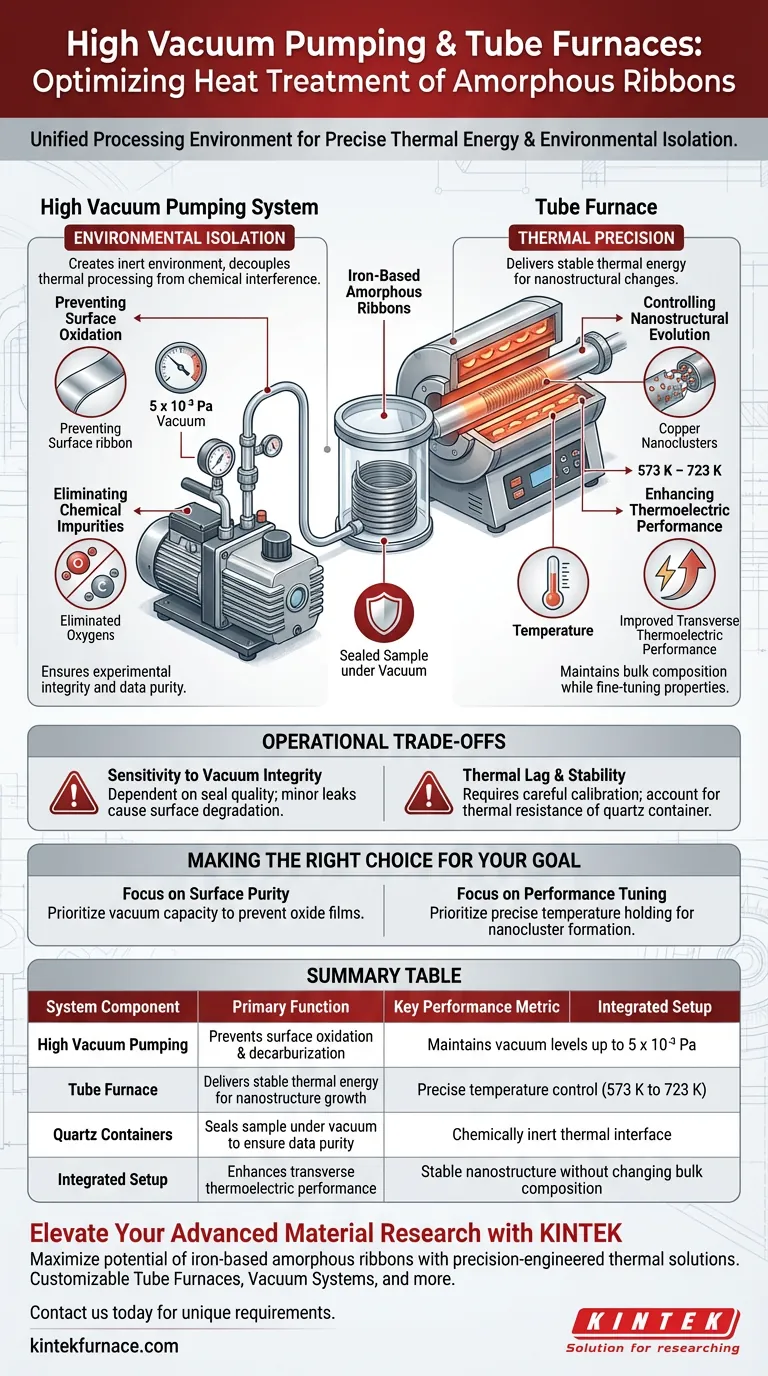
A high vacuum pumping system paired with a tube furnace acts as a unified processing environment designed to isolate iron-based amorphous ribbons from atmospheric contamination while delivering precise thermal energy. The vacuum system removes air to prevent surface oxidation and impurity intrusion, while the tube furnace maintains specific annealing temperatures (typically between 573 K and 723 K) required to drive nanostructural changes without altering the material's bulk composition.
The core function of this setup is to decouple thermal processing from chemical interference. By creating an inert environment, researchers can fine-tune internal nanostructures—such as copper nanoclusters—to significantly enhance transverse thermoelectric performance.

The Role of Environmental Isolation
Preventing Surface Oxidation
The primary danger during heat treatment is the reaction between the ribbon surface and atmospheric oxygen.
A high vacuum pumping system mitigates this by evacuating the chamber to extremely low pressures, such as 5 x 10⁻³ Pa.
This prevents the formation of oxide films that would otherwise degrade the material's surface quality and performance characteristics.
