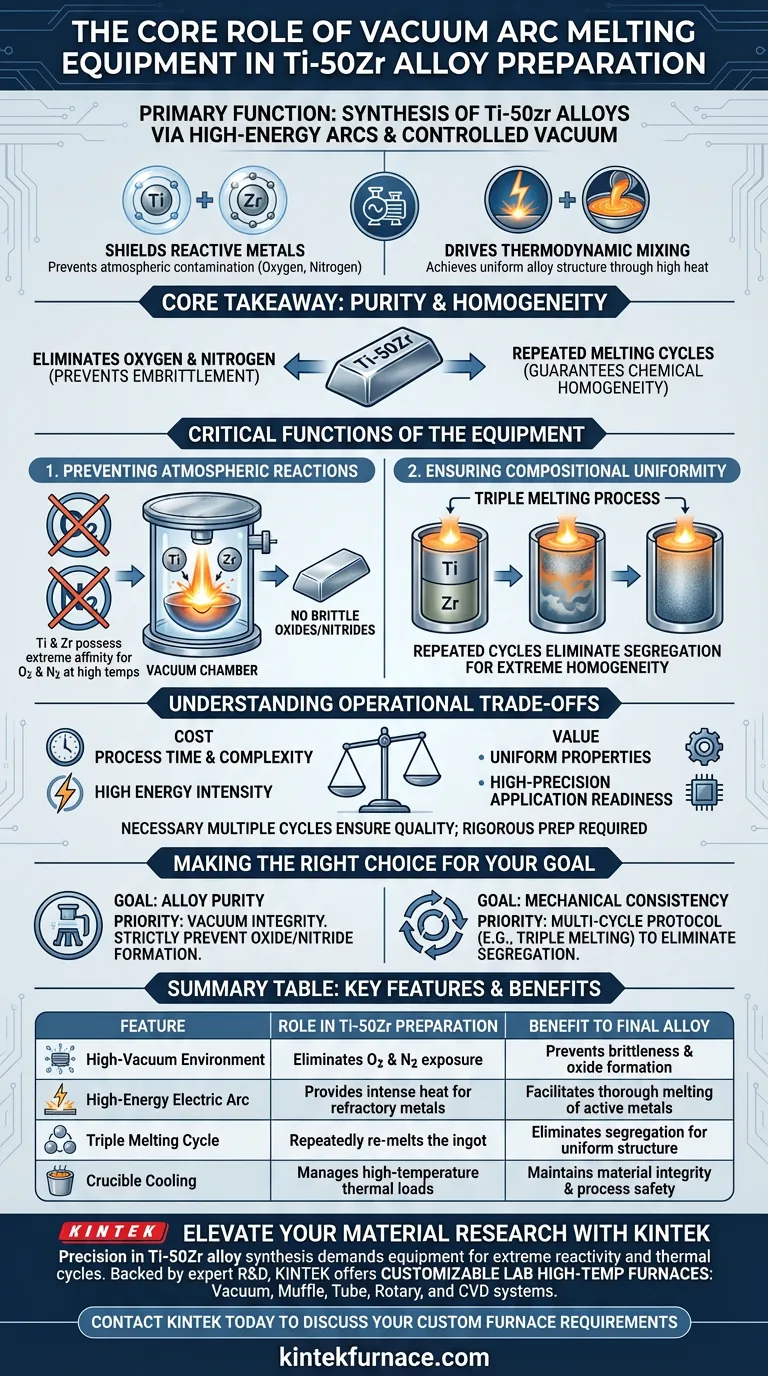
The primary function of vacuum arc melting equipment is to facilitate the synthesis of Ti–50Zr alloys by utilizing high-energy electric arcs within a strictly controlled vacuum environment. This equipment serves the dual purpose of shielding highly reactive metals from atmospheric contamination while driving the thermodynamic mixing required to achieve a uniform alloy structure.
Core Takeaway Titanium and zirconium are chemically active metals that degrade instantly if melted in the presence of air. Vacuum arc melting is the critical standard for these alloys because it eliminates oxygen and nitrogen from the processing environment, ensuring purity, while simultaneously using repeated melting cycles to guarantee chemical homogeneity.
