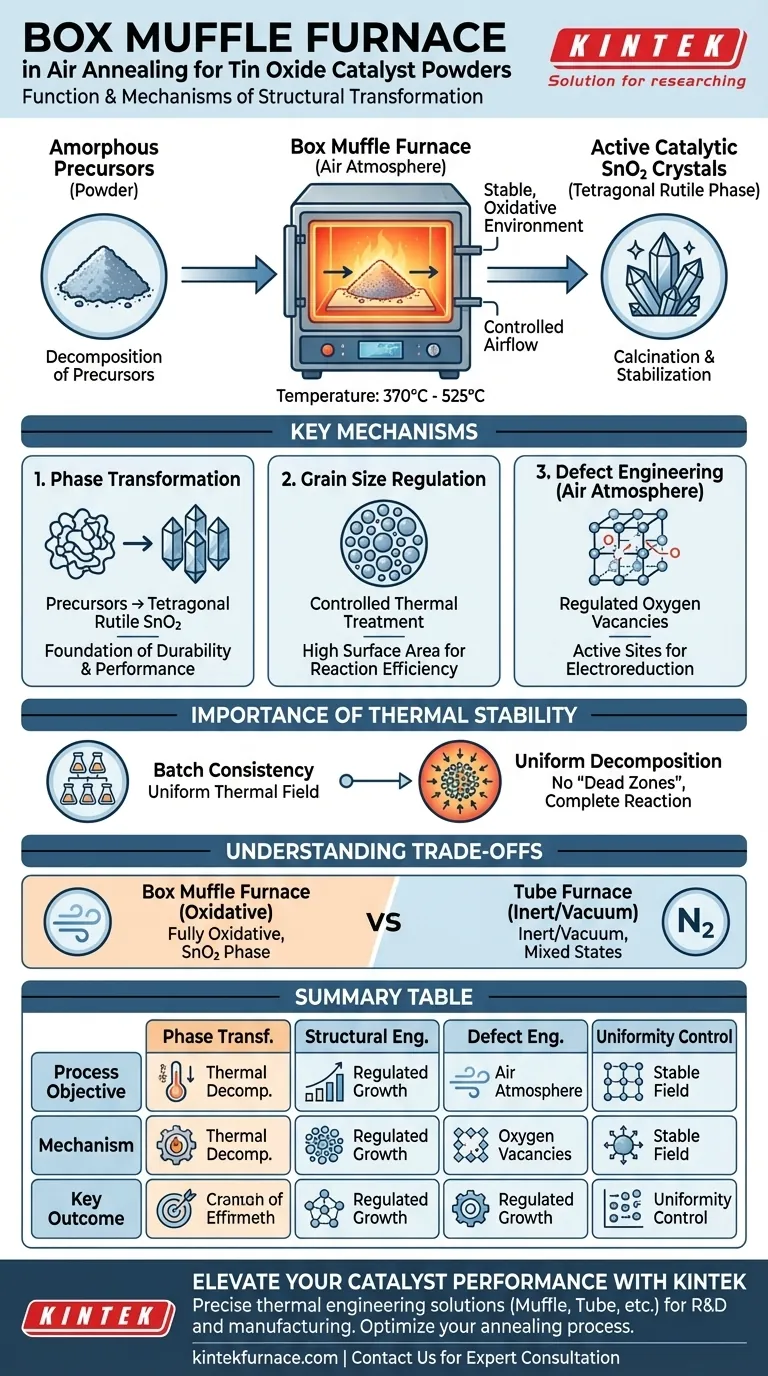
The primary function of a box muffle furnace in this process is to provide a stable, oxidative thermal environment that converts tin oxide precursors into active catalytic crystals. By subjecting the powder to precise temperatures—typically between 370 °C and 525 °C—in an air atmosphere, the furnace drives the calcination process necessary to stabilize the material for electrochemical applications.
The furnace does not simply dry the material; it engineers the catalyst's atomic structure. By controlling heat in an oxygen-rich environment, the box muffle furnace dictates the phase purity, grain size, and oxygen vacancy density required for efficient carbon dioxide electroreduction.

Mechanisms of Structural Transformation
Converting Precursors to Active Crystals
The initial role of the furnace is to facilitate the decomposition of amorphous precursors. Through controlled heating, these precursors undergo a phase transformation, converting into a crystalline structure known as the tetragonal rutile phase SnO2. This crystalline stability is the foundation of the catalyst's durability and performance.
