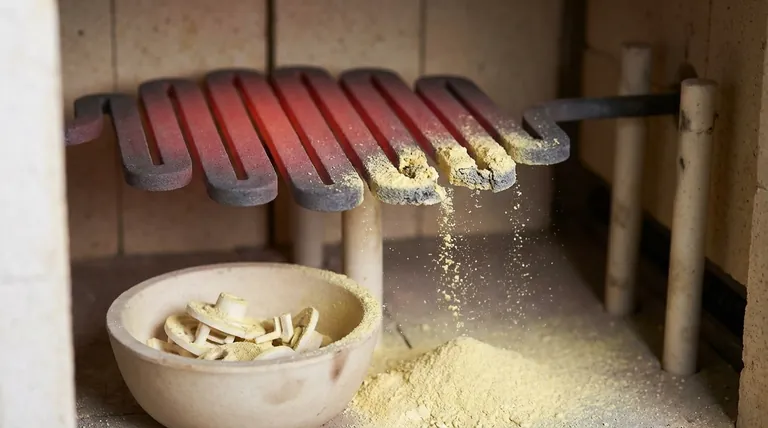
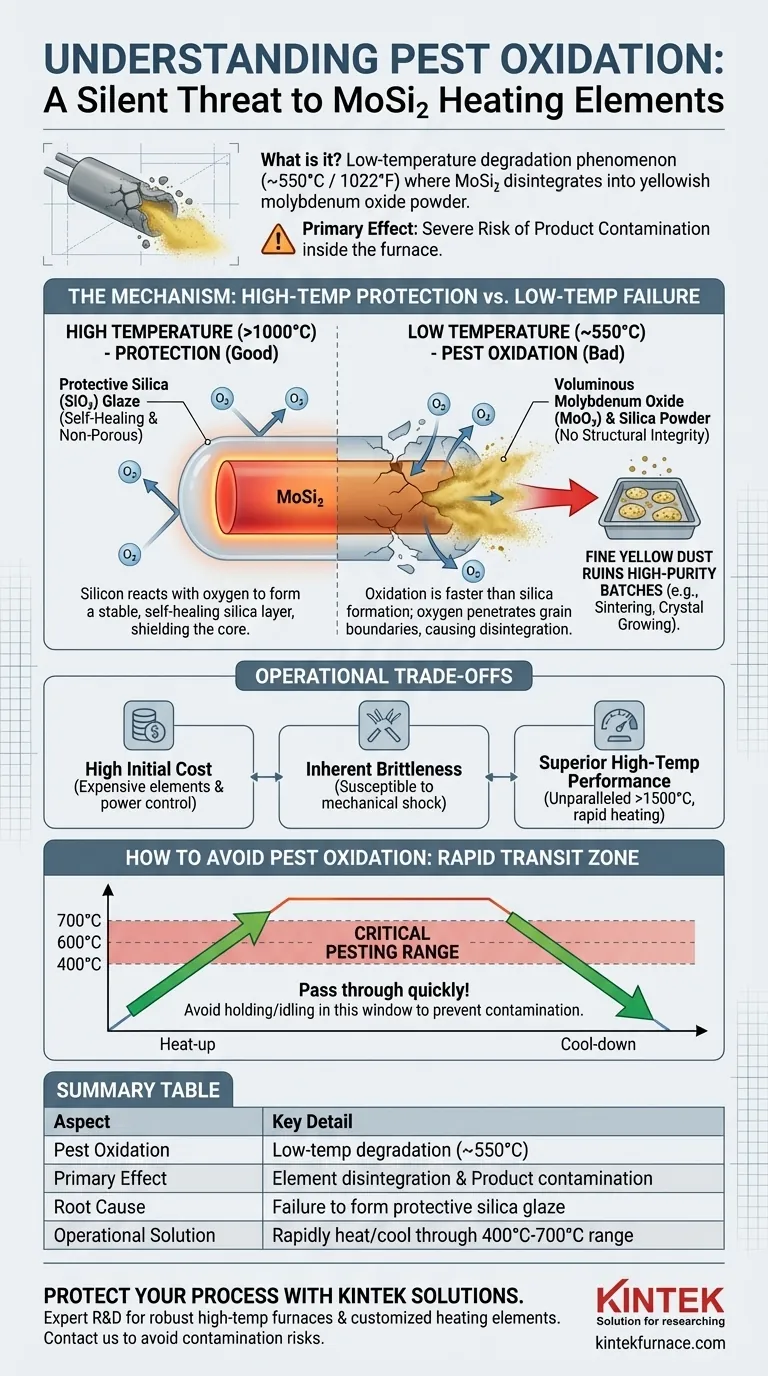
In short, pest oxidation is a low-temperature degradation phenomenon affecting Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) heating elements. When these elements operate in the presence of air around 550°C (approximately 1022°F), they can rapidly disintegrate, forming a yellowish powder of molybdenum oxide. While this does not immediately impact the element's heating capability, its primary effect is the severe risk of contaminating the products inside the furnace.
