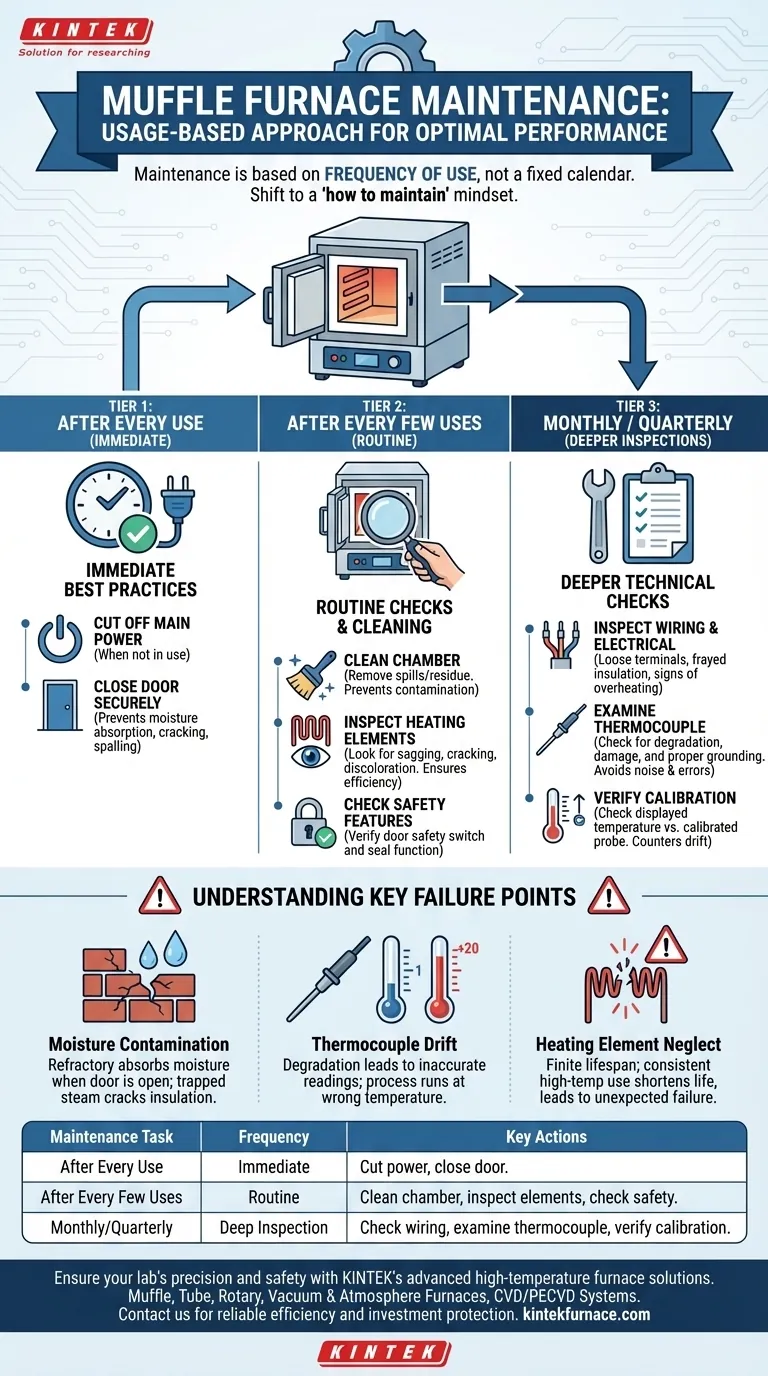
The maintenance schedule for a muffle furnace is not based on a fixed calendar, but on its frequency of use. For optimal performance and safety, you should perform short-term checks after every few uses, with more in-depth inspections conducted on a less frequent but regular basis. This usage-based approach ensures the furnace remains accurate, efficient, and safe throughout its operational life.
The key to muffle furnace longevity is shifting from a "when to maintain" mindset to a "how to maintain" one. Regular, use-dependent checks prevent minor issues from becoming catastrophic failures, protecting both your investment and your process results.
