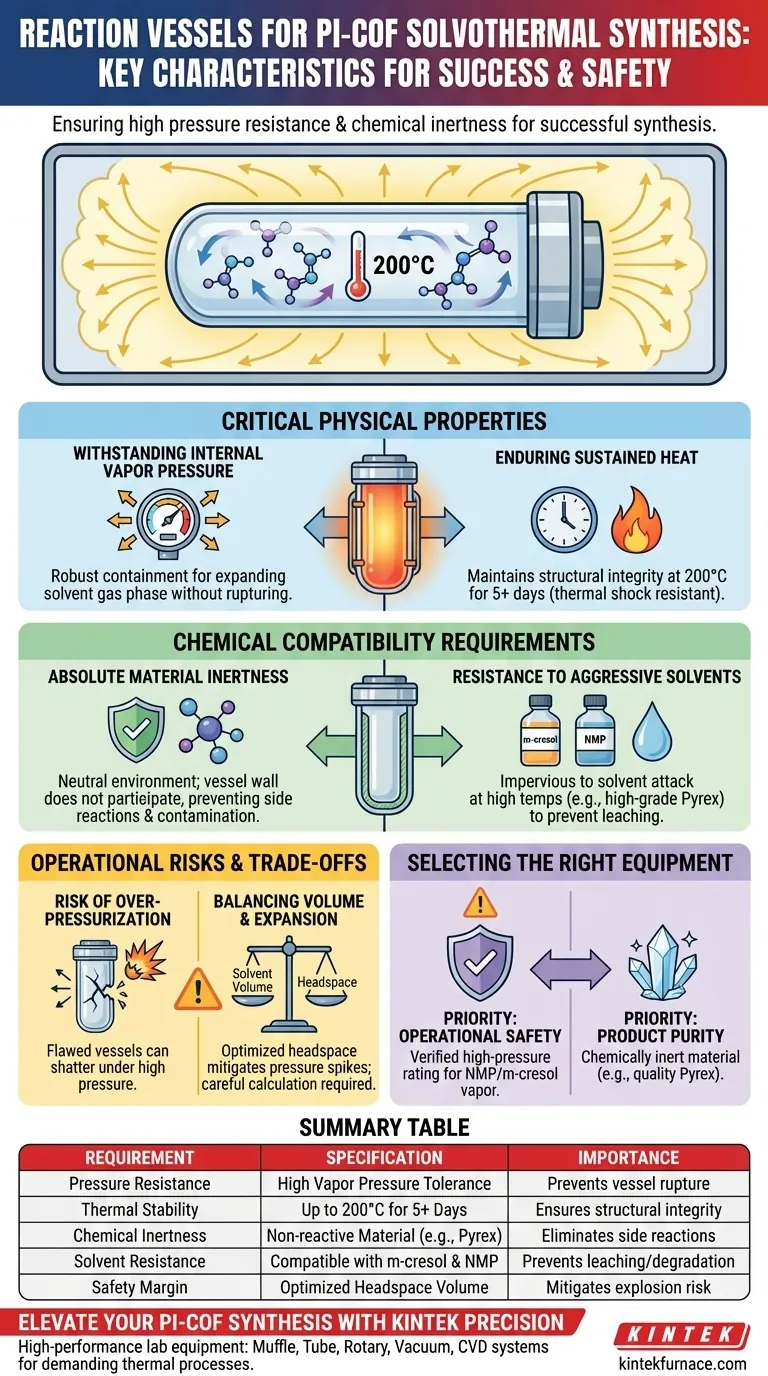
To ensure the successful solvothermal synthesis of Polyimide Covalent Organic Frameworks (PI-COFs), the reaction vessels must primarily possess high pressure resistance and absolute chemical inertness. Common choices, such as sealed Pyrex tubes, are specifically selected to withstand extended heating cycles (often up to five days) at temperatures around 200°C without compromising structural integrity or contaminating the chemical reaction.
The success of PI-COF synthesis relies on maintaining a closed system that can handle the vapor pressure of aggressive solvents like m-cresol and NMP. The vessel acts as a passive but critical containment unit that ensures safety and reaction purity under sustained thermal stress.

Critical Physical Properties
Withstanding Internal Vapor Pressure
Solvothermal synthesis occurs within a closed system to facilitate crystallization. As the temperature rises, the solvents used in the process generate significant internal vapor pressure.
