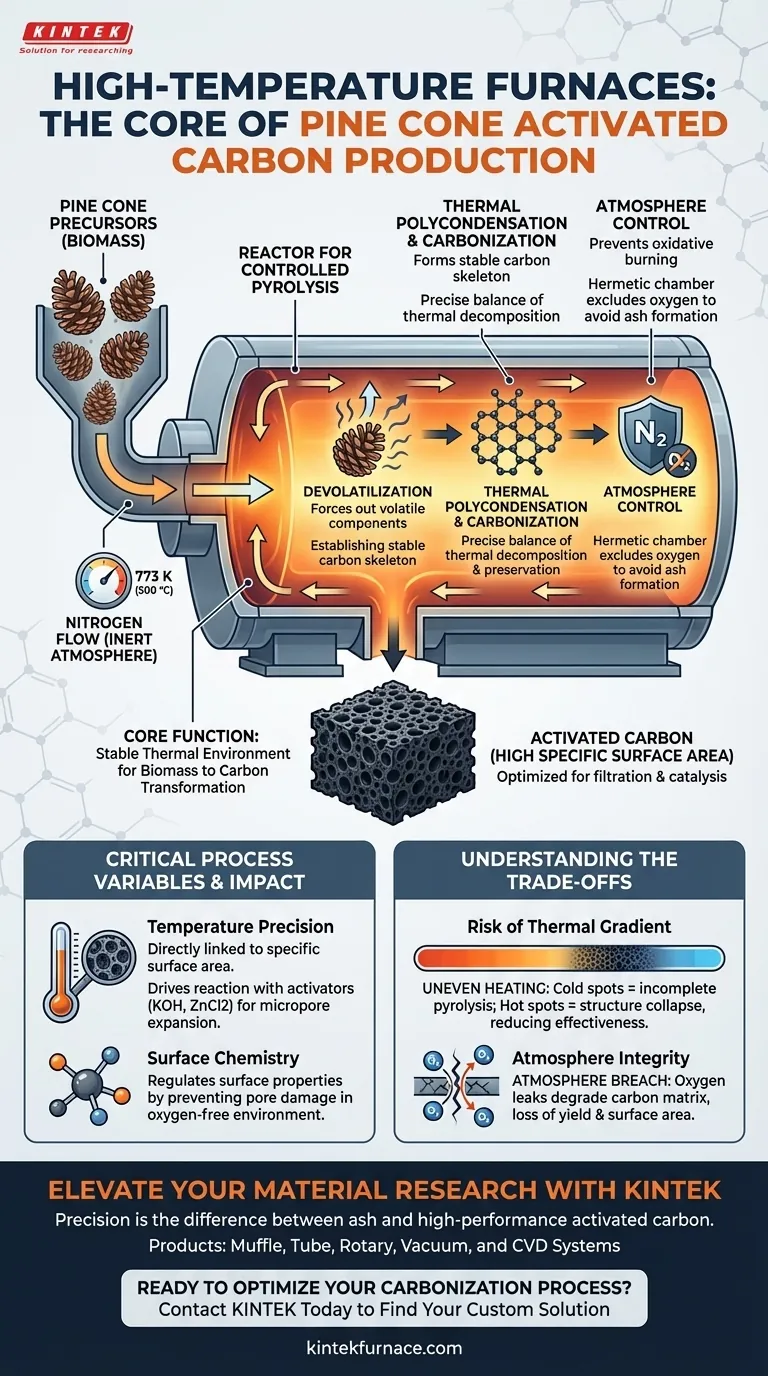
The primary function of a high-temperature box or tube furnace in this context is to act as a reactor for controlled pyrolysis. It provides a stable thermal environment, typically maintained at 773 K (500 °C), under a protective nitrogen flow to convert pine cone precursors into activated carbon. This equipment is essential for driving the chemical changes required to transform raw biomass into a material with high specific surface area.
Core Insight: The furnace does not merely heat the material; it orchestrates a precise balance between thermal decomposition and structural preservation. Its ability to maintain a uniform temperature within an inert atmosphere is the determining factor in creating complex pore structures while preventing the carbon substrate from burning away.

The Mechanism of Transformation
Facilitating Critical Chemical Reactions
The furnace provides the thermal energy necessary to initiate three specific processes: devolatilization, thermal polycondensation, and carbonization.