Eliminating Chemical Impurities
Beyond simple oxidation, the vacuum environment protects against other atmospheric interactions.
It specifically prevents decarburization and the intrusion of external impurities.
This isolation ensures that any observed changes in the material are solely the result of the thermal history, rather than chemical contamination.
Ensuring Experimental Integrity
For research focused on structure and magnetic properties, data purity is paramount.
By sealing the ribbons in quartz tube containers under vacuum, the system guarantees that experimental results regarding annealing times are free from interference.
This establishes a reliable baseline for analyzing how heat affects the material's properties.
The Role of Thermal Precision
Controlling Nanostructural Evolution
The tube furnace provides the stable thermal energy required to manipulate the ribbon's internal structure.
Operating within a precise window of 573 K to 723 K, the furnace facilitates the formation of specific features, such as copper nanoclusters.
This evolution is critical for tailoring the material's functional behaviors.
Enhancing Transverse Thermoelectric Performance
The ultimate goal of this thermal processing is often the enhancement of specific material properties.
Through controlled annealing, the development of nanostructures improves the transverse thermoelectric performance of the ribbons.
Remarkably, this performance boost is achieved without changing the average chemical composition of the iron-based alloy.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Sensitivity to Vacuum Integrity
The effectiveness of this process is entirely dependent on the quality of the seal.
Even minor leaks or insufficient vacuum levels can reintroduce oxygen, leading to immediate surface degradation.
Operators must ensure the vacuum sealing technology is robust enough to maintain $5 \times 10^{-3}$ Pa throughout the entire heating cycle.
Thermal Lag and Stability
While tube furnaces offer precision, they require careful calibration to ensure the sample temperature matches the setpoint.
The use of quartz containers inside the vacuum adds a layer of thermal resistance.
One must account for this to ensure the ribbons actually experience the target temperatures (e.g., 550 °C) for the correct duration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of this equipment, focus your parameters on your specific material objectives:
- If your primary focus is surface purity: Prioritize the vacuum system's capacity to reach and maintain $5 \times 10^{-3}$ Pa to prevent oxide film formation and decarburization.
- If your primary focus is performance tuning: Focus on the tube furnace's ability to hold precise temperatures between 573 K and 723 K to optimize copper nanocluster formation.
Success in processing amorphous ribbons relies on balancing absolute isolation with precise thermal control.
Summary Table:
| System Component | Primary Function | Key Performance Metric |
|---|---|---|
| High Vacuum Pumping | Prevents surface oxidation and decarburization | Maintains vacuum levels up to $5 \times 10^{-3}$ Pa |
| Tube Furnace | Delivers stable thermal energy for nanostructure growth | Precise temperature control (573 K to 723 K) |
| Quartz Containers | Seals sample under vacuum to ensure data purity | Chemically inert thermal interface |
| Integrated Setup | Enhances transverse thermoelectric performance | Stable nanostructure without changing bulk composition |
Elevate Your Advanced Material Research with KINTEK
Maximize the potential of your iron-based amorphous ribbons and alloys with KINTEK’s precision-engineered thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-performance Tube Furnaces, Vacuum Systems, Muffle, Rotary, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific research or production needs.
Our systems ensure the exact environmental isolation and thermal stability required to drive nanostructural evolution without contamination. Contact us today to discuss your unique laboratory requirements and discover how our high-temperature technology can optimize your results.
Visual Guide
References
- Ravi Gautam, H. Sepehri‐Amin. Creation of flexible spin-caloritronic material with giant transverse thermoelectric conversion by nanostructure engineering. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-46475-6
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a laboratory tube furnace and how is it designed? Master Precise Heating for Your Lab
- How does a tube furnace convert energy to achieve heating? Master Precise Thermal Control for Your Lab
- What technical requirements must a laboratory tube furnace meet for SOFC testing? Ensure Precise Fuel Cell Analysis
- What are the key features of an atmosphere tube furnace? Unlock Precise Heat and Gas Control
- What are the key advantages of using fluidized bed technology in vertical tube furnaces? Boost Efficiency and Uniformity
- What role does a tube furnace play in the co-pyrolysis of MIPW and COS? Unlock Precise Thermal Waste Transformation
- What industrial applications commonly use tube furnaces? Achieve Precise Heating for Advanced Manufacturing
- What was the original design concept for tube heating furnace systems? Discover the Kettle-Inspired Roots of Modern Heating



















