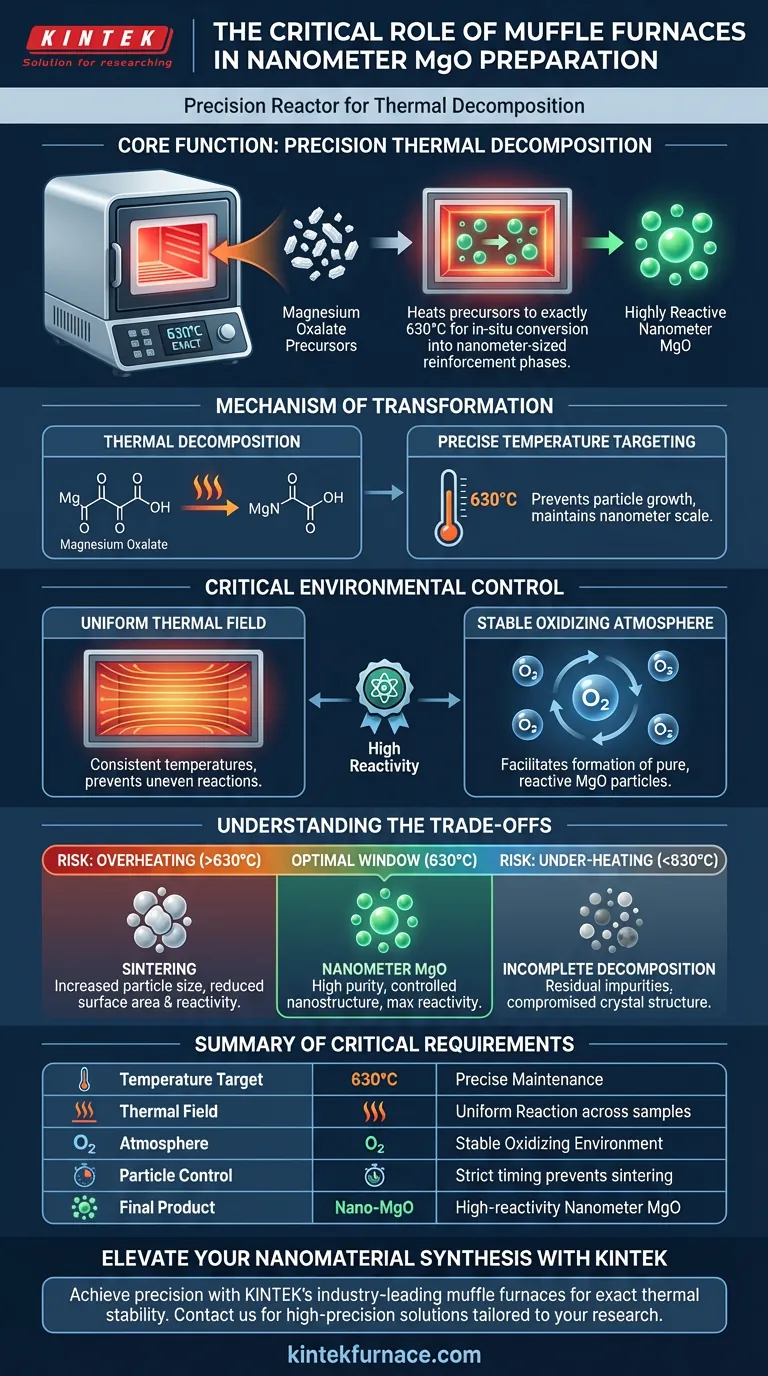
The muffle furnace functions as a precision reactor for thermal decomposition. In the preparation of nanometer-sized Magnesium Oxide (MgO), its primary role is to heat magnesium oxalate precursors to exactly 630°C. This specific thermal treatment drives the in-situ conversion of the precursor into highly reactive, nanometer-sized reinforcement phases.
Core Takeaway The muffle furnace is not merely a heater; it is a stability control system. By maintaining a uniform thermal field and a stable oxidizing atmosphere, it ensures the complete chemical breakdown of precursors without compromising the reactivity or size distribution of the final MgO nanoparticles.

The Mechanism of Transformation
Thermal Decomposition
The central chemical process occurring within the furnace is the breakdown of magnesium oxalate.
The furnace provides the energy required to sever the chemical bonds of the precursor. At the target temperature, the oxalate component decomposes, leaving behind the desired magnesium structure.