By maintaining the temperature at approximately 773 K, the equipment forces volatile components out of the impregnated pine cone biomass. This thermal decomposition is the first step in establishing a stable carbon skeleton.
The Role of Atmosphere Control
A defining feature of this process is the use of a protected nitrogen flow.
The furnace acts as a hermetic chamber that excludes oxygen. Without this inert atmosphere, the high temperatures would cause the carbon substrate to undergo unnecessary oxidative consumption (burning into ash) rather than carbonizing into a useful structure.
Ensuring Structural Stability
The furnace is responsible for uniform heat distribution across the material.
Precise temperature control dictates the conversion efficiency of the pine cone precursors. Uniform heating ensures that the devolatilization occurs evenly, preventing structural defects and ensuring the final product possesses a stable, highly developed network of micropores and mesopores.
Critical Process Variables
Temperature Precision and Pore Formation
The specific surface area of the final activated carbon is directly linked to the furnace's ability to hold a constant temperature.
When chemical activators like Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) or Zinc Chloride (ZnCl2) are used, the furnace must provide accurate heating rates. This precision drives the reaction between the activator and the carbon matrix, expanding micropore structures and significantly increasing surface area.
Impact on Surface Chemistry
Beyond physical structure, the furnace environment regulates surface chemistry.
By sustaining an oxygen-free environment during heat treatment, the equipment prevents damage to the pore structure. This allows for the retention or modification of specific chemical properties, ensuring the material is optimized for its intended filtration or catalytic application.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Thermal Gradient
If the furnace fails to maintain uniform heat distribution, the pine cone biomass will carbonize unevenly.
"Cold spots" in the chamber may lead to incomplete pyrolysis, leaving behind volatile impurities. Conversely, "hot spots" can lead to excessive sintering, which collapses the delicate pore structures you are trying to create, drastically reducing the material's effectiveness.
Atmosphere Integrity
The most common point of failure is a breach in the inert atmosphere.
Even minor oxygen leaks during the high-temperature phase will degrade the carbon matrix. This results in a loss of yield and a reduction in the specific surface area, negating the benefits of the thermal treatment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of pine cone-based activated carbon, align your furnace operation with your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is maximizing Surface Area: Prioritize a furnace with high-precision temperature control to drive the expansion of micropores during the activation phase with agents like KOH.
- If your primary focus is Structural Stability and Yield: Ensure your furnace creates a flawless anaerobic environment with continuous nitrogen flow to prevent oxidative consumption of the carbon substrate.
Success in producing high-quality activated carbon lies in the rigorous control of the thermal and atmospheric environment.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Furnace Function | Critical Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Devolatilization | Forces out volatile components | Rapid, uniform heat distribution |
| Carbonization | Forms stable carbon skeleton | Precise 773 K (500 °C) stability |
| Atmosphere Control | Prevents oxidative burning | Flawless inert nitrogen flow |
| Activation | Expands micropore networks | High-precision thermal ramp rates |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between ash and high-performance activated carbon. KINTEK provides industry-leading Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to give you total control over your thermal environment.
Whether you are refining biomass pyrolysis or developing advanced catalysts, our expert-backed R&D and customizable lab furnaces ensure uniform heating and atmosphere integrity for every experiment.
Ready to optimize your carbonization process? Contact KINTEK Today to Find Your Custom Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Yassine Jari, Bouchaib Gourich. Porous activated carbons derived from waste Moroccan pine cones for high-performance adsorption of bisphenol A from water. DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29645
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the primary process objectives of using a vacuum annealing furnace for treating HEA multilayer films?
- What is the purpose of using a vacuum in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Achieve Superior Material Purity
- Why is a high-vacuum probe station necessary for SnS2 analysis? Ensure Pure Electrical Characterization
- What roles do vacuum furnaces and pulse power supplies play in plasma nitriding? Enhance Steel Hardening & Uniformity
- How do controlled atmospheres and automated temperature cycles in a sintering furnace impact alloy quality?
- What are the advantages of graphite's lightweight and high strength in vacuum furnaces? Lower Costs & Superior Performance
- What is the significance of precise temperature control in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Quality, Consistency, and Reliability
- What is a major limitation of hot wall vacuum furnaces? Temperature Capability and Design Trade-offs



















