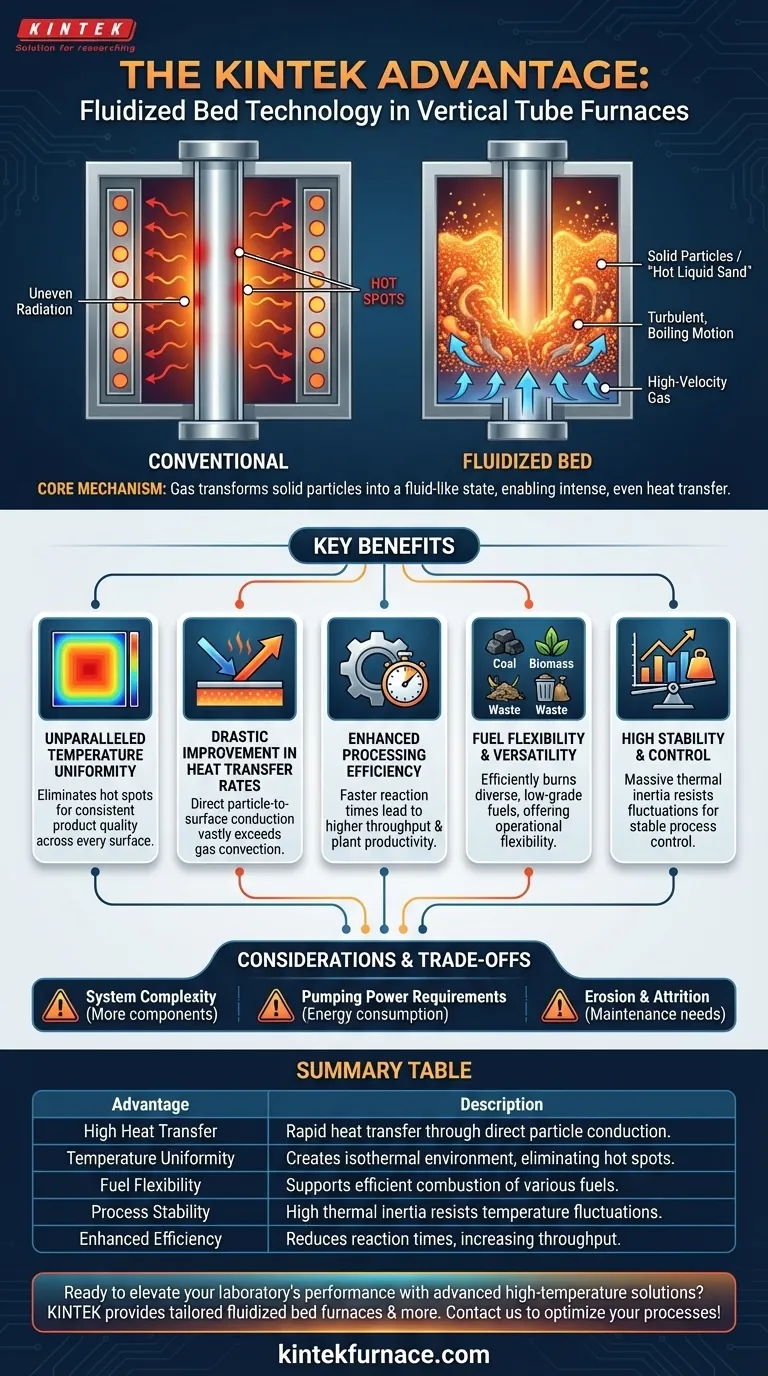
The fundamental advantage of integrating fluidized bed technology into a vertical tube furnace lies in its ability to achieve exceptionally high rates of heat transfer and near-perfect temperature uniformity. This combination enhances processing efficiency for a wide range of materials and improves the quality and consistency of the final product.
A fluidized bed transforms a bed of solid particles, like sand, into a turbulent, fluid-like state. This "hot liquid sand" engulfs the furnace tubes, transferring heat with an intensity and evenness that is simply unattainable in a conventional furnace that relies on gas convection or radiation alone.
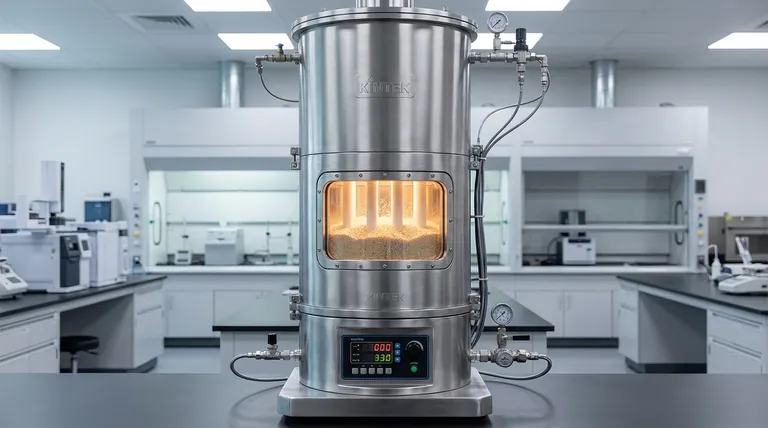

The Core Mechanism: How Fluidization Revolutionizes Heat Transfer
To appreciate the advantages, you must first understand the principle. A vertical fluidized bed tube furnace does not heat the tubes with just hot gas; it uses a solid medium to do the heavy lifting.
