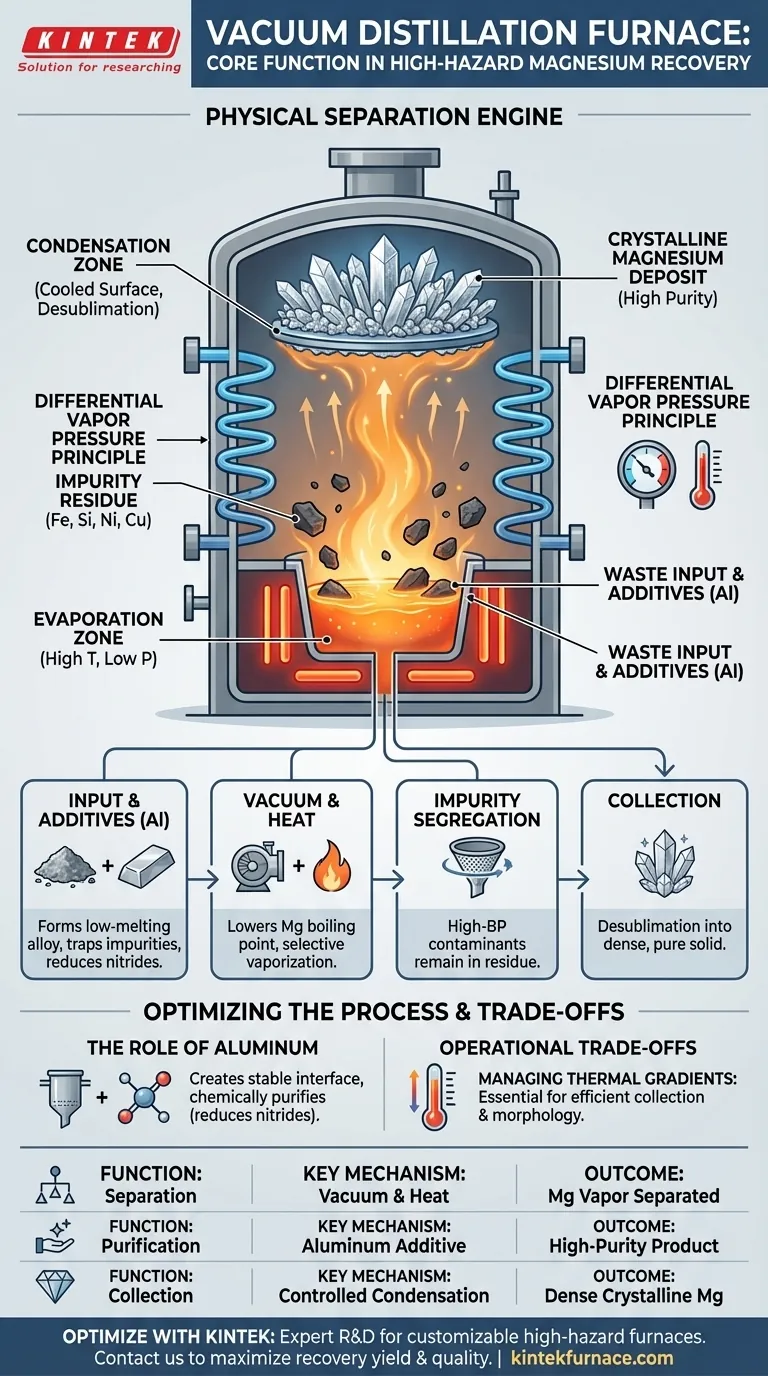
The core function of a vacuum distillation furnace in high-hazard magnesium recovery is to act as a physical separation engine. Utilizing a high-temperature, low-pressure environment, the furnace selectively vaporizes magnesium from waste materials while keeping impurities in a solid or liquid state, eventually collecting the purified metal through controlled condensation.
The furnace operates on the principle of differential vapor pressure. By creating a vacuum, it lowers the boiling point of magnesium, allowing it to evaporate at safer temperatures while leaving high-boiling-point contaminants like iron and silicon behind in the residue.

Creating the Separation Environment
Manipulating Pressure and Temperature
The furnace creates a low-pressure environment by evacuating the chamber. This is the fundamental mechanism that allows magnesium to vaporize at temperatures significantly lower than its atmospheric boiling point.
Simultaneously, the internal heating system provides precise thermal control. This ensures the temperature is high enough to evaporate the magnesium but remains low enough to prevent the vaporization of impurities.
