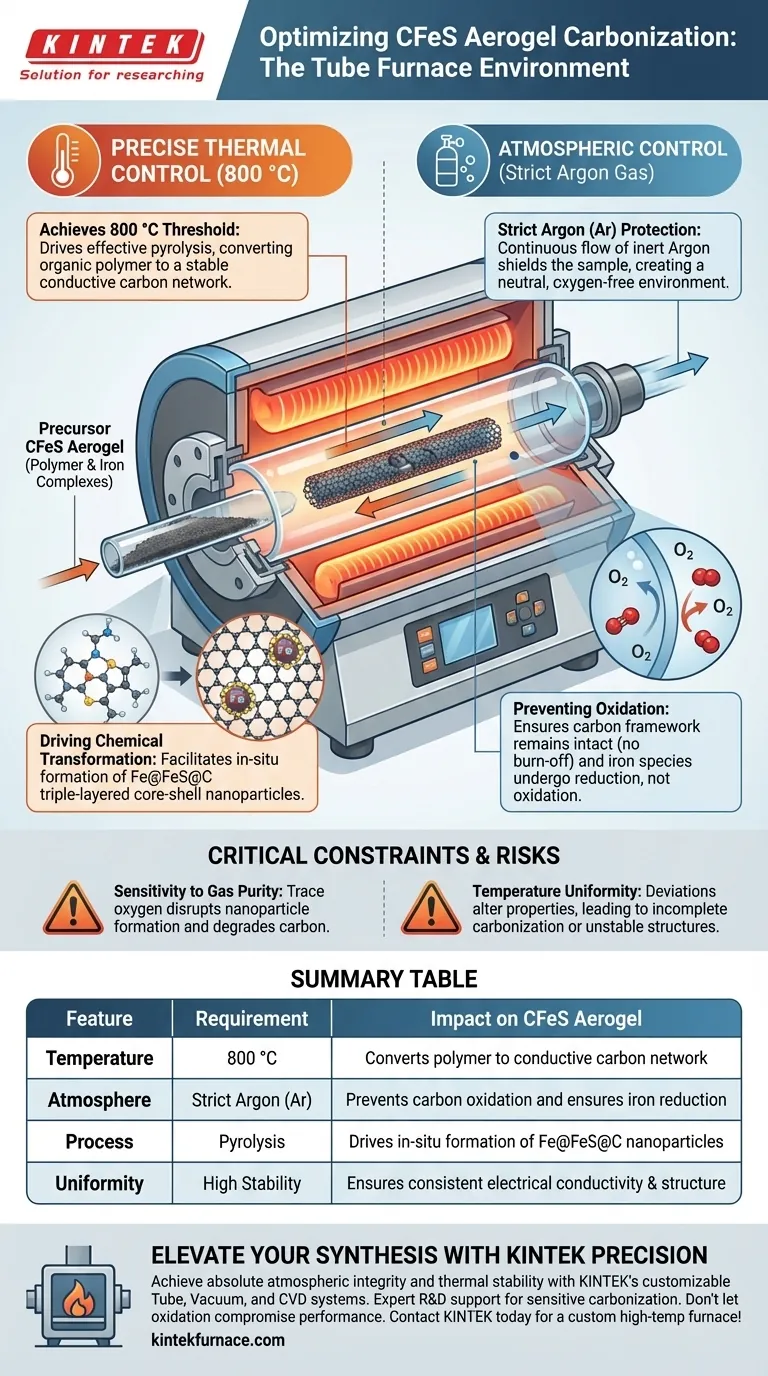
Precise thermal and atmospheric control is the defining contribution of a tube furnace in the synthesis of CFeS aerogels. Specifically, the furnace provides a rigorous high-temperature environment of 800 °C while maintaining a strict blanket of inert argon (Ar) gas to protect the material during processing.
The tube furnace creates an oxygen-free, high-heat environment that simultaneously converts the polymer framework into a conductive carbon network and drives the in-situ transformation of iron complexes into high-performance Fe@FeS@C nanoparticles.

