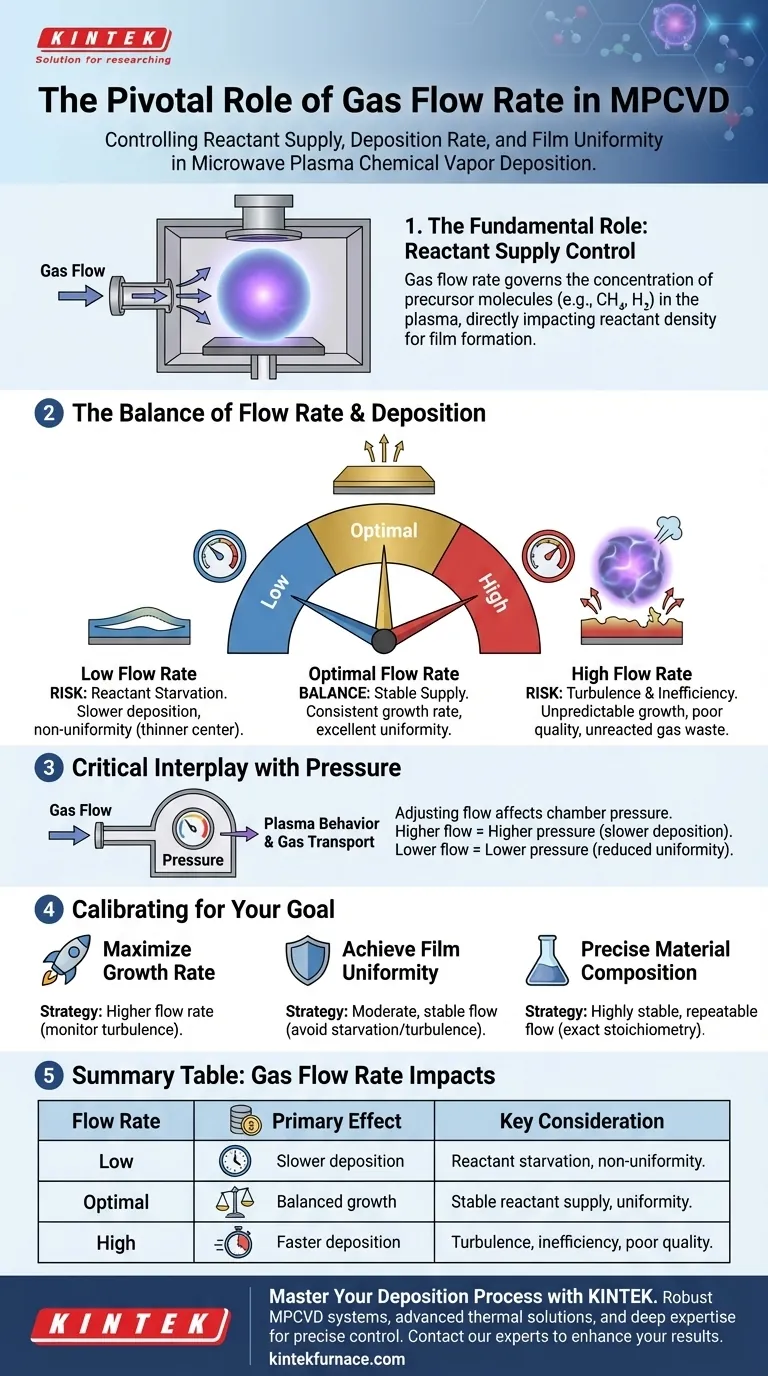
In Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition (MPCVD), the gas flow rate is the primary mechanism for controlling the supply of reactant precursors to the substrate. It directly governs the concentration of chemical species within the plasma, which in turn determines the rate of film growth, its final thickness, and its uniformity across the substrate surface.
The core challenge of MPCVD is not just supplying gas, but managing the concentration and distribution of reactive species at the growth surface. Gas flow rate is your most direct control over this delicate balance, acting as the primary lever for tuning both the speed and the quality of your deposition.
The Fundamental Role of Gas Flow: Controlling Reactant Supply
To master an MPCVD process, you must understand gas flow not as a simple speed, but as a control for reactant concentration. This perspective is key to diagnosing and optimizing your results.
