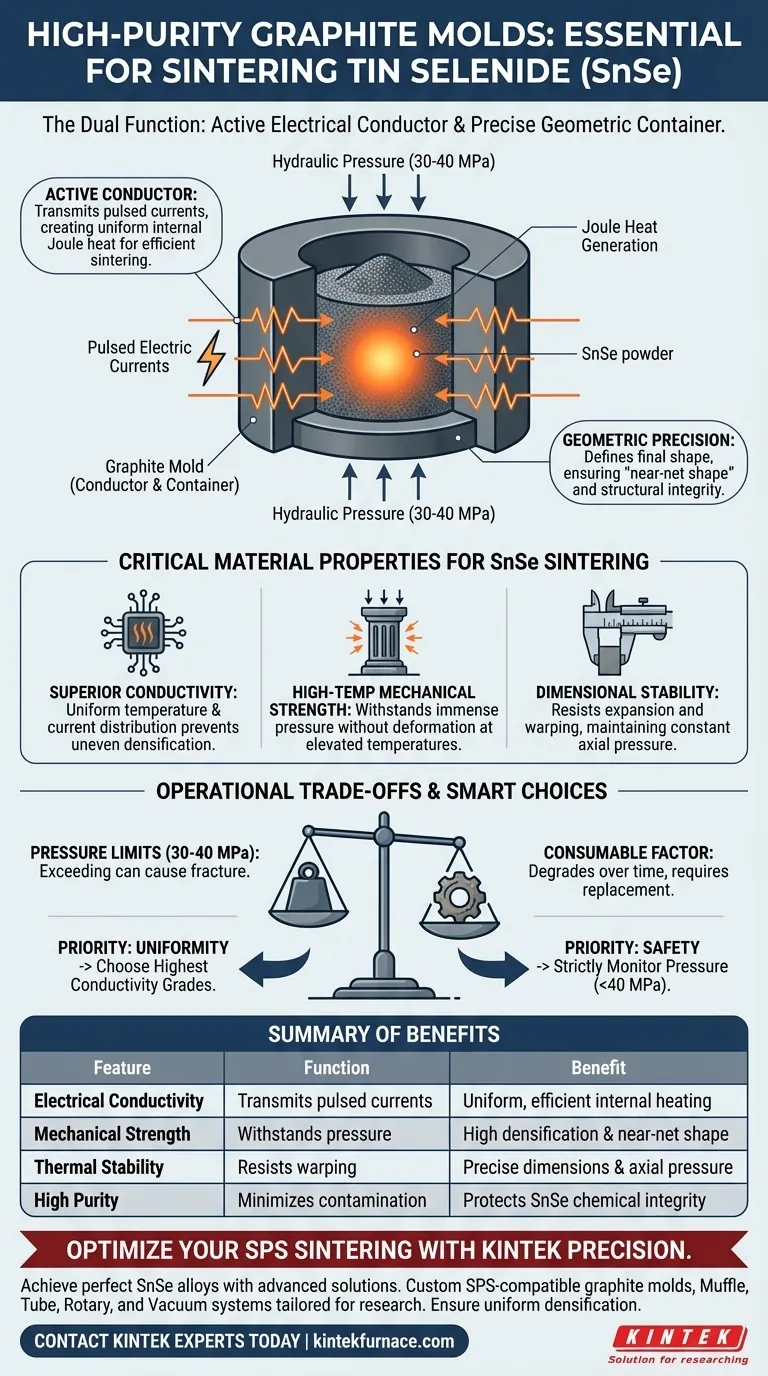
High-purity graphite molds are essential for sintering Tin Selenide (SnSe) because they perform a unique dual function: acting simultaneously as a precise geometric container and an active electrical conductor.
During the Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) process, these molds transmit pulsed electric currents to generate the necessary Joule heat while withstanding the mechanical pressure required to densify the alloy.
The core value of high-purity graphite lies in its ability to facilitate uniform Joule heating and pressure distribution, ensuring the Tin Selenide alloy achieves high density and structural integrity without deformation.
The Dual Role in Spark Plasma Sintering
The sintering of SnSe is not merely about applying heat; it requires a vessel that participates in the physics of the process.
Acting as an Active Conductor
Unlike traditional ceramic molds, graphite is electrically conductive. In SPS, the mold transmits pulsed electric currents directly to the material.
