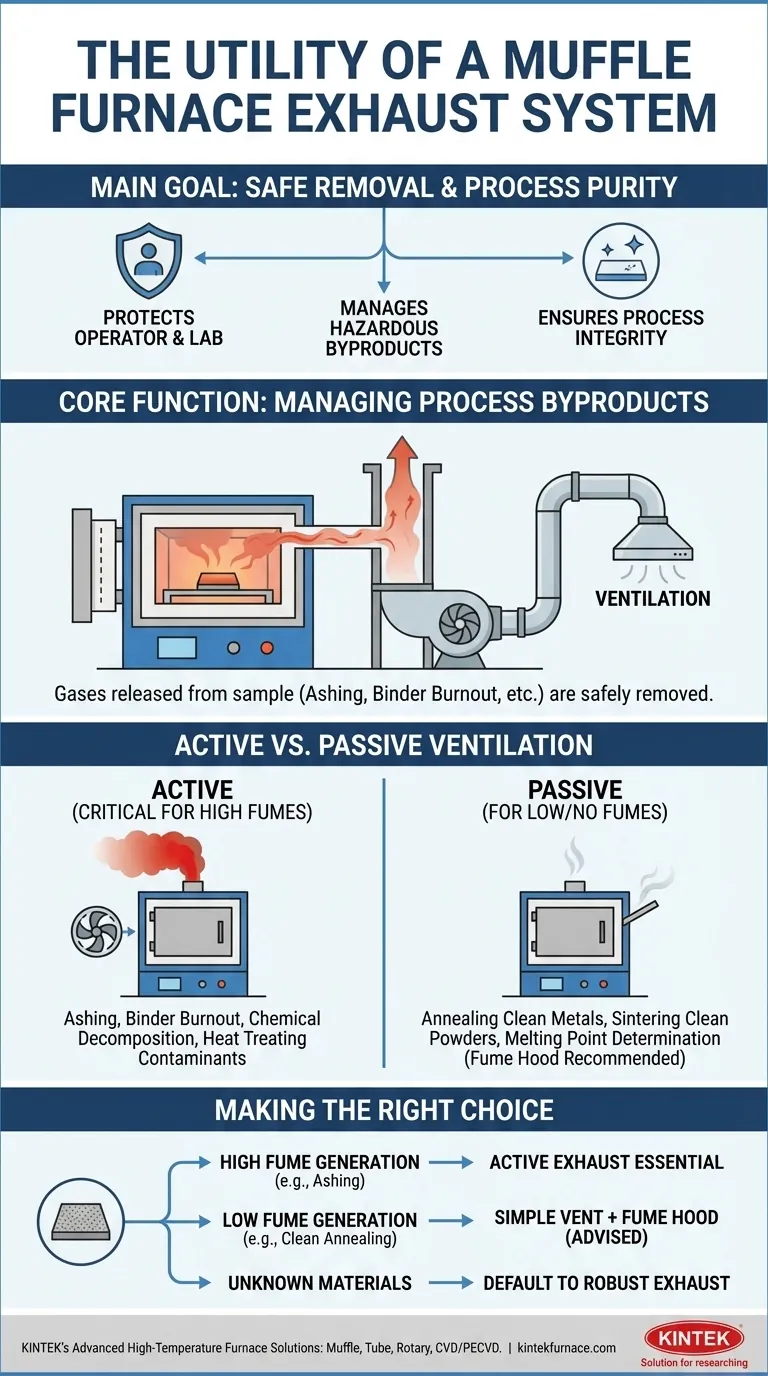
In short, the main utility of the exhaust system in a muffle furnace is to safely remove hazardous gases, smoke, and fumes that are released from the material being heated. This ventilation is critical for protecting the operator, the laboratory environment, and ensuring the purity of the process.
The core purpose of a muffle furnace is to provide a clean, controlled heating environment. The exhaust system is not for the furnace itself, but to manage the often-toxic byproducts created by the sample during heating, thereby upholding both safety and process integrity.

The Core Function: Managing Process Byproducts
A muffle furnace's primary job is to heat a sample without contaminating it. However, the heating process itself often causes the sample to release substances into the chamber atmosphere. The exhaust system is designed to manage these emissions.
Why Gases Are Produced
Many high-temperature applications involve the chemical or physical transformation of a material. Processes like ashing, binder burnout, and determining volatile matter are designed specifically to burn off or drive out components of a sample.
These processes inherently generate byproducts such as smoke, fumes, and potentially toxic or corrosive gases.
Ensuring Operator Safety
The gases released can be harmful if inhaled. An exhaust system, often vented into a laboratory fume hood or directly outside, is a critical safety feature that removes these hazardous substances from the work area.
Without proper ventilation, these fumes would accumulate in the lab, posing a direct health risk to personnel.
Maintaining Process Integrity
Removing byproducts is also essential for accurate results. If fumes and gases were allowed to remain in the chamber, they could interact with the sample, cause unwanted chemical reactions, or redeposit onto the material.
This "sanitizes the chamber," as stated in technical literature, ensuring the controlled environment is not compromised by the very process it is enabling.
The Role of Exhaust in the Muffle Principle
Understanding the furnace's basic design clarifies the exhaust system's role. The term "muffle" refers to the insulated inner chamber that isolates the sample from the heating elements.
Isolation is Key
The core principle of a muffle furnace is to create a pristine heating chamber. In modern electric furnaces, there are no byproducts from combustion (like in a gas-fired furnace).
Therefore, any gases present in the chamber are generated exclusively by the sample itself. The exhaust system is the only way to remove them.
Active vs. Passive Ventilation
Simple muffle furnaces may only have a small, passive vent port to allow pressure to escape.
However, furnaces intended for processes that generate significant fumes are equipped with active exhaust systems, often featuring a chimney or port for connection to a powerful extraction system.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential for many tasks, an active exhaust system isn't always a mandatory feature for every application. The necessity is dictated entirely by the process being performed.
When an Exhaust System is Critical
An active exhaust is non-negotiable for processes that are known to generate fumes. This includes:
- Ashing of organic or polymer-based materials.
- Binder burnout in ceramics or metallurgy.
- Chemical decomposition or pyrolysis.
- Heat treating materials with oils, coatings, or contaminants.
When Simpler Ventilation May Suffice
For applications where the sample is stable and does not off-gas, an active exhaust may be less critical. This can include:
- Annealing or tempering of clean metals.
- Sintering of pre-cleaned ceramic or metal powders.
- Melting point determination of stable, pure substances.
Even in these cases, placing the furnace under a general laboratory fume hood is always a recommended safety practice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a furnace setup depends on the materials you intend to process.
- If your primary focus is ashing, chemical analysis, or binder burnout: A furnace with an integrated, active exhaust system is essential for safety and accuracy.
- If your primary focus is heat treating clean metals or stable ceramics: A simple vent port may be adequate, but operating the furnace inside a fume hood is strongly advised.
- If your primary focus is safety when working with unknown materials: Always default to using a furnace with a robust exhaust system to prepare for unexpected off-gassing.
Ultimately, understanding the function of the exhaust system is key to performing safe and reliable high-temperature work.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Remove hazardous gases | Protects operator and lab environment | Ashing, binder burnout, chemical decomposition |
| Maintain process purity | Prevents sample contamination and ensures accurate results | Heat treating with contaminants, pyrolysis |
| Active vs. passive ventilation | Tailored to fume generation levels | Annealing clean metals (passive), volatile processes (active) |
Ensure your laboratory's safety and efficiency with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable exhaust systems in our Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability precisely meets your unique experimental requirements, from handling toxic byproducts to optimizing process integrity. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your high-temperature applications with tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production



