The Critical Functions of the Equipment
Preventing Atmospheric Reactions
Titanium and zirconium are classified as active metals. At the high temperatures required for melting, they possess an extreme affinity for oxygen and nitrogen.
If exposed to air during melting, these metals react to form brittle oxides and nitrides. This contamination compromises the mechanical properties of the final alloy.
The vacuum arc melting equipment solves this by establishing a high-vacuum environment before the arc is struck. This effectively removes reactive gases, allowing the metals to melt without absorbing embrittling impurities.
Ensuring Compositional Uniformity
Creating a Ti–50Zr alloy requires more than just melting the two metals together once. A single pass often results in compositional segregation, where the ratio of Titanium to Zirconium varies across the ingot.
The equipment facilitates a process known as triple melting. By subjecting the alloy to repeated melting cycles, the equipment forces a thorough mixing of the elements.
This repetition eliminates segregation, ensuring that the final ingot possesses extreme homogeneity and a uniform chemical distribution throughout the material.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
The Necessity of Multiple Cycles
The primary "cost" of using vacuum arc melting for high-quality alloys is process time and complexity.
Achieving the required homogeneity is not instantaneous. As noted, a specific protocol (often triple melting) is required to eliminate segregation.
Skipping these cycles to save time will almost invariably lead to an inferior product with inconsistent mechanical properties, rendering the alloy unsuitable for high-precision applications.
Energy and Preparation Intensity
Vacuum arc melting is an energy-intensive process due to the generation of high-temperature arcs.
Furthermore, the process demands rigorous preparation of the raw materials to ensure the vacuum chamber remains uncontaminated. The equipment relies on the purity of the input to maintain the integrity of the vacuum environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure you maximize the utility of vacuum arc melting equipment for Ti–50Zr preparation:
- If your primary focus is Alloy Purity: Prioritize the integrity of the vacuum environment to strictly prevent the formation of oxides and nitrides that cause embrittlement.
- If your primary focus is Mechanical Consistency: Adhere strictly to a multi-cycle melting protocol (such as triple melting) to eliminate compositional segregation and ensure a uniform microstructure.
The effective use of this equipment dictates that you never compromise on the number of melting cycles when working with segregation-prone refractory metals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Ti–50Zr Preparation | Benefit to Final Alloy |
|---|---|---|
| High-Vacuum Environment | Eliminates oxygen and nitrogen exposure | Prevents brittleness and oxide/nitride formation |
| High-Energy Electric Arc | Provides intense heat for refractory metals | Facilitates thorough melting of active metals |
| Triple Melting Cycle | Repeatedly re-melts the ingot | Eliminates segregation for a uniform chemical structure |
| Crucible Cooling | Manages high-temperature thermal loads | Maintains material integrity and process safety |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision in Ti–50Zr alloy synthesis demands equipment that can handle extreme reactivity and rigorous thermal cycles. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of lab high-temp furnaces—including Vacuum, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique metallurgical needs.
Whether you require extreme purity for active metals or specialized homogeneity through advanced vacuum melting, our technical team is ready to assist. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace requirements and ensure your high-precision alloys meet the highest industry standards.
Visual Guide
References
- Improved Strength and Corrosion Resistance of Ti–50Zr Alloy Through Heat Treatment. DOI: 10.1002/adem.202501828
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the main components of a steel shell structure induction furnace? An In-Depth System Breakdown
- How does the alternating current power supply contribute to the induction heater's operation? Unlock Efficient, Contactless Heating
- What is inductive stirring in melting applications? Master Metallurgical Control for Superior Melt Quality
- Why is a vacuum arc melting system necessary for RHEAs? Achieve Pure, Homogeneous Refractory High-Entropy Alloys
- How does an induction furnace improve the purity of melted gold? Achieve Maximum Purity and Yield
- What are the cost implications of using electric crucible furnaces? Uncover the True Total Cost of Ownership
- What role does a vacuum arc melting furnace play in Ti-6Al-7Nb-xTa alloys? Precision Melting & Purity
- What is the primary function of high-temperature melting furnaces in aluminum alloy production? Master the Melt



