This generates Joule heat within the mold and the sample itself. This internal heating mechanism is far more efficient than external heating methods for these specific alloys.
Defining Geometric Precision
The mold serves as the physical boundary for the powder. It acts as a container that defines the final geometric shape of the SnSe sample.
By maintaining its shape under stress, the mold ensures the final product is a "near-net shape," reducing the need for extensive machining later.
Critical Material Properties
To successfully sinter SnSe, the mold material must possess specific physical characteristics that graphite uniquely provides.
Superior Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
Graphite’s high conductivity is the key to consistency. It ensures that both temperature and electrical current are distributed uniformly throughout the sample.
Without this uniformity, the SnSe alloy could suffer from uneven densification or localized overheating, compromising the material's performance.
High-Temperature Mechanical Strength
Sintering environments place immense stress on the containment vessel. Graphite retains its mechanical integrity even at elevated temperatures.
This allows the mold to transmit mechanical force from the hydraulic system to the powder compact—forcing it to densify—without deforming or collapsing under the thermal load.
Dimensional Stability
Graphite molds resist expansion and warping at high heat. This stability ensures that the pressure applied to the SnSe powder remains constant and axial.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
While high-purity graphite is the standard for this application, it is not without limitations that must be managed.
Mechanical Pressure Limits
Graphite is strong, but it is brittle. While it facilitates densification, it generally has a pressure threshold, often limited to around 30-40 MPa.
Exceeding this limit in an attempt to force higher density can lead to catastrophic mold breakage.
The Consumable Factor
Graphite molds are considered critical consumables. Because they are subjected to high friction, heat, and electrical current, they degrade over time.
This requires regular replacement to maintain the precision of the final SnSe cake and ensuring the surface quality remains high.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When designing your sintering process for Tin Selenide, your priorities will dictate how you manage your graphite tooling.
- If your primary focus is Uniformity: Prioritize high-purity graphite grades with the highest thermal conductivity to ensure even Joule heating across the entire sample volume.
- If your primary focus is Process Safety: strictly monitor hydraulic pressure to stay within the 30-40 MPa range to prevent mold fracture during densification.
By leveraging the conductive and structural properties of graphite, you turn the mold from a simple container into an active tool for material densification.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in SnSe Sintering | Benefit to Material |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Transmits pulsed currents for Joule heating | Ensures uniform, efficient internal heating |
| Mechanical Strength | Transmits 30-40 MPa of hydraulic pressure | Achieves high densification and near-net shape |
| Thermal Stability | Resists warping at high temperatures | Maintains dimensional precision and axial pressure |
| High Purity | Minimizes contamination during process | Protects the chemical integrity of the SnSe alloy |
Optimize Your SPS Sintering with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect Tin Selenide (SnSe) alloy requires more than just heat—it requires high-performance tooling and precise thermal control. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-temperature solutions backed by expert R&D and manufacturing.
Whether you need advanced SPS-compatible graphite molds, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, or Vacuum systems, our lab furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique materials research needs. Ensure uniform densification and structural integrity for your next project.
Contact KINTEK experts today to discuss your customized furnace solutions
Visual Guide
References
- Nan Lin, Yuan Yu. Metavalent Bonding in Cubic SnSe Alloys Improves Thermoelectric Properties over a Broad Temperature Range. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202315652
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Ultra-High Vacuum Flange Aviation Plug Glass Sintered Airtight Circular Connector for KF ISO CF
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do 15x80mm technical openings and seals boost electric furnace efficiency? Maximize Thermal Performance Today
- What role does a heat-resistant steel retort play in sintering? Mastering Isolation and Pressure for High-Purity Results
- What is the function of a forced air drying oven in zeolite preparation? Protect Pore Integrity and Ensure Uniformity
- Why use a covered crucible for g-C3N4 calcination? Enhance Surface Area via Self-Exfoliation
- What are the benefits of sealing SAC305 solder in vacuum quartz tubes? Ensure High-Reliability Alloy Integrity
- How does the optical clarity of quartz tubes benefit laboratory processes? Enhance Control and Accuracy in High-Temp Experiments
- Why are Zirconium Dioxide (ZrO2) crucibles used for slag-metal experiments? Ensure High-Temperature Chemical Purity
- What is the purpose of an alumina powder bed? Optimize Thermal Debinding for 3D-Printed Ceramic Parts







