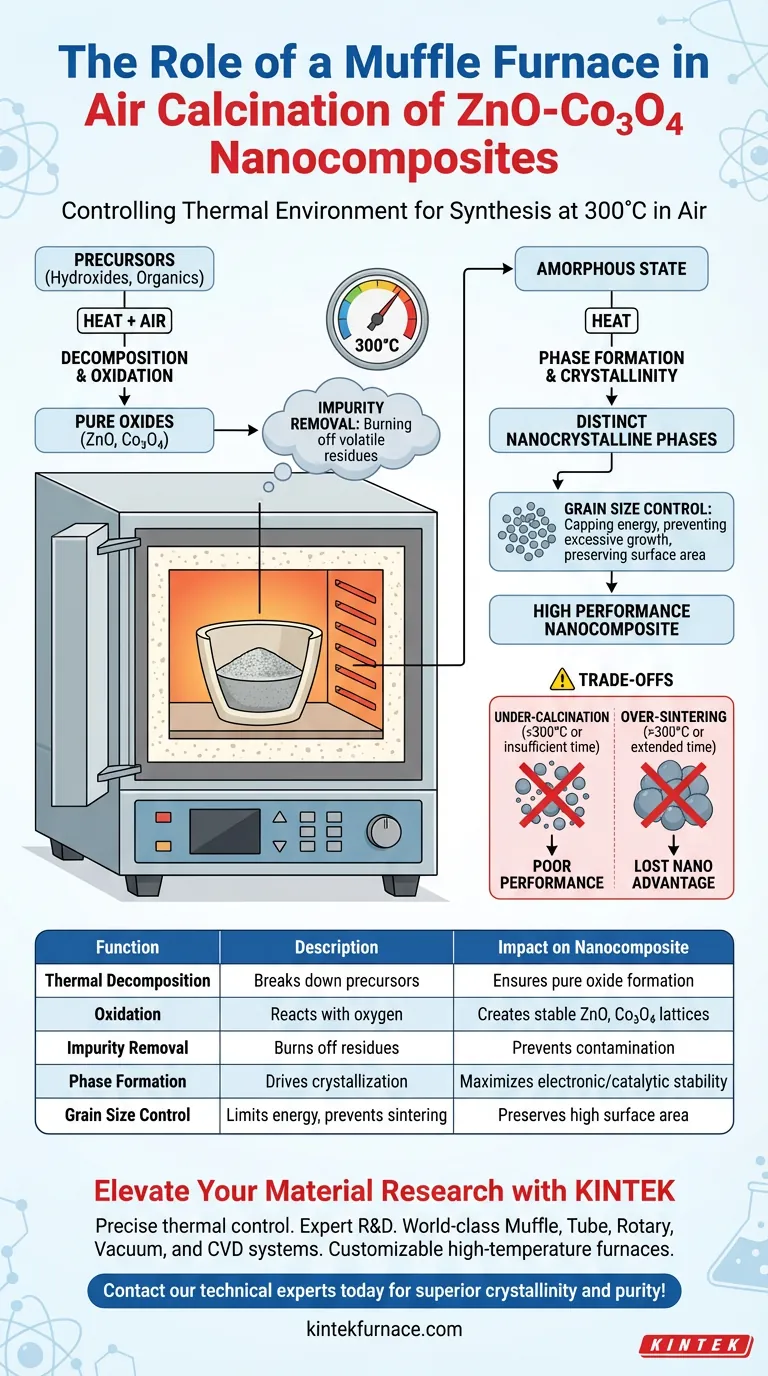
In the synthesis of ZnO-Co3O4 nanocomposites, a muffle furnace functions as a controlled thermal environment designed to drive the decomposition and oxidation of precursor materials. Specifically, it maintains a stable air atmosphere at 300°C, enabling the complete removal of organic residues and the simultaneous formation of distinct zinc oxide and cobalt oxide phases.
The muffle furnace is the critical instrument for determining the final purity and structure of the nanocomposite. It balances the energy required to convert precursors into oxides with the precise thermal control needed to preserve specific nanocrystalline grain sizes.

The Mechanics of Air Calcination
Thermal Decomposition and Oxidation
The primary function of the furnace during this process is to induce thermal decomposition. Precursor materials, often containing hydroxides or organic components, must be broken down to leave behind only the desired metal oxides.
