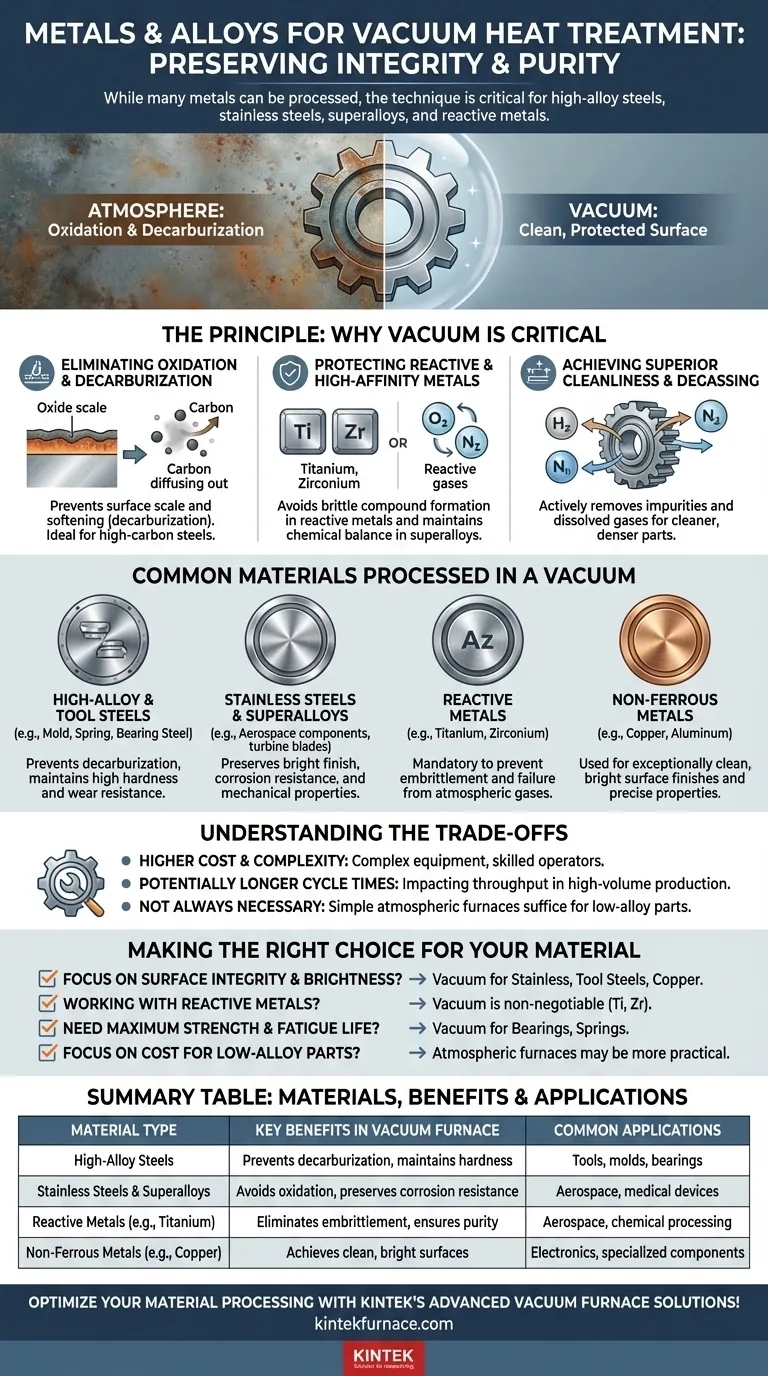
While many metals can be processed in a vacuum, the technique is most critical for materials where surface integrity and chemical purity are paramount. Vacuum heat treatment is specifically suited for high-alloy steels (like tool and mold steel), stainless steels, high-temperature superalloys, and reactive metals such as titanium and zirconium, which are highly susceptible to damage from atmospheric gases at high temperatures.
The core challenge in heat treatment is not just controlling temperature, but also controlling the material's interaction with its environment. Vacuum furnaces solve this by removing the atmosphere, thereby preventing unwanted surface reactions like oxidation and decarburization that can compromise a component's performance and integrity.

The Principle: Why a Vacuum Environment Is Critical
The decision to use a vacuum furnace is driven by the need to protect the material's surface and internal structure from harmful reactions that occur in the presence of air.
Eliminating Oxidation and Decarburization
At elevated temperatures, oxygen in the air reacts with a metal's surface, forming a layer of oxide scale. This process, oxidation, alters dimensions and can ruin surface finish.