Creating a "Fluid" from Solid Particles
A high-velocity gas is forced upward through a bed of fine, solid particles (such as sand, alumina, or catalyst particles). At a specific velocity, the gas flow counteracts gravity, causing the particles to become suspended and move in a turbulent, boiling motion. This mixture of gas and solid behaves exactly like a liquid.
Unparalleled Temperature Uniformity
The constant, chaotic mixing of millions of solid particles within the bed creates an isothermal environment. The entire volume of the bed exists at a virtually identical temperature.
This completely eliminates the hot spots that plague conventional furnaces, ensuring every surface of the internal tubes is exposed to precisely the same thermal conditions.
Drastic Improvement in Heat Transfer Rates
Heat transfer is vastly more effective from a solid particle to a surface than from a gas to a surface. A fluidized bed leverages this by having millions of hot particles constantly colliding with the tube walls.
This direct conduction results in heat transfer coefficients that can be an order of magnitude higher than those seen in standard convection or radiation-based furnaces.
Key Benefits for Industrial Processes
The unique heat transfer characteristics of a fluidized bed translate directly into tangible operational advantages across industries like power generation, chemical processing, and metallurgy.
Enhanced Processing Efficiency
Because heat is delivered to the process tubes so quickly, reaction times can be significantly reduced. This leads directly to higher material throughput and greater overall plant productivity.
Superior Material Quality and Consistency
For temperature-sensitive processes, uniformity is paramount. By eliminating hot spots, fluidized beds prevent thermal degradation of the product, reduce unwanted side-reactions, and ensure highly consistent material properties from batch to batch.
Fuel Flexibility and Versatility
The turbulent mixing in a fluidized bed allows for the efficient combustion of a wide variety of fuels, including low-grade coals, biomass, and industrial wastes that are difficult to burn in conventional systems. This provides significant operational flexibility and potential cost savings.
High Stability and Control
The massive thermal inertia of the particle bed acts as a powerful temperature buffer. It resists rapid temperature fluctuations, making the process inherently stable and easier to control, even with variations in fuel feed or process load.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, this technology is not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires acknowledging its inherent complexities.
System Complexity
A fluidized bed system involves more components than a simple furnace, including blowers for the fluidizing gas, systems for particle handling, and potentially cyclones for capturing fine particles. This can increase capital cost and maintenance requirements.
Pumping Power Requirements
The fan or blower needed to suspend the particle bed consumes a significant amount of energy. This parasitic load must be factored into the overall energy efficiency calculation of the plant.
Erosion and Attrition
The constant, turbulent motion of abrasive particles can cause erosion of the furnace tubes and other internal components over time. Furthermore, the bed particles themselves can break down (attrition), requiring periodic replacement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating technology depends entirely on your primary process objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput and process speed: A fluidized bed is an exceptional choice due to its superior heat transfer rates.
- If your primary focus is product quality for temperature-sensitive materials: The unparalleled temperature uniformity of a fluidized bed is its most critical advantage.
- If your primary focus is fuel flexibility and burning low-grade fuels: The combustion characteristics of a fluidized bed are ideal for this goal.
- If your primary focus is simplicity, low initial cost, and non-critical heating: A conventional radiant or convective tube furnace may be a more practical solution.
Ultimately, choosing a fluidized bed furnace is a strategic decision to prioritize process performance and uniformity over system simplicity.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| High Heat Transfer | Achieves rapid heat transfer through direct conduction from solid particles, improving processing speed. |
| Temperature Uniformity | Creates an isothermal environment, eliminating hot spots for consistent product quality. |
| Fuel Flexibility | Supports efficient combustion of various fuels, including low-grade coals and biomass. |
| Process Stability | High thermal inertia resists temperature fluctuations, ensuring stable and controlled operations. |
| Enhanced Efficiency | Reduces reaction times, increasing throughput and productivity in industrial applications. |
Ready to elevate your laboratory's performance with advanced high-temperature solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide tailored fluidized bed furnaces and more, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering superior heat transfer, uniformity, and efficiency. Don't settle for less—contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes and drive innovation in your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