Simultaneously, the furnace facilitates oxidation by maintaining an air-rich environment. This ensures that the Zinc and Cobalt species react fully with oxygen to form stable ZnO and Co3O4 lattices.
Removal of Impurities
During synthesis, precursor materials often retain organic residues or volatile components. The 300°C environment effectively burns these off.
If these residues were left behind, they would act as contaminants, potentially hindering the material's electrochemical or catalytic performance.
Controlling Material Properties
Phase Formation and Crystallinity
Heat treatment is not just about removal; it is about creation. The thermal energy provided by the muffle furnace drives the phase transformation from amorphous or intermediate states into highly crystalline structures.
This process ensures the ZnO and Co3O4 phases are fully formed and distinct. High crystallinity is essential for maximizing the stability and electronic properties of the final composite.
Regulating Grain Size
One of the most delicate functions of the furnace is managing the size of the crystals. The goal is to achieve a nanocrystalline structure rather than bulk material.
By capping the temperature at 300°C, the furnace provides enough energy to form the crystal lattice but limits the energy available for excessive grain growth. This preserves the high surface area characteristic of nanocomposites.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Under-Calcination
If the furnace temperature fluctuates below the target 300°C or the duration is insufficient, the decomposition process remains incomplete.
This leads to a composite plagued by organic impurities and unstable intermediate phases, which dramatically reduces material performance.
The Danger of Over-Sintering
Conversely, exceeding the optimal temperature or extending the time unnecessarily can lead to sintering.
In this scenario, the nanocrystals merge into larger aggregates. While the material becomes highly crystalline, it loses the "nano" advantage—specifically the high surface-to-volume ratio required for reactivity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To achieve the best results with ZnO-Co3O4 nanocomposites, you must view the muffle furnace as a precision tool for structural engineering.
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Ensure the furnace maintains a consistent 300°C to guarantee the complete oxidation of precursors and total removal of organic residues.
- If your primary focus is Surface Area: Strictly monitor thermal exposure to prevent grain growth; the goal is to crystallize the material without sintering the nanoparticles.
Precise thermal regulation is the defining factor that separates a high-performance nanocomposite from a contaminated bulk oxide.
Summary Table:
| Function | Description | Impact on Nanocomposite |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Decomposition | Breaks down precursors (hydroxides/organics) | Ensures pure metal oxide formation |
| Oxidation | Facilitates reaction with oxygen in air | Creates stable ZnO and Co3O4 lattices |
| Impurity Removal | Burns off volatile organic residues | Prevents contamination and improves performance |
| Phase Formation | Drives transformation to crystalline states | Maximizes electronic and catalytic stability |
| Grain Size Control | Limits energy to prevent sintering | Preserves high surface-to-volume ratio |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precise thermal control is the difference between a high-performance nanocomposite and a failed batch. At KINTEK, we understand the delicate balance of calcination. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-precision Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet your most rigorous laboratory requirements.
Whether you are synthesizing ZnO-Co3O4 or developing next-generation catalysts, our customizable high-temperature furnaces ensure the uniform heating and atmospheric stability your research demands.
Ready to achieve superior crystallinity and purity? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect thermal solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
References
- Х. А. Абдуллин, Abay Serikkanov. Enhancing the Electrochemical Performance of ZnO-Co3O4 and Zn-Co-O Supercapacitor Electrodes Due to the In Situ Electrochemical Etching Process and the Formation of Co3O4 Nanoparticles. DOI: 10.3390/en17081888
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is a key feature of box furnaces regarding temperature control? Achieve Precise and Uniform Heating for Your Lab
- What is the mechanism of a laboratory convection furnace for H13 DED steel? Mastering Heat Treatment Precision
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature muffle furnace for post-annealing? Enhance Metal Oxide Performance
- Why are box furnaces important in scientific research? Unlock Precision and Control for Breakthroughs
- How should the furnace door be handled during use? Ensure Safe Operation and Prevent Damage
- How does the calcination process in a precision muffle furnace affect CuO nanoparticles? Optimize Your Synthesis.
- Why are muffle furnaces popular in industrial sectors? Discover Their Key Benefits for Clean, Precise Heating
- What are the typical uses of muffle furnaces in laboratory settings? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment for Your Lab



















