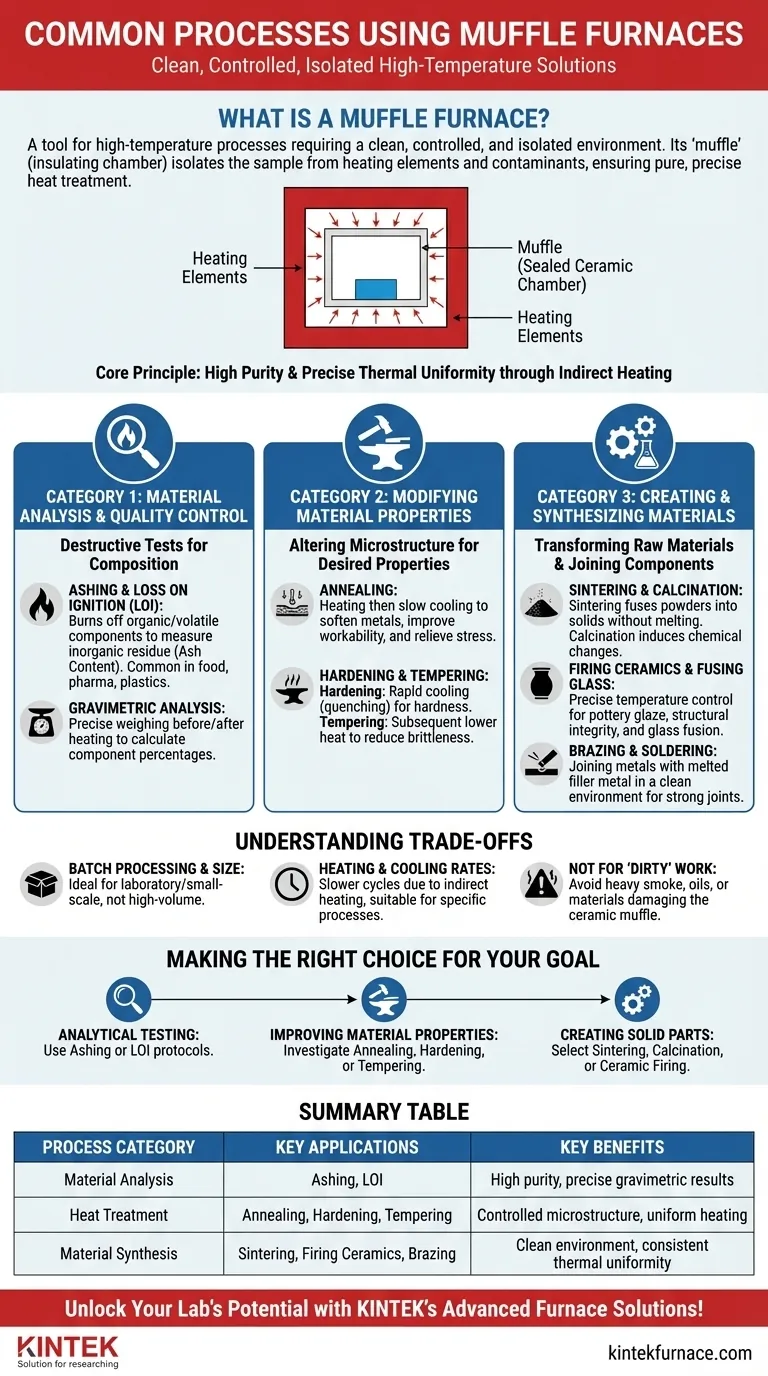
At its core, a muffle furnace is used for any high-temperature process that requires a clean, controlled, and isolated heating environment. Common applications fall into three main categories: analyzing a material's composition (like ashing), modifying a material's physical properties (like annealing metals), and synthesizing new materials (like firing ceramics or sintering powders).
A muffle furnace's defining feature is not just high heat, but its "muffle"—an insulating chamber that isolates the sample from the heating elements and fuel contaminants. This guarantees that the heat treatment is pure and precisely controlled, which is the underlying reason it is chosen for sensitive laboratory and industrial work.

The Core Principle: Why an Insulated Chamber Matters
Before listing applications, it is critical to understand why a muffle furnace is the tool of choice. Its unique design solves a fundamental problem in high-temperature work: contamination and uneven heating.
Understanding the "Muffle"
A muffle is a sealed inner chamber, typically made of high-temperature ceramic, that contains the material being heated.
The heating elements warm the outside of this chamber, and the heat radiates inward. This separation prevents any byproducts of combustion or material flaking from the heating elements from contaminating the sample.
Achieving High Purity
This design is essential for processes like ashing, where the goal is to measure the tiny amount of inorganic residue left after combustion. Any external contamination would invalidate the results.