The core issue is a mismatch between the element's design and its operating conditions. MoSi₂ elements are engineered for extreme high-temperature performance, where they form a protective layer; pest oxidation occurs at low temperatures where this protective mechanism fails.

The Principle of High-Temperature Protection
MoSi₂ elements are renowned for their exceptional performance and longevity at very high temperatures, often exceeding 1800°C. This resilience is not inherent to the base material alone but comes from a crucial chemical reaction.
Forming the Protective Glaze
At high temperatures in an oxidizing atmosphere, the silicon in the element reacts with oxygen to form a thin, non-porous layer of silica (SiO₂) glass on its surface. This glassy layer acts as a passivation shield, preventing further oxygen from reaching and reacting with the underlying molybdenum disilicide.
Self-Healing Properties
This silica glaze is the key to the element's long life. If a crack or imperfection develops in the layer at high temperatures, it will quickly "heal" itself as the newly exposed material reacts with oxygen to form more protective silica, resealing the element.
The Anomaly of Pest Oxidation
The protective mechanism described above only works effectively at high temperatures. Pest oxidation is what happens when the element is held for extended periods in a specific low-temperature window where this protection cannot form properly.
The Critical Temperature Range
This phenomenon is most aggressive around 550°C. In this range, the rate of molybdenum oxidation is significantly faster than the rate of silica formation. Oxygen penetrates the material's grain boundaries and reacts with both molybdenum and silicon.
The Destructive Mechanism
Instead of a stable, glassy SiO₂ layer, the reaction produces a voluminous, powdery mix of molybdenum oxide (MoO₃) and silica. This yellowish powder has no structural integrity and causes the element to crumble and disintegrate, a process often called "pesting."
The Primary Consequence: Contamination
The most immediate effect of this powder is product contamination. For high-purity processes, such as sintering dental zirconia or growing crystals, this fine yellow dust can ruin an entire batch. While the element is failing, the more pressing business risk is the loss of valuable product.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Choosing MoSi₂ elements involves understanding their strengths and weaknesses. Pest oxidation is a critical weakness, but it exists alongside other considerations.
High Initial Cost
MoSi₂ elements are among the most expensive heating element options. They also require costly low-voltage, high-current power control equipment, typically involving transformers, which adds to the total system cost.
Inherent Brittleness
As a ceramic-based material, MoSi₂ is brittle and susceptible to mechanical shock, especially when cold. This requires careful handling during installation and maintenance to prevent fractures.
Superior High-Temperature Performance
Despite the drawbacks, their performance above 1500°C is unparalleled. They can last significantly longer than other elements like Silicon Carbide (SiC) in extreme heat, offering rapid heating cycles and excellent thermal uniformity.
How to Apply This to Your Process
The key to successfully using MoSi₂ elements is to operate them in a way that minimizes time spent in the problematic temperature range.
- If your primary focus is process purity: You must pass through the 400°C to 700°C range as quickly as possible during both heat-up and cool-down to prevent pesting and contamination.
- If your primary focus is element longevity: Avoid any process that requires holding or idling the furnace within the pest oxidation temperature window for extended periods.
- If your process operates below 1400°C: Consider if MoSi₂ is the right choice, as other elements like SiC may offer a more robust and cost-effective solution without the risk of pesting.
Ultimately, understanding pest oxidation is about using this specialized tool for its intended purpose: rapid, clean, and reliable heating at extreme temperatures.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Pest Oxidation | Low-temperature degradation (around 550°C / 1022°F) |
| Primary Effect | Element disintegration into powder, causing product contamination |
| Root Cause | Failure to form protective silica glaze at low temperatures |
| Operational Solution | Rapidly heat/cool through the 400°C-700°C range |
Protect your high-temperature processes and valuable products. Pest oxidation is a critical failure mode for standard MoSi2 elements. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems with robust, high-temp furnace solutions. Our experts can help you select or customize the right heating elements and furnace design to avoid contamination risks and ensure reliable performance. Contact our team today for a consultation tailored to your unique thermal processing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions



















