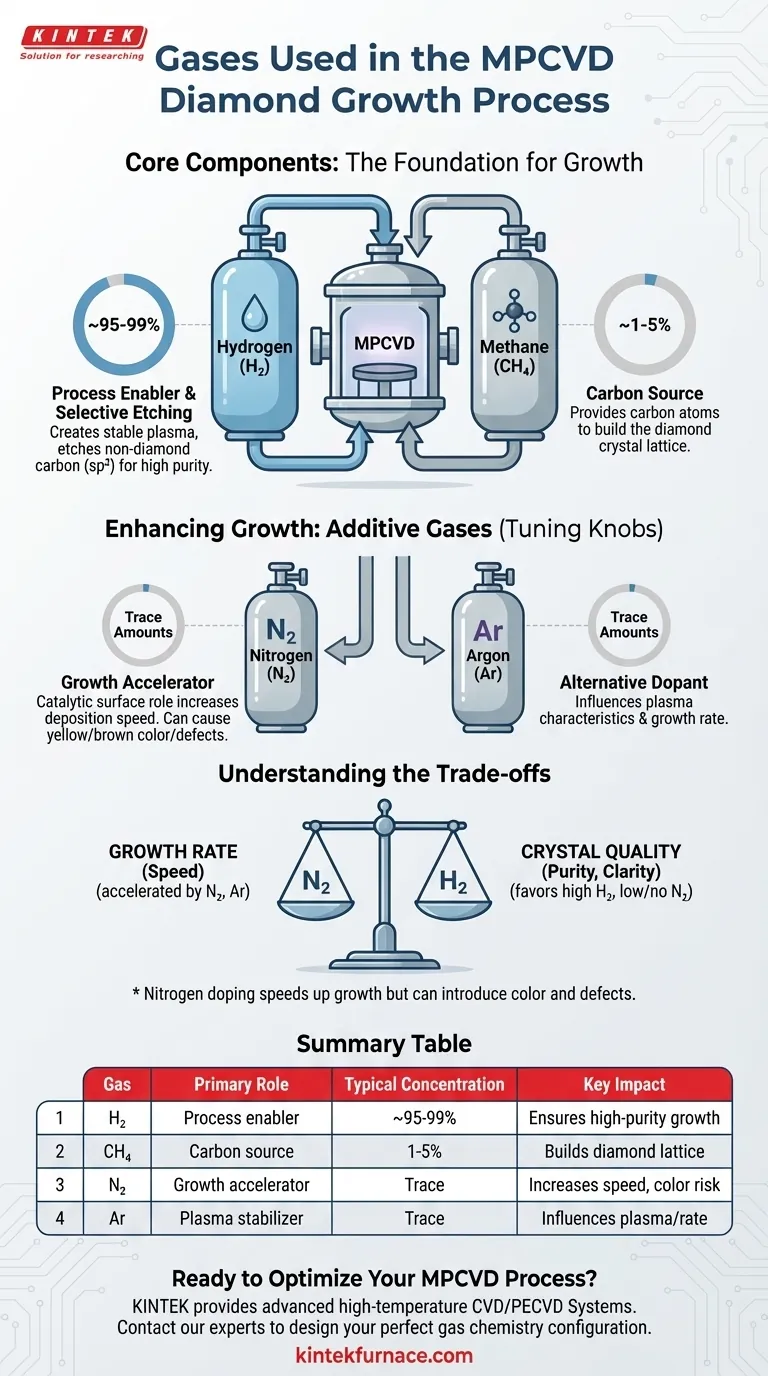
In the MPCVD process for growing diamond, the standard gas mixture consists of a high-purity carrier gas, hydrogen, and a carbon-source gas, almost always methane. These two gases form the foundation of the process, but other gases like nitrogen or argon are often introduced in small, controlled amounts to manipulate the growth characteristics, particularly the speed of deposition.
The core of MPCVD gas chemistry is a balance between a carbon source (methane) to build the diamond and a dominant process gas (hydrogen) to create the right plasma environment and ensure quality. Additives are then used as a tuning knob to optimize for specific outcomes like growth rate.
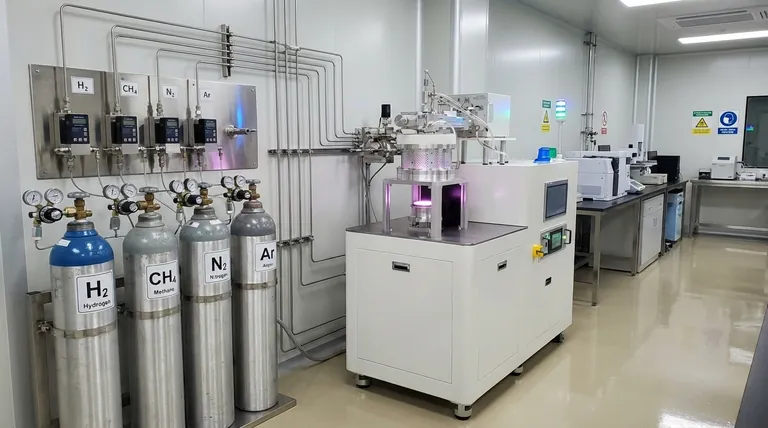

The Core Components: Hydrogen and Methane
The foundation of any MPCVD diamond growth recipe rests on two primary gases. Their ratio and purity are critical variables that directly influence the final product.