It is also vital in electronics and ceramics, where even microscopic impurities can drastically alter the final product's properties.
Ensuring Precise Thermal Uniformity
By heating the chamber walls instead of the sample directly, a muffle furnace creates an exceptionally uniform thermal environment. This ensures the entire sample experiences the same temperature, which is critical for consistent results in heat treatment and material synthesis.
Category 1: Material Analysis and Quality Control
A primary use of muffle furnaces is to determine the composition of a sample through heat. These are destructive tests used in labs and quality control departments.
Ashing and Loss on Ignition (LOI)
This is the most common analytical application. A sample is heated to a high temperature (e.g., 550°C or 900°C) to completely burn off all organic and volatile components.
The remaining non-combustible material is the ash content. This is a standard quality metric in industries like food science, pharmaceuticals, plastics, and coal analysis.
Gravimetric Analysis
Both ashing and LOI are forms of gravimetric analysis. By precisely weighing the sample before and after heating, technicians can calculate the percentage of organic matter, inorganic matter, or moisture content.
Category 2: Modifying Material Properties (Heat Treatment)
Muffle furnaces are ideal for precisely altering the microstructure of metals and other materials to achieve desired physical properties like hardness, ductility, or strength.
Annealing
This process involves heating a material to a specific temperature and then cooling it slowly. Annealing is used to soften metals, make them easier to work with, and relieve internal stresses created during manufacturing.
Hardening and Tempering
Hardening involves heating a metal (like steel) and then cooling it rapidly (quenching) to lock in a hard, brittle crystal structure.
The material is often too brittle after hardening, so it undergoes a subsequent, lower-temperature heat treatment called tempering. This process, also done in a muffle furnace, reduces brittleness while retaining most of the hardness.
Category 3: Creating and Synthesizing Materials
This category involves using heat to transform raw materials into a final, solid product or to join components together.
Sintering and Calcination
Sintering is a process that uses heat to fuse powdered materials—like ceramics or metals—into a solid, dense object without melting them completely. This is fundamental to powder metallurgy and technical ceramic manufacturing.
Calcination involves heating a material to induce a chemical change, such as driving off carbon dioxide from limestone to create lime.
Firing Ceramics and Fusing Glass
The uniform, high-temperature environment of a muffle furnace is perfect for firing pottery and ceramics, where precise temperature ramps and holds are necessary to achieve the desired glaze and structural integrity. It is also used for fusing pieces of glass together in art and manufacturing.
Brazing and Soldering
Brazing is a process for joining two pieces of metal by melting a filler metal into the joint. A muffle furnace, sometimes with a controlled atmosphere, provides the clean, consistent heat needed for strong, reliable joints without melting the base metals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, muffle furnaces are not the solution for every heating task. Understanding their limitations is key to using them effectively.
Batch Processing and Size
Muffle furnaces are inherently batch processors and are generally smaller than industrial-scale ovens. They are best suited for laboratory work, small-scale production, or processing high-value components rather than high-volume manufacturing.
Heating and Cooling Rates
Because the heat must transfer indirectly through the muffle chamber walls, heating and cooling cycles can be slower compared to direct-flame furnaces or induction heating. This can be an advantage for processes like annealing but a disadvantage when rapid cycles are needed.
Not for "Dirty" Work
The muffle furnace's greatest strength—its clean environment—is also a constraint. It is not intended for processes involving heavy smoke, oils, or materials that could damage the delicate ceramic muffle.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific application will determine which process you use. The common thread is always the need for a pure, precisely controlled thermal environment.
- If your primary focus is analytical testing: You will use ashing or loss-on-ignition protocols to determine the inorganic or non-volatile content of a sample.
- If your primary focus is improving a material's workability or strength: You should investigate annealing, hardening, or tempering cycles specific to your material.
- If your primary focus is creating solid parts from powders or raw materials: Processes like sintering, calcination, or ceramic firing will be your main applications.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is the definitive tool when the integrity of your sample and the precision of the temperature profile are paramount.
Summary Table:
| Process Category | Key Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Material Analysis | Ashing, Loss on Ignition | High purity, precise gravimetric results |
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, Hardening, Tempering | Controlled microstructure, uniform heating |
| Material Synthesis | Sintering, Firing Ceramics, Brazing | Clean environment, consistent thermal uniformity |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions!
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with reliable muffle, tube, rotary, vacuum, atmosphere furnaces, and CVD/PECVD systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering superior purity, precise temperature control, and consistent results for processes like ashing, annealing, and sintering.
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency and accuracy? Contact us today to discuss your needs and discover how our tailored solutions can drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















