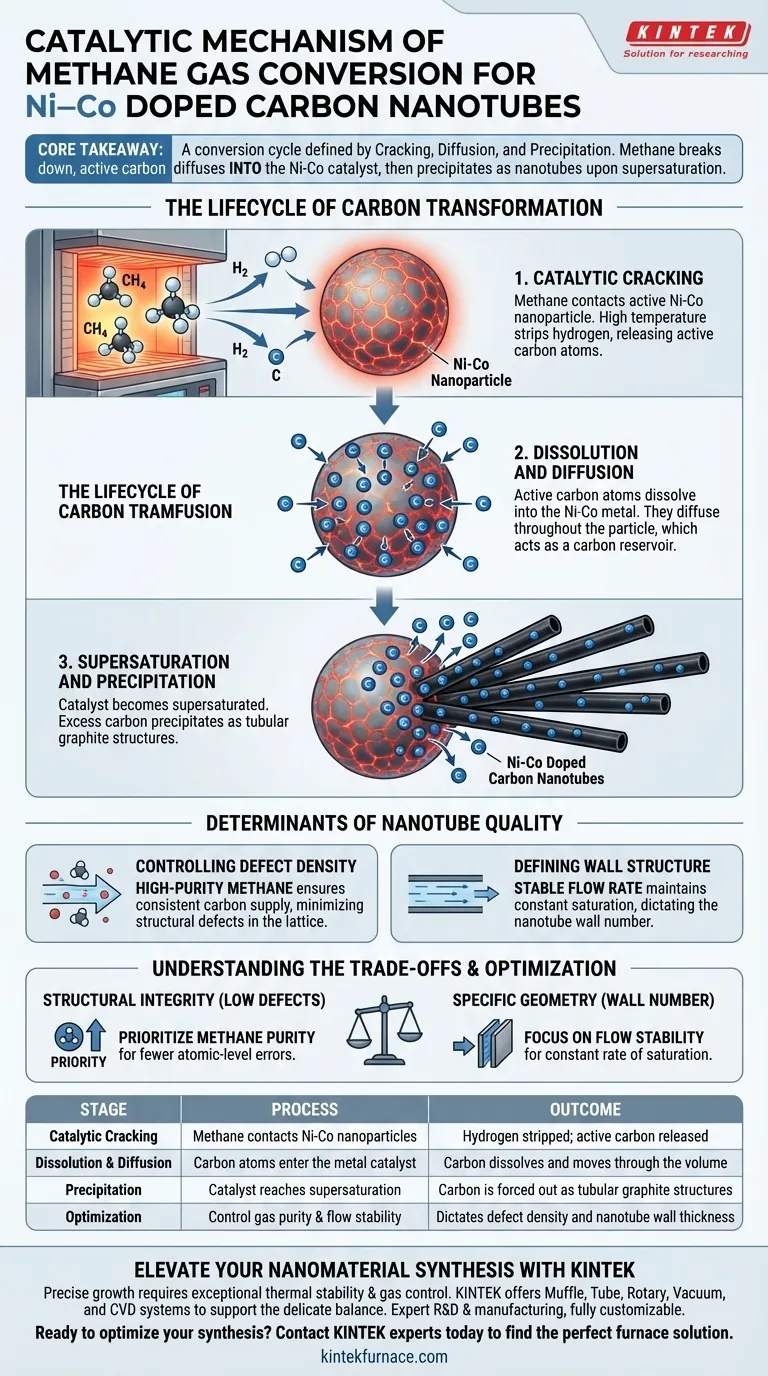
The catalytic mechanism acts as a conversion cycle defined by cracking, diffusion, and precipitation. Within the high-temperature furnace, methane gas serves as the carbon feedstock that contacts active Nickel-Cobalt (Ni-Co) nanoparticles. This contact triggers a reaction where the methane cracks to release carbon atoms, which then dissolve into the metal catalyst until they precipitate as solid tubular graphite structures.
Core Takeaway The synthesis of Ni-Co doped carbon nanotubes is driven by a solution-precipitation mechanism. Methane does not simply build up on the surface; it is chemically broken down so that active carbon atoms can diffuse into the catalyst, eventually forcing their way out as nanotubes once the metal becomes supersaturated.
The Lifecycle of Carbon Transformation
The conversion of methane into carbon nanotubes is not instantaneous. It follows a distinct sequence of atomic-level events governed by the interaction between the gas and the Ni-Co catalyst.
