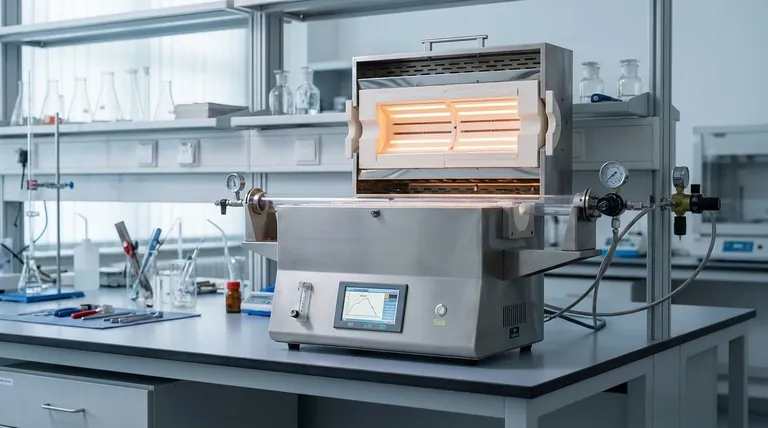
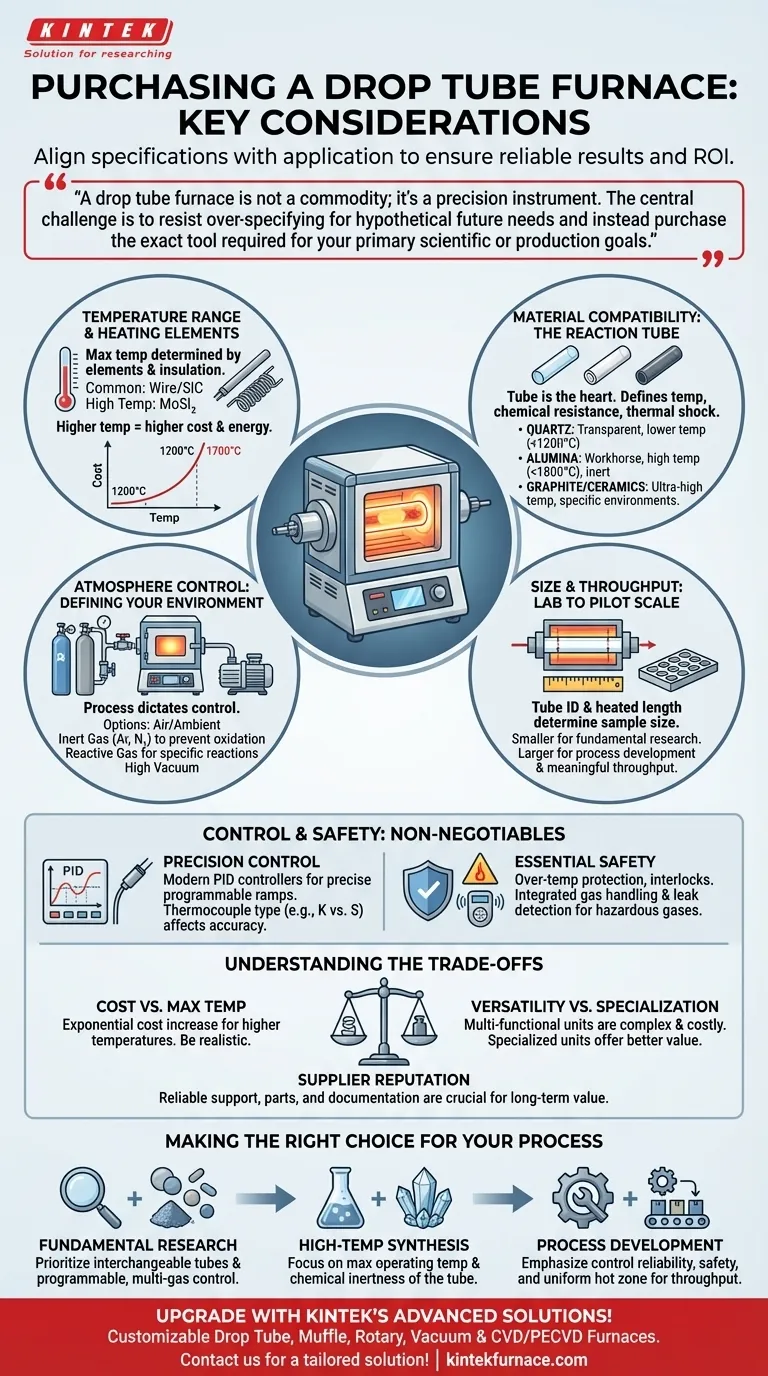
When purchasing a drop tube furnace, the decision hinges on a few core technical specifications that must align with your specific application. The most critical factors are the required temperature range, the chemical compatibility of the reaction tube material with your samples, the necessary atmosphere control (vacuum, inert, or reactive gas), and the physical size or throughput capacity needed for your process.