The Concept of Reactant Concentration
Gas flow rate determines the number of precursor molecules (like methane and hydrogen for diamond growth) introduced into the reaction chamber per unit of time.
This directly sets the density of reactive species available in the plasma. A higher flow rate increases this density, providing more raw material for the chemical reactions that form the film.
Impact on Deposition Rate
The rate of film deposition is strongly correlated with the flow rate.
A lower flow rate delivers fewer reactants, inherently slowing down the growth process. Conversely, a higher flow rate can increase the deposition rate, but only up to a certain point.
Impact on Film Uniformity
Uniformity is achieved when reactants are distributed evenly across the entire substrate.
The flow rate is critical here. An optimal rate ensures a consistent and stable supply of reactants to all areas of the growth surface, leading to uniform film thickness and composition.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
Simply turning the flow rate up or down without considering the consequences is a common mistake. The ideal flow rate is a carefully calibrated balance between competing factors.
The Risk of Low Flow Rates
Operating with an insufficient gas flow rate leads to "reactant starvation."
This not only slows deposition to impractical levels but can also cause non-uniformity. The edges of the substrate may consume the available reactants before they can reach the center, resulting in a film that is thinner in the middle.
The Risk of High Flow Rates
Excessively high flow rates are also detrimental. They can create turbulence inside the chamber, disrupting the stable boundary layer of gas above the substrate.
This leads to unpredictable, non-uniform growth. Furthermore, it can be inefficient, as unreacted precursor gases are swept out of the chamber by the vacuum pump before they have a chance to contribute to the film.
The Critical Interplay with Pressure
Gas flow rate and chamber pressure are not independent variables; they are intrinsically linked. Increasing the gas flow into the chamber while the pumping speed remains constant will cause the overall chamber pressure to rise.
Pressure itself affects the plasma characteristics and gas transport. Higher pressure can slow the deposition rate, while low pressure can also degrade uniformity. Therefore, any adjustment to the flow rate must be considered in the context of its effect on the chamber pressure.
Calibrating Flow Rate for Your Specific Goal
The "correct" flow rate is not a single number but is dependent on your specific material, system geometry, and desired outcome. Use the following principles as your guide.
- If your primary focus is maximizing growth rate: You will likely operate at a higher flow rate, but you must carefully monitor uniformity and stop increasing the flow before turbulence degrades your film quality.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum film uniformity: Aim for a moderate and stable flow rate that provides a consistent supply of reactants without creating turbulence or reactant starvation zones.
- If your primary focus is precise material composition: Your priority is a highly stable and repeatable flow rate that maintains the exact ratio of precursor gases required for your desired stoichiometry.
Mastering gas flow rate transforms your MPCVD process from a fixed recipe into a precisely controlled engineering tool.
Summary Table:
| Gas Flow Rate | Primary Effect | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Low | Slower deposition, risk of reactant starvation | Can cause non-uniform thickness (thinner center) |
| Optimal | Balanced growth rate and excellent uniformity | Ensures stable, consistent reactant supply |
| High | Faster deposition, but risk of turbulence | Can lead to inefficient gas use and poor film quality |
| Key Interaction | Flow rate and chamber pressure are linked | Adjusting flow affects pressure, which impacts plasma behavior |
Struggling to Optimize Your MPCVD Process?
Precise control over gas flow rate is critical for achieving high-quality, uniform diamond films. At KINTEK, we leverage our deep expertise in advanced thermal solutions to provide robust MPCVD systems and expert support.
Our Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems are engineered for exceptional process stability and control. With strong in-house R&D and manufacturing capabilities, we offer deep customization to perfectly match your unique research or production requirements.
Let us help you master your deposition process. Contact our experts today for a consultation on how our solutions can enhance your MPCVD results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- MPCVD Machine System Reactor Bell-jar Resonator for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- What are the two main methods of synthetic diamond production? Discover HPHT vs. CVD for Lab-Grown Gems
- What are the key advantages of MPCVD in diamond synthesis? Achieve High-Purity, Scalable Diamond Production
- How does MPCVD compare to other CVD methods like HFCVD and plasma torch? Uncover Superior Film Purity and Uniformity
- Who should perform maintenance on MPCVD equipment? Trust Certified Experts for Safety and Precision
- What is the relationship between diamond growth rate and quality in the MPCVD method? Balancing Speed and Purity for Your Application



