Catalytic Cracking
The process begins when methane gas comes into contact with the surface of the active Ni-Co nanoparticles.
The high temperature and the catalytic properties of the metal cause the methane molecules to break apart. This "cracking" process strips the hydrogen away, releasing active carbon atoms ready for synthesis.
Dissolution and Diffusion
Once released, the carbon atoms do not immediately form a structure. Instead, they dissolve into the Ni-Co metal particles.
Driven by the concentration gradient, these atoms diffuse throughout the volume of the nanoparticle. The metal acts as a reservoir, absorbing carbon much like water absorbs salt.
Supersaturation and Precipitation
The metal particle eventually reaches a tipping point known as supersaturation.
At this stage, the catalyst can no longer hold the dissolved carbon. The excess carbon is forced out of the metal, precipitating in the form of tubular graphite structures—the carbon nanotubes.
Determinants of Nanotube Quality
The physical properties of the resulting nanotubes are not random. They are directly controlled by the stability and quality of the methane gas input.
Controlling Defect Density
The purity of the methane gas is the primary variable affecting the structural integrity of the nanotube.
High-purity methane ensures a consistent supply of carbon atoms without contaminants. Variations in purity directly correlate to the defect density found in the final carbon lattice.
Defining Wall Structure
The number of walls in the nanotube (e.g., single-walled vs. multi-walled) is influenced by the delivery of the gas.
Flow stability is critical here. A stable flow rate maintains a consistent level of carbon saturation within the catalyst, which dictates the resulting wall number of the nanotubes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the mechanism is straightforward, achieving high-quality synthesis requires balancing delicate process variables.
The Saturation Balance
The process relies entirely on the Ni-Co particle reaching supersaturation.
If the carbon supply is too low (due to low flow), precipitation may stall. Conversely, inconsistencies in the feed can disrupt the uniform precipitation required for consistent tubular structures.
Sensitivity to Feedstock Quality
The mechanism is highly sensitive to the inputs. Because the catalyst must absorb and extrude carbon atoms, any impurities in the methane can interfere with the diffusion process.
This sensitivity means that purity and flow stability are not just operational details—they are the defining factors of the material's final grade.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your synthesis of Ni-Co doped carbon nanotubes, you must tune your inputs based on the specific structural characteristic you wish to prioritize.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity (Low Defects): Prioritize the purity of your methane source to minimize atomic-level errors in the carbon lattice.
- If your primary focus is Specific Geometry (Wall Number): Focus on the flow stability of the gas to ensure a constant rate of saturation and precipitation.
By strictly controlling the purity and flow of methane, you command the diffusion rate within the catalyst and dictate the quality of the final nanotube.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Process | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Catalytic Cracking | Methane contacts Ni-Co nanoparticles | Hydrogen is stripped; active carbon atoms are released |
| Dissolution & Diffusion | Carbon atoms enter the metal catalyst | Carbon dissolves and moves through the nanoparticle volume |
| Precipitation | Catalyst reaches supersaturation | Carbon is forced out as tubular graphite structures |
| Optimization | Control gas purity & flow stability | Dictates defect density and nanotube wall thickness |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise carbon nanotube growth requires exceptional thermal stability and gas control. KINTEK provides industry-leading Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all engineered to support the delicate balance of methane cracking and carbon precipitation.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique research or production needs. Ensure consistent saturation and superior structural integrity for your Ni-Co doped nanotubes.
Ready to optimize your synthesis? Contact KINTEK experts today to find the perfect furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- A. Shameem, P. Sivaprakash. A High-Performance Supercapacitor Based on Hierarchical Template-Free Ni/SnO2 Nanostructures via Hydrothermal Method. DOI: 10.3390/ma17081894
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What role do low-temperature carbonization furnaces play in carbon fiber manufacture? Build a Strong Structural Foundation
- What role does a releasing agent play during the assembly process of titanium-steel composite plates?
- What is the purpose of using a laboratory blast drying oven at 107°C for 17 hours for reforming catalysts?
- Why is it necessary to preheat casting molds to 300°C? Expert Thermal Control for Recycled Aluminum Alloy Production
- How does a high-temperature annealing furnace regulate cold-rolled steel? Optimize Manganese Steel Performance
- Why is thermal treatment of Mn1/CeO2 catalysts necessary? Unlock Peak Activation and Purity
- Why is the vacuum drying process essential for the synthesis of phthalonitrile-modified titanium dioxide? Expert Guide



