Regulating Grain Size
Thermal treatment is the primary lever for controlling the physical size of the catalyst particles. The box muffle furnace allows for the precise regulation of grain size, which directly correlates to the available surface area for chemical reactions. Consistent heating ensures that these grains grow uniformly, preventing disparities that could hinder catalytic activity.
Defect Engineering via Atmosphere
Unlike vacuum or inert gas treatments, the box muffle furnace operates in an air atmosphere. This environment is critical for regulating the content of oxygen vacancies within the crystal lattice. These vacancies act as active sites during electroreduction; therefore, the furnace's ability to maintain a consistent oxidative atmosphere is as important as its temperature control.
The Importance of Thermal Stability
Ensuring Batch Consistency
In catalyst preparation, reproducibility is paramount. A high-quality laboratory muffle furnace offers excellent thermal field stability, ensuring that the temperature is uniform throughout the chamber.
Decomposing Precursors Uniformly
The furnace facilitates the complete dehydration and decomposition of metal salts. By adhering to a preset temperature curve, it ensures that every particle of the powder undergoes the same thermal history. This uniformity prevents the formation of "dead zones" in the powder where precursors might remain unreacted.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Oxidative vs. Inert Environments
It is vital to distinguish the box muffle furnace from a high-temperature tube furnace. A box muffle furnace creates a fully oxidative environment (air), which drives the material toward the stable SnO2 phase.
Limitations in Oxidation State Control
If your goal is to create mixed oxidation states (such as Sn3O4 or Sn2O3), a box muffle furnace is generally unsuitable. Those mixed states typically require the oxygen-deficient environment of a tube furnace using inert nitrogen gas. The box muffle furnace is designed specifically for full oxidation and stabilization.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your tin oxide catalyst, align your equipment choice with your specific structural requirements:
- If your primary focus is standardizing catalytic activity: Prioritize a box muffle furnace with high thermal field stability to ensure uniform grain size and consistent oxygen vacancy content across batches.
- If your primary focus is achieving the tetragonal rutile phase: Use the box muffle furnace in air at temperatures between 370 °C and 525 °C to fully convert amorphous precursors into stable SnO2.
- If your primary focus is exploring mixed oxidation states: Do not use a box muffle furnace; instead, opt for a tube furnace with inert gas flow to restrict oxygen supply and stabilize intermediate phases.
Control the heat and atmosphere precisely, and you control the fundamental efficiency of your catalyst.
Summary Table:
| Process Objective | Mechanism | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Phase Transformation | Thermal decomposition of precursors | Stable Tetragonal Rutile Phase SnO2 |
| Structural Engineering | Regulated grain growth | High surface area & reaction efficiency |
| Defect Engineering | Air atmosphere (oxidative) | Controlled oxygen vacancy density |
| Uniformity Control | Stable thermal field | Batch-to-batch consistency and purity |
Elevate Your Catalyst Performance with KINTEK
Precise thermal engineering is the difference between a mediocre material and a high-efficiency catalyst. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-temperature solutions—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—specifically designed to meet the rigorous demands of laboratory R&D and manufacturing.
Whether you are stabilizing the tetragonal rutile phase of SnO2 or need a custom thermal profile for unique material synthesis, our expert-backed equipment is fully customizable to your specific needs.
Ready to optimize your annealing process? Contact KINTEK today to consult with our experts and find the perfect furnace for your research.
Visual Guide
References
- Nicolò B. D. Monti, Katarzyna Bejtka. Effects of Annealing Conditions on the Catalytic Performance of Anodized Tin Oxide for Electrochemical Carbon Dioxide Reduction. DOI: 10.3390/nano15020121
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of the muffle furnace heat treatment in Si@Sn@C preparation? Unlock Structural Stability
- What are the special features of muffle furnaces? Achieve Clean, Precise Heat for Your Lab
- What safety features should be considered when selecting a muffle furnace? Ensure Lab Safety with Advanced Protection Systems
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the OBD process for Ti-6Al-4V? Enhance Alloy Surface Hardening Precision
- How is the temperature controlled in a muffle furnace? Master Precise Heating for Your Lab
- What is the main utility of the exhaust system in a muffle furnace? Safely Remove Hazardous Gases for Lab Safety
- What are some common processes that use muffle furnaces? Achieve Pure, Controlled High-Temperature Applications
- Why is 400 °C annealing in a muffle furnace necessary for ZnO thin films? Optimize Crystallinity and Performance



