Precise Temperature Targeting
According to the primary technical data, the critical operating temperature for this specific process is 630°C.
Maintaining this constant temperature is vital. It allows for the complete conversion of the material into Magnesium Oxide (MgO) while preventing the particles from growing too large, which would negate their "nanometer-sized" classification.
The Role of Environmental Control
A Uniform Thermal Field
Achieving a "nanometer" scale requires consistency.
The muffle furnace creates a uniform thermal field, ensuring that every part of the sample experiences the exact same temperature. This prevents uneven reaction rates, which could lead to a mix of fully reacted MgO and unreacted precursor.
Stable Oxidizing Atmosphere
To form Magnesium Oxide, oxygen must be present and stable.
The furnace maintains an oxidizing atmosphere throughout the heating duration. This environment facilitates the chemical reaction necessary to convert the decomposing magnesium oxalate into pure, reactive MgO particles.
Enhancement of Reactivity
The result of this controlled environment is high reactivity.
By managing the heat and atmosphere precisely, the furnace produces MgO particles that are not only pure but also possess the surface energy required to act as effective reinforcement phases in composite materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Overheating (Sintering)
While high heat is necessary for decomposition, excessive heat is detrimental to nanotechnology.
If the furnace exceeds the optimal temperature window (significantly above 630°C) or holds it for too long, the nanoparticles may begin to fuse together. This process, known as sintering, increases particle size and drastically reduces the surface area and reactivity of the MgO.
The Consequence of Under-heating
Conversely, failing to reach or maintain 630°C results in incomplete decomposition.
In this scenario, residual organic impurities or unreacted magnesium oxalate will remain in the sample. This compromises the purity of the material and prevents the formation of the intended crystal structure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the successful synthesis of MgO reinforcement phases, align your furnace operation with your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Ensure the furnace is calibrated to hold exactly 630°C to guarantee the complete removal of oxalate precursors.
- If your primary focus is Particle Size (Nanostructure): Prioritize a furnace with excellent thermal uniformity to prevent hot spots that cause particle sintering and growth.
Success in nanomaterial preparation relies on the strict control of the thermal decomposition environment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in MgO Preparation | Critical Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Target | Thermal decomposition of magnesium oxalate | Precise 630°C maintenance |
| Thermal Field | Ensures uniform reaction rates across samples | High spatial uniformity |
| Atmosphere | Provides oxygen for MgO formation | Stable oxidizing environment |
| Particle Control | Prevents sintering and grain growth | Strict timing and heat stability |
| Final Product | High-reactivity nanometer-sized MgO | Purity and controlled nanostructure |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between successful MgO nanoparticles and failed chemical precursors. KINTEK provides industry-leading muffle furnaces designed to deliver the precise 630°C thermal stability and uniform oxidizing atmospheres required for advanced material reinforcement.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a full suite of laboratory solutions, including:
- High-Precision Muffle & Tube Furnaces for exact thermal targeting.
- Rotary & Vacuum Systems for specialized atmospheric control.
- CVD Systems and customizable high-temp furnaces tailored to your unique research needs.
Don't settle for temperature fluctuations that compromise your reactivity. Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect thermal solution for your lab and ensure the purity of your nanometer-sized reinforcement phases.
Visual Guide
References
- Qian Zhao, Minfang Chen. Effect of MgO Contents on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behavior of Low-Alloyed Mg-Zn-Ca Alloy. DOI: 10.3390/met14030274
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What function does a Muffle Furnace serve in ZTO thin film post-treatment? Optimize Solar Cell Performance
- What is the primary role of a muffle furnace in the calcination of Pt-xWO3/SiO2? Optimize Catalyst Phase-Engineering
- Why are muffle furnaces considered indispensable in laboratory and industrial settings? Discover Their Key Benefits for Clean, Controlled Heating
- What is the application of electric muffle furnace? Achieve Precise Heat Treatment for Your Lab
- How often should a muffle furnace be maintained? Optimize Performance with Proactive Care
- How are a muffle furnace and ceramic crucible used for MoO3? Master High-Purity Synthesis Today
- What is the significance of a high-temperature chamber sintering furnace in alumina lattice performance? Master Densification
- What advanced features do muffle furnaces include? Boost Precision and Safety in Your Lab



