The Role of the Thermal Environment
Achieving the 800 °C Threshold
For CFeS aerogels, the tube furnace must maintain a stable temperature of 800 °C.
This specific thermal energy is required to drive the pyrolysis process effectively. Lower temperatures may not provide sufficient energy for the necessary structural changes.
Driving Chemical Transformation
The high heat facilitates two simultaneous transformations.
First, it converts the organic polymer framework into a stable carbon network.
Second, it enables the in-situ transformation of iron complexes. This results in the formation of specific Fe@FeS@C triple-layered core-shell nanoparticles, which are critical for the material's final performance.
The Importance of Atmospheric Control
Strict Argon (Ar) Protection
The tube furnace isolates the sample from the ambient atmosphere using a continuous flow of argon gas.
Argon acts as an inert shield. Because it is a noble gas, it does not react with the sample, ensuring the chemical environment remains neutral.
Preventing Oxidation
At 800 °C, carbon materials are highly susceptible to oxidation.
If oxygen were present, the carbon framework would burn off as carbon dioxide rather than graphitizing.
The argon atmosphere ensures the carbon remains intact and that the iron species undergo reduction rather than oxidation.
Critical Constraints and Risks
Sensitivity to Gas Purity
The success of this process relies heavily on the "strict" nature of the argon protection.
Even trace amounts of oxygen can disrupt the formation of the core-shell nanoparticles or degrade the carbon skeleton. The tube furnace's ability to seal and purge the chamber is paramount.
Temperature Uniformity
While 800 °C is the target, deviations can alter the material properties.
Incomplete heating may leave behind non-conductive polymer chains. Conversely, uncontrolled fluctuations could destabilize the crystalline phases of the iron complexes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the CFeS aerogels achieve the desired reduction performance and electrical conductivity, you must prioritize the stability of the furnace environment.
- If your primary focus is Electrical Conductivity: Ensure the furnace holds 800 °C consistently to guarantee the complete conversion of the polymer into a conductive carbon network.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Structure (Nanoparticles): Prioritize the purity of the argon gas flow to facilitate the precise in-situ reduction of Fe complexes into Fe@FeS@C shells without oxidation.
By strictly adhering to these parameters, you ensure the successful synthesis of high-performance CFeS aerogels.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Requirement | Impact on CFeS Aerogel |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 800 °C | Converts polymer to conductive carbon network |
| Atmosphere | Strict Argon (Ar) | Prevents carbon oxidation and ensures iron reduction |
| Process | Pyrolysis | Drives in-situ formation of Fe@FeS@C nanoparticles |
| Uniformity | High Stability | Ensures consistent electrical conductivity & structure |
Elevate Your Aerogel Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect 800 °C environment for CFeS aerogels requires more than just heat—it requires absolute atmospheric integrity and thermal stability. KINTEK delivers high-performance Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the most sensitive carbonization processes.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our customizable lab furnaces provide the strict argon shielding and precise temperature uniformity your research demands. Don't let oxidation compromise your core-shell nanoparticles.
Ready to optimize your material performance? Contact KINTEK today for a custom high-temp furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Jianzheng Yang, Jinming Zhang. Superior‐Selective and Complete Recycling of Trace Precious Metals From Wastewater by Magnetic Trilayer Carbon‐Aerogels. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202500858
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What role does a tube pyrolysis reactor play in sludge and chloride co-pyrolysis? Enhanced Heavy Metal Removal
- What materials can be melted in horizontal tube furnaces? Unlock precise high-temperature melting for metals, ceramics, and more
- Why is a vacuum-sealed quartz tube necessary for 4.5 inch InP crystals? Ensure Stability and Purity
- Why is vacuum control critical when using a horizontal tube furnace for the 550 °C annealing of a-SiC:H films?
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in POLO contact structures? Unlock High-Efficiency Silicon Contacts
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in the post-treatment of Ir-TiO2 samples? Master Material Purity
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature tube sintering furnace for selenization? Optimize PC-CNT Porosity
- What is the mechanism of the drive-in process in a tube furnace? Master Dopant Redistribution with Nitrogen Shielding



