Methane (CH₄): The Carbon Source
Methane's role is straightforward: it provides the carbon atoms necessary to build the diamond's crystal lattice. Inside the high-energy plasma, methane molecules (CH₄) are broken apart, releasing carbon that can then deposit onto the substrate.
The concentration of methane is typically very low, often just 1-5% relative to the hydrogen. Too little methane starves the process, while too much can lead to the formation of non-diamond carbon, like graphite, which degrades crystal quality.
Hydrogen (H₂): The Process Enabler
Hydrogen is much more than just a carrier gas; it performs several critical functions simultaneously. It makes up the vast majority of the gas mixture and is essential for creating a stable, high-quality plasma environment.
Its most crucial role is selective etching. Hydrogen atoms preferentially etch away any weakly bonded, non-diamond carbon (sp²) that deposits on the surface, leaving behind only the desired, strongly bonded diamond carbon (sp³). This continuous "cleaning" action is what ensures high-purity diamond growth.
Enhancing Growth with Additive Gases
While hydrogen and methane are sufficient to grow diamond, the process can be slow. To increase the growth rate for industrial and commercial applications, small amounts of other gases are often introduced.
Nitrogen (N₂): The Growth Accelerator
Adding a small, controlled amount of nitrogen is a common technique to significantly increase the diamond growth rate. Even trace amounts can have a dramatic effect on deposition speed.
The Catalytic Role of Nitrogen
Contrary to what might be assumed, nitrogen does not work by simply helping to break down more methane. Instead, it acts as a surface catalyst.
Nitrogen changes the chemical pathways on the diamond's growing surface, increasing the concentration of CN (carbon-nitrogen) groups. This accelerates the chemical reactions that incorporate carbon atoms into the lattice, effectively speeding up the entire growth cycle.
Argon (Ar): An Alternative Dopant
Argon is another inert gas that is sometimes used as an additive. Like nitrogen, it can be used to influence the plasma characteristics and increase the growth rate, though the mechanisms can differ.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of gas mixture is not just about a recipe; it's about managing a set of critical trade-offs that connect process parameters to the final diamond's properties.
Growth Rate vs. Crystal Quality
The most fundamental trade-off is speed versus quality. While nitrogen doping accelerates growth, it can also lead to the incorporation of nitrogen atoms into the diamond lattice. This creates defects that can impact the diamond's optical and electronic properties.
The Impact of Nitrogen on Color
A direct consequence of nitrogen incorporation is color. Nitrogen defects absorb blue light, causing the diamond to appear yellow or brown. For applications where water-clear transparency is paramount (like high-end gems or optical windows), nitrogen use must be minimized or avoided entirely.
Selecting the Right Gas Mixture for Your Goal
Your choice of gases should be dictated by the desired outcome for the final diamond product. There is no single "best" recipe.
- If your primary focus is high purity and optical clarity: Stick to a high-purity hydrogen and methane mixture and avoid nitrogen, focusing on optimizing pressure, temperature, and power.
- If your primary focus is maximizing growth rate for industrial applications: Controlled nitrogen doping is the standard approach to accelerate production, as color and minor defects are often acceptable for abrasives or heat sinks.
Ultimately, mastering the gas chemistry is fundamental to controlling the outcome of the MPCVD process.
Summary Table:
| Gas | Primary Role | Typical Concentration | Key Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H₂) | Process enabler & selective etching | ~95-99% | Ensures high-purity diamond growth |
| Methane (CH₄) | Carbon source | 1-5% | Builds the diamond crystal lattice |
| Nitrogen (N₂) | Growth accelerator (additive) | Trace amounts | Increases deposition speed, can cause yellow/brown color |
| Argon (Ar) | Plasma stabilizer (additive) | Trace amounts | Influences plasma characteristics & growth rate |
Ready to Optimize Your MPCVD Process?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and specialized CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for diamond film research and production.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you design the perfect gas chemistry and system configuration for your specific diamond growth goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- MPCVD Machine System Reactor Bell-jar Resonator for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- Who should perform maintenance on MPCVD equipment? Trust Certified Experts for Safety and Precision
- What are the key advantages of MPCVD in diamond synthesis? Achieve High-Purity, Scalable Diamond Production
- How does MPCVD compare to other CVD methods like HFCVD and plasma torch? Uncover Superior Film Purity and Uniformity
- How is MPCVD used in manufacturing polycrystalline diamond optical components? Achieve Superior Optical Performance
- In which industries is the microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition system commonly used? Unlock High-Purity Material Synthesis



