For carbon-containing steels, the heat can also cause carbon to diffuse out of the surface, a process called decarburization. This softens the outer layer, drastically reducing wear resistance and fatigue life. A vacuum environment eliminates the reactive gases that cause these issues.
Protecting Reactive and High-Affinity Metals
Certain metals have a very high affinity for oxygen and nitrogen, especially when hot. Reactive metals like titanium, zirconium, and hafnium become brittle and unusable if they react with even trace amounts of atmospheric gases during treatment.
Similarly, superalloys used in aerospace and high-temperature applications rely on a precise chemical balance. A vacuum ensures this balance is maintained, preserving their critical mechanical properties.
Achieving Superior Cleanliness and Degassing
A vacuum does more than just prevent new contaminants from forming; it actively cleans the material. The process helps remove surface impurities and draws out dissolved gases like hydrogen and nitrogen from within the metal itself, a process known as degassing.
This results in a cleaner, denser final product with improved mechanical properties, such as enhanced strength and durability. The finished parts emerge from the furnace bright and clean, often without needing subsequent cleaning operations.
Common Materials Processed in a Vacuum
While the list is extensive, several categories of metals are prime candidates for vacuum heat treatment.
High-Alloy and Tool Steels
This category includes mold steel, spring steel, and bearing steel. These materials contain high levels of carbon and other alloying elements to achieve their desired hardness and wear resistance. Vacuum treatment is essential to prevent decarburization, which would negate their primary function.
Stainless Steels and Superalloys
The corrosion resistance of stainless steel and the extreme heat resistance of superalloys depend on their specific alloy compositions. Vacuum furnaces protect these expensive materials from surface oxidation, ensuring they retain their bright finish and performance characteristics without compromising the carefully engineered alloy mix.
Reactive Metals
For metals like titanium alloys, vacuum heat treatment is not just beneficial—it is often mandatory. Their extreme reactivity at processing temperatures means any exposure to oxygen or nitrogen would lead to embrittlement and component failure.
Non-Ferrous Metals
While less common, other non-ferrous metals like copper and aluminum can also be processed in a vacuum. This is typically done for specialized applications where an exceptionally clean, bright surface finish is required or to achieve specific properties through precise thermal control.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its advantages, vacuum heat treatment is not a universal solution. It involves clear trade-offs that make it unsuitable for certain applications.
Higher Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are more expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain than conventional atmospheric furnaces. The equipment required to create and hold a high vacuum is complex, and the process requires skilled operators.
Potentially Longer Cycle Times
Pulling a vacuum, processing, and then performing a controlled backfill or quench can take longer than a simple atmospheric heat treatment cycle. This can impact throughput and scheduling in a high-volume production environment.
Not Always Necessary
For many low-carbon or low-alloy steels where a thin layer of surface oxide is acceptable or will be machined off later, the benefits of a vacuum do not justify the added cost. In these cases, simpler and more economical atmospheric furnaces are the practical choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Material
Selecting the correct heat treatment process depends entirely on your material's composition and the final requirements for the component.
- If your primary focus is surface integrity and brightness: Vacuum treatment is the best choice for preserving the finish and chemistry of stainless steels, tool steels, and copper alloys.
- If you are working with reactive metals: Vacuum treatment is non-negotiable for materials like titanium, zirconium, and other high-affinity alloys to prevent catastrophic embrittlement.
- If you need maximum strength and fatigue life: The clean, controlled environment is ideal for critical components like bearings, springs, and high-strength fasteners where decarburization is unacceptable.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness on low-alloy parts: A simpler atmospheric furnace is often the more practical and economical solution, provided a small amount of surface oxidation is tolerable.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum heat treatment is a strategic decision to protect material integrity when surface chemistry is as critical as the thermal profile.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Benefits in Vacuum Furnace | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| High-Alloy Steels | Prevents decarburization, maintains hardness | Tools, molds, bearings |
| Stainless Steels & Superalloys | Avoids oxidation, preserves corrosion resistance | Aerospace, medical devices |
| Reactive Metals (e.g., Titanium) | Eliminates embrittlement, ensures purity | Aerospace, chemical processing |
| Non-Ferrous Metals (e.g., Copper) | Achieves clean, bright surfaces | Electronics, specialized components |
Optimize your material processing with KINTEK's advanced vacuum furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, enhancing performance and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your projects with tailored heat treatment technologies!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety



