A drop tube furnace is not a commodity; it's a precision instrument. The central challenge is to resist over-specifying for hypothetical future needs and instead purchase the exact tool required for your primary scientific or production goals. This ensures a better return on investment and more reliable results.

Deconstructing the Core Specifications
The furnace you choose is defined by its physical and thermal limits. Understanding how these components interact is the first step toward making an informed decision.
Temperature Range and Heating Elements
Your primary requirement is the maximum operating temperature. This is determined by the heating elements and insulation materials used in the furnace construction.
Common heating elements like resistance wires or silicon carbon (SiC) rods are suitable for many applications, while more advanced silicon molybdenum (MoSi₂) rods are required for very high temperatures. Paying for a higher temperature range than you need directly increases both the initial cost and long-term energy consumption.
Material Compatibility: The Reaction Tube
The tube is the heart of the furnace, containing your sample and atmosphere. The material choice is critical and dictates temperature limits, chemical resistance, and thermal shock tolerance.
- Quartz: Best for lower temperatures (typically up to 1100-1200°C). Its transparency is a key advantage for visually observing processes, but it is susceptible to thermal shock and can devitrify at high temperatures.
- Alumina (Corundum): The workhorse for high-temperature applications (up to 1700-1800°C). It offers excellent thermal stability and is chemically inert in most situations.
- Graphite/Specialty Ceramics: Used for ultra-high temperatures or specific reactive environments where alumina or quartz would fail.
Atmosphere Control: Defining Your Environment
A drop tube furnace excels at creating a precisely controlled environment. Your process dictates what kind of control you need.
Capabilities range from simple air or ambient atmosphere operation to sophisticated systems that allow for high vacuum, purging with inert gas (like Argon or Nitrogen) to prevent oxidation, or introducing reactive gases to study specific chemical transformations like combustion or reduction.
Size and Throughput: From Lab to Pilot Scale
Consider the physical size of the furnace and, more importantly, the inner diameter and heated length of the tube. This determines the maximum sample size you can process.
For fundamental research, a smaller tube may be sufficient. For process development or small-scale production, a larger diameter and longer uniform hot zone are necessary to achieve meaningful throughput.
Control and Safety: The Non-Negotiables
Beyond the core specifications, the systems that manage and safeguard the furnace's operation are what guarantee repeatable results and a safe lab environment.
The Precision of Your Control System
Modern furnaces use PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers to precisely manage temperature. Look for systems that allow for programmable heating and cooling ramps, which are essential for many material processing applications.
The type of thermocouple (e.g., K-type vs. S-type) also matters, as it determines the accuracy and upper limit of temperature measurement.
Essential Safety Features
High-temperature work demands robust safety protocols. Key features include over-temperature protection that automatically shuts down the furnace if it exceeds a set limit and interlocks that prevent operation under unsafe conditions. For systems using flammable or toxic gases, integrated gas handling and leak detection are mandatory.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing capability, cost, and complexity. Being aware of these trade-offs is crucial for avoiding common purchasing mistakes.
Cost vs. Maximum Temperature
The relationship between cost and maximum temperature is not linear. As you push past ~1200°C and then ~1700°C, the cost of heating elements, insulation, and tube materials increases exponentially. Be realistic about your actual temperature needs.
Versatility vs. Specialization
A furnace that can do everything—ultra-high temperature, multiple gas inputs, high vacuum—is significantly more expensive and complex than a specialized unit. If your work only involves calcination in air, you do not need to pay for a complex gas manifold and vacuum system.
Supplier Reputation and Support
A lower-cost furnace from a supplier with a poor reputation can become a liability. Consider the availability of technical support, spare parts, and comprehensive documentation. A reliable supplier provides value long after the initial purchase by ensuring your instrument remains operational.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your selection should be guided by a clear understanding of your primary application.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research with varied materials: Prioritize a furnace with options for interchangeable tubes and a programmable, multi-gas control system for maximum flexibility.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature synthesis (e.g., ceramics, nanomaterials): Your most critical factors are the maximum operating temperature and the chemical inertness of an alumina or specialty ceramic tube.
- If your primary focus is process development or quality control: Emphasize control system reliability for repeatability, robust safety features, and a uniform hot zone sufficient for your sample throughput.
Ultimately, the right furnace is the one whose capabilities are perfectly matched to the demands of your work.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Determined by heating elements (e.g., SiC, MoSi₂); higher temps increase cost and energy use |
| Material Compatibility | Tube material (e.g., quartz, alumina) affects chemical resistance and thermal limits |
| Atmosphere Control | Options include vacuum, inert, or reactive gases for precise environmental control |
| Size and Throughput | Tube diameter and heated length influence sample size and processing capacity |
| Control and Safety | PID controllers, programmable ramps, over-temperature protection, and gas safety features |
| Cost vs. Capability | Balance between temperature needs, versatility, and budget to avoid overspecification |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable drop tube furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for enhanced precision, safety, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















