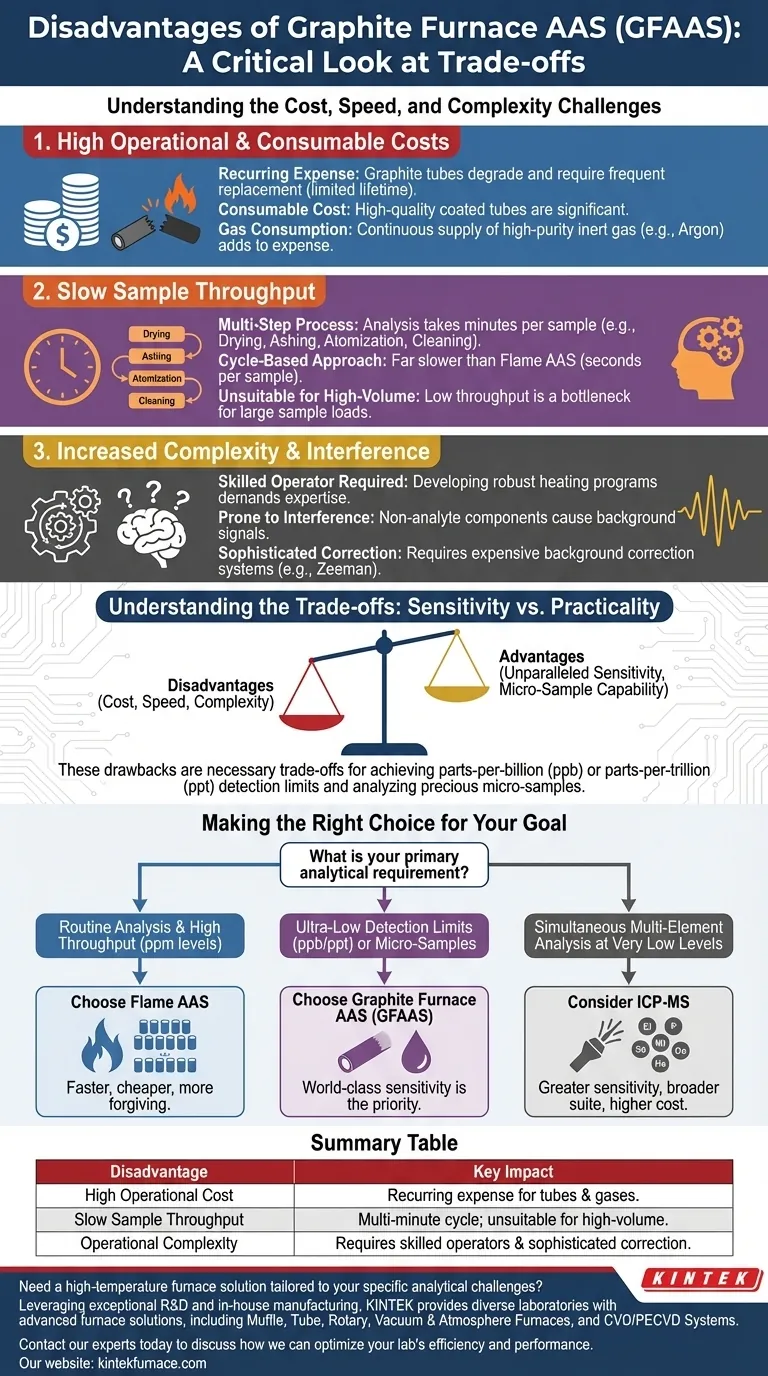
The primary disadvantages of a graphite furnace are its high operational cost, slow analysis time, and increased operational complexity compared to other atomic absorption techniques. These factors stem from the nature of the graphite tube itself, which is a consumable part that degrades with each use, and the multi-step heating process required for each individual sample.