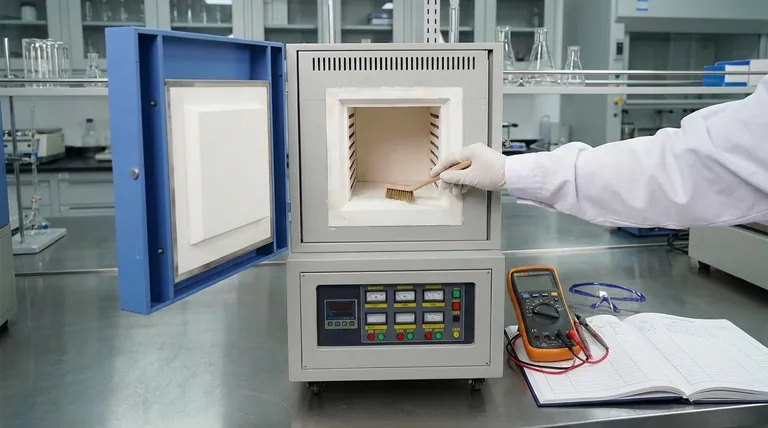

A Tiered Approach to Furnace Maintenance
Effective maintenance is not a single event but a continuous process. By categorizing tasks based on their frequency, you create a simple yet powerful system for preserving the furnace's integrity and performance.
After Every Use: Immediate Best Practices
The most frequent maintenance happens the moment you finish a cycle. These simple habits are your first line of defense against long-term damage.
When the furnace is not in use, always cut off the main power supply.
After it has cooled sufficiently, close the furnace door securely. This simple step is critical for protecting the internal refractory materials from absorbing atmospheric moisture, which can cause cracking and spalling during the next heat-up cycle.
After Every Few Uses: Routine Checks
After a handful of operational cycles, a more detailed inspection is required. This is the core of your preventative maintenance program.
First, clean the furnace chamber. Remove any spills, residue, or debris from the furnace floor and walls. A clean chamber prevents cross-contamination and ensures uniform heat radiation.
Next, perform a visual inspection of the heating elements. Look for any signs of sagging, cracking, or discoloration. Damaged elements lead to inefficient heating, temperature inaccuracies, and eventual failure.
Finally, check all safety features. Ensure the door's safety switch, which cuts power when the door is opened, is functioning correctly. A quick inspection of the door seal will confirm that heat is not escaping.
Monthly or Quarterly: Deeper Inspections
Less frequently, you must perform deeper technical checks that are vital for accuracy and electrical safety.
Inspect all wiring and electrical connections on both the furnace and the external controller. Look for loose terminals, frayed insulation, or signs of overheating. Secure connections are essential for both safety and stable operation.
Examine the thermocouple for signs of degradation or physical damage. Crucially, confirm it is properly seated and has a solid electrical ground. Poor grounding can introduce electrical noise, leading to significant temperature measurement errors.
Verify the furnace's calibration. Over time, temperature controllers and thermocouples can drift. Periodically checking the displayed temperature against a calibrated external probe ensures your process is running at the correct setpoint.
Understanding Key Failure Points
Neglecting maintenance introduces specific risks. Understanding these failure points highlights the importance of a consistent routine.
The Risk of Moisture Contamination
Refractory insulation is porous. Leaving the furnace door open allows it to act like a sponge, absorbing humidity from the air. When you next run the furnace, this trapped moisture turns to steam, creating internal pressure that can crack the insulation and shorten the furnace's life.
The Impact of Thermocouple Drift
A thermocouple is the furnace's primary sensor. Over time, especially at high temperatures, it can degrade and provide inaccurate readings—a phenomenon known as "drift." A furnace reading 1000°C might actually be at 980°C, compromising your entire process without any obvious alarm. Regular verification is the only way to catch this.
The Cost of Neglecting Heating Elements
Heating elements are consumables with a finite lifespan. Running them consistently at their maximum rated temperature drastically shortens this life. Inspecting them allows you to spot degradation early, preventing an unexpected mid-process failure that results in costly downtime and ruined samples.
Creating Your Maintenance Checklist
Tailor your maintenance plan to your specific operational needs and goals.
- If your primary focus is process accuracy: Prioritize regular thermocouple inspection and calibration verification to ensure your results are repeatable and reliable.
- If your primary focus is operational uptime: Concentrate on proactive inspection of heating elements and electrical connections to prevent unexpected failures.
- If your primary focus is lab safety: Make the inspection of door seals, safety interlocks, and wiring your top and most frequent priority.
A consistent, proactive maintenance routine is the most effective strategy for guaranteeing your muffle furnace's reliability.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Key Actions |
|---|---|---|
| After Every Use | Immediate | Cut power, close door securely to prevent moisture absorption |
| After Every Few Uses | Routine | Clean chamber, inspect heating elements, check safety features |
| Monthly/Quarterly | Deep Inspection | Check wiring, examine thermocouple, verify calibration |
Ensure your lab's precision and safety with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our reliable furnaces can enhance your efficiency and protect your investment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals



