The vessel acts as a pressure containment unit. It must be robust enough to withstand the force exerted by the expanding gas phase of the solvents without rupturing.
Enduring Sustained Heat
The synthesis of PI-COFs is not a rapid reaction; it requires a sustained thermal drive. The vessel must be capable of maintaining structural integrity at temperatures as high as 200°C.
Furthermore, this heat is often applied for extended durations, such as five days. The vessel material must resist thermal shock and fatigue over this long operational window.
Chemical Compatibility Requirements
Absolute Material Inertness
The vessel must provide a neutral environment for the chemistry to occur. Chemical inertness is essential to ensure that the vessel wall does not participate in the reaction.
If the vessel material is reactive, it causes side reactions. This consumes reactants meant for the polymer network and introduces impurities into the final COF product.
Resistance to Aggressive Solvents
The synthesis utilizes specific, potent solvents like m-cresol and N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP).
At high temperatures, these solvents become increasingly aggressive. The vessel, typically made of high-grade borosilicate glass (Pyrex), must be impervious to solvent attack to prevent leaching or degradation.
Operational Risks and Trade-offs
The Risk of Over-Pressurization
While sealed Pyrex tubes are the standard, they rely on the glass being free of microscopic flaws. A compromised tube can shatter under the high pressure generated by the solvents at 200°C.
Balancing Volume and Expansion
There is a trade-off between maximizing yield and maintaining safety. Overfilling the vessel reduces the headspace available for vapor expansion.
This can lead to pressure spikes that exceed the vessel's rating. Careful calculation of solvent volume relative to vessel capacity is required to maintain a safe margin.
Selecting the Right Equipment for Your Synthesis
To achieve a high-quality PI-COF yield while maintaining laboratory safety, align your equipment choice with these priorities:
- If your primary focus is operational safety: Prioritize vessels with a verified high-pressure rating capable of containing the vapor pressure of NMP and m-cresol at 200°C.
- If your primary focus is product purity: Ensure the vessel material is chemically inert (such as high-quality Pyrex) to prevent side reactions during the prolonged 5-day synthesis.
The integrity of your reaction vessel is the single most critical factor in safely bridging the gap between volatile precursors and a stable crystalline framework.
Summary Table:
| Requirement | Specification | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Resistance | High Vapor Pressure Tolerance | Prevents vessel rupture from expanding gases |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 200°C for 5+ Days | Ensures structural integrity during long heating cycles |
| Chemical Inertness | Non-reactive Material (e.g., Pyrex) | Eliminates side reactions and product contamination |
| Solvent Resistance | Compatible with m-cresol & NMP | Prevents material leaching or degradation |
| Safety Margin | Optimized Headspace Volume | Mitigates risk of over-pressurization and explosion |
Elevate Your PI-COF Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Don't compromise your laboratory safety or material purity. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance laboratory equipment designed for the most demanding thermal processes. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, as well as customizable lab high-temp furnaces tailored to your unique solvothermal synthesis needs.
Whether you are scaling up PI-COF production or refining crystalline frameworks, our solutions ensure consistent thermal profiles and robust containment. Contact us today to find the perfect high-temperature solution for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- Atsushi Nagai, Atsunori Matsuda. Synthesis and Electrical Property of Graphite Oxide-like Mesoporous <i>N</i>-Carbon Derived from Polyimide-Covalent Organic Framework Templates. DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c03968
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are graphite crucible furnaces used in vacuum or protective atmosphere environments? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Purity
- Why must a rotary vane vacuum pump be integrated into the curing platform for phenolic laminates? Key to Void-Free Parts
- What is the role of a Teflon-lined autoclave in CQD synthesis? Master Hydrothermal Carbonization for Precision Carbon Dots
- What materials are commonly used for furnace tubes to withstand high heat? Choose the Best for Your Lab
- Why are high-temperature ceramic crucibles used for chalcopyrite? Ensure Purity in Ore Thermal Treatment
- Why is a mechanical vacuum pump essential for Ti-50Nb-xMo melting? Ensure Purity & Prevent Alloy Embrittlement
- Why are high-purity graphite molds essential for the sintering of Tin Selenide (SnSe) alloys? Key to Precise SPS Results
- What role do contact thermocouples play during the high-temperature annealing experiments of oriented silicon steel?



