While a graphite furnace provides exceptional sensitivity for trace metal analysis, its significant drawbacks in cost, speed, and complexity mean it is a specialized tool, not a general-purpose workhorse. The decision to use it is a direct trade-off between achieving the lowest possible detection limits and practical laboratory efficiency.

The Core Challenges of Graphite Furnace AAS
Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (GFAAS) is an electrothermal atomization method. Unlike a flame that continuously aspirates a sample, a graphite furnace uses a precise, multi-stage heating program to analyze a single, small aliquot of a sample, introducing several practical challenges.
High Operational & Consumable Costs
The heart of the system, the graphite tube, is a consumable with a limited lifetime. It may last for only a few hundred analysis cycles before its performance degrades and it requires replacement.
These tubes, especially high-quality coated versions, represent a significant and recurring operational cost. Furthermore, the furnace requires a continuous supply of high-purity inert gas, such as argon, to protect the tube from oxidation at high temperatures, adding to the expense.
Slow Sample Throughput
A single GFAAS analysis is a multi-step process that can take several minutes per sample. Each measurement involves a carefully programmed sequence:
- Drying: To slowly evaporate the solvent.
- Ashing (Pyrolysis): To burn off the sample matrix.
- Atomization: A rapid temperature jump to vaporize the target analyte.
- Cleaning: A final high-temperature step to remove any residue.
This cycle-based approach makes GFAAS far slower than Flame AAS, which can analyze samples in a matter of seconds. This low throughput makes it unsuitable for laboratories that need to process a large number of samples quickly.
Increased Complexity and Interference
Operating a GFAAS system requires a higher level of operator skill than other methods. Developing a robust heating program for a complex sample matrix is a methodical process that requires expertise.
The technique is also more prone to background interference, where non-analyte components in the sample absorb light and create a false signal. This necessitates sophisticated background correction systems (e.g., Zeeman or Deuterium lamp), which adds to the instrument's cost and complexity.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Sensitivity vs. Practicality
The disadvantages of a graphite furnace are not inherent flaws but rather the necessary trade-offs for its principal advantage: unparalleled sensitivity.
The Power of Unmatched Sensitivity
GFAAS is used because it can achieve detection limits hundreds or even thousands of times lower than Flame AAS. It is the go-to method for quantifying elements at parts-per-billion (ppb) or even parts-per-trillion (ppt) concentrations.
Micro-Sample Capability
Because it analyzes a discrete aliquot (typically 5-50 microliters), GFAAS is ideal when the sample is precious or available only in very small quantities. This is a critical advantage in clinical, forensic, and biological research.
When the Costs Are Justified
The high costs and slow speed become acceptable when the analytical goal is to measure trace or ultra-trace element concentrations that are simply undetectable by faster, cheaper methods. In environmental monitoring, clinical toxicology, and semiconductor manufacturing, this level of sensitivity is often a requirement, not a choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct atomic absorption technique depends entirely on your specific analytical requirements for sensitivity, sample throughput, and budget.
- If your primary focus is routine analysis and high sample throughput (ppm levels): Choose Flame AAS. It is faster, less expensive to operate, and more forgiving for a wider range of sample matrices.
- If your primary focus is ultra-low detection limits (ppb/ppt levels) or you have very little sample: Choose Graphite Furnace AAS. Its disadvantages are the necessary price for achieving world-class sensitivity.
- If your primary focus is analyzing many different elements simultaneously at very low levels: Consider Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS), which offers even greater sensitivity for a broader suite of elements, albeit at a significantly higher instrument cost.
Understanding these fundamental trade-offs empowers you to select the most effective and efficient tool for your analytical goal.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| High Operational Cost | Recurring expense for graphite tubes & high-purity gases. |
| Slow Sample Throughput | Multi-minute cycle per sample; unsuitable for high-volume labs. |
| Operational Complexity | Requires skilled operators and sophisticated background correction. |
Need a high-temperature furnace solution tailored to your specific analytical challenges? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your lab's efficiency and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