Segregating Impurities
The primary goal is the exclusion of contaminants. As the magnesium turns to vapor, impurities with higher boiling points—specifically aluminum, iron, nickel, copper, and silicon—remain in the crucible.
This residue creates a clear physical separation between the waste slag and the valuable product. The furnace effectively filters the material at the atomic level, isolating the volatile magnesium from the stable waste.
Enhancing Stability with Additives
The Critical Role of Aluminum
In specific high-hazard processes, aluminum is added to the raw material to serve two distinct functions. First, it forms a low-melting-point magnesium-aluminum alloy layer.
This liquid layer creates a stable, uniform interface for evaporation and helps trap high-boiling-point impurities physically.
Chemical Purification
Beyond physical trapping, aluminum acts as a purifying agent. It reacts with nitrides present on the surface of the raw magnesium.
By reducing the nitrogen content, the added aluminum significantly improves the overall purity of the final distilled product.
The Collection Mechanism
Controlled Condensation
Once the magnesium is in vapor form, it migrates to the condensation zone, typically located in the upper part of the furnace or on a water-cooled lid.
This area is an independently cooled surface positioned away from the primary heating zone.
Desublimation into Crystalline Form
Because the condenser surface is maintained at a temperature significantly below the freezing point of magnesium, the vapor undergoes desublimation.
It transitions rapidly from a gas directly into a solid, depositing as dense, high-purity crystalline magnesium. This integrated design allows for extraction and collection within the same vessel.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Managing Thermal Gradients
A successful process requires maintaining a strict thermal gradient within a single vessel. You must sustain high heat for evaporation at the bottom while simultaneously cooling the top for condensation.
Failure to control this gradient leads to poor collection efficiency or "loose" morphology in the magnesium crystals.
The Cost of Purity
While adding aluminum aids in purification and stability, it introduces an additional material variable to the process.
This requires precise calculation of ratios to ensure the aluminum effectively traps impurities and reduces nitrides without contaminating the final product or creating excessive alloy slag.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your magnesium recovery process, you must tune the furnace parameters to your specific objective:
- If your primary focus is Maximum Purity: Prioritize the addition of aluminum to neutralize nitrides and strictly control the evaporation temperature to ensure zero carry-over of high-boiling contaminants like iron or nickel.
- If your primary focus is Product Morphology: Focus on the precise temperature control of the condenser surfaces, as the cooling rate directly dictates the density and quality of the crystalline magnesium deposit.
Effective recovery relies on balancing the vacuum level with thermal input to drive evaporation without activating the impurities.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Mechanism | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Separation | Creates a vacuum to lower magnesium's boiling point, allowing selective vaporization. | Magnesium vapor is separated from solid/liquid impurities (e.g., Fe, Si). |
| Purification | Utilizes additives like aluminum to trap impurities and chemically reduce nitrides. | Achieves a high-purity final magnesium product. |
| Collection | Cools vapor on a condenser surface, causing desublimation directly into solid crystals. | Collects dense, crystalline magnesium within the same vessel. |
Optimize Your High-Hazard Metal Recovery Process with KINTEK
Navigating the precise balance of temperature, pressure, and additives is critical for efficient and safe magnesium recovery. Our expertise ensures you get the purity and product morphology your operation demands.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, CVD systems, and other lab high-temp furnaces, all customizable for unique needs like high-hazard waste processing.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK vacuum distillation furnace can be tailored to maximize your recovery yield and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What types of metals and alloys are suitable for vacuum heat treatment furnaces? Essential Guide for High-Performance Materials
- What are the key differences in maximum temperature between low vacuum and high vacuum furnaces? Unlock Higher Heat for Purity
- How does a bell-type plasma nitriding furnace enhance GGG60 ductile iron? Superior Surface Hardening Solutions
- Why is a laboratory vacuum drying oven essential for the recovery of synthesized nanocomposite powders? | KINTEK
- What is the typical working vacuum degree for most heat treatment vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Process with the Right Vacuum Level
- What are the specific process advantages of using a vacuum drying oven for powder drying? Enhance Material Purity
- Why does magnesium distillation use a two-stage pump? A strategic division of labor for efficiency.
- What types of heating elements are used in vacuum furnaces and what are their temperature capabilities? Optimize Your High-Temp Processes



















