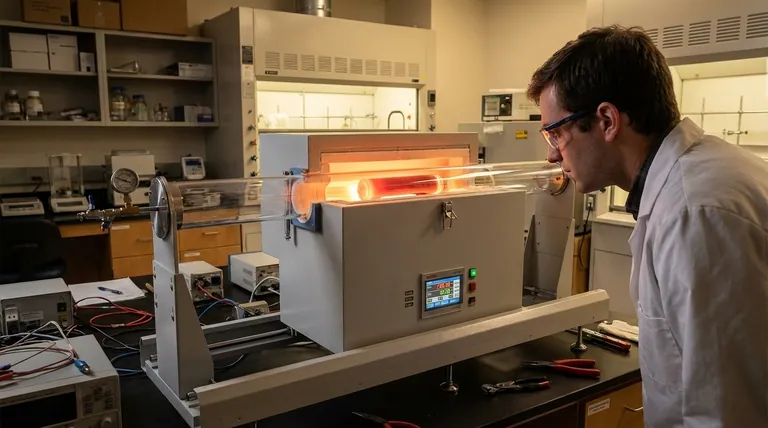
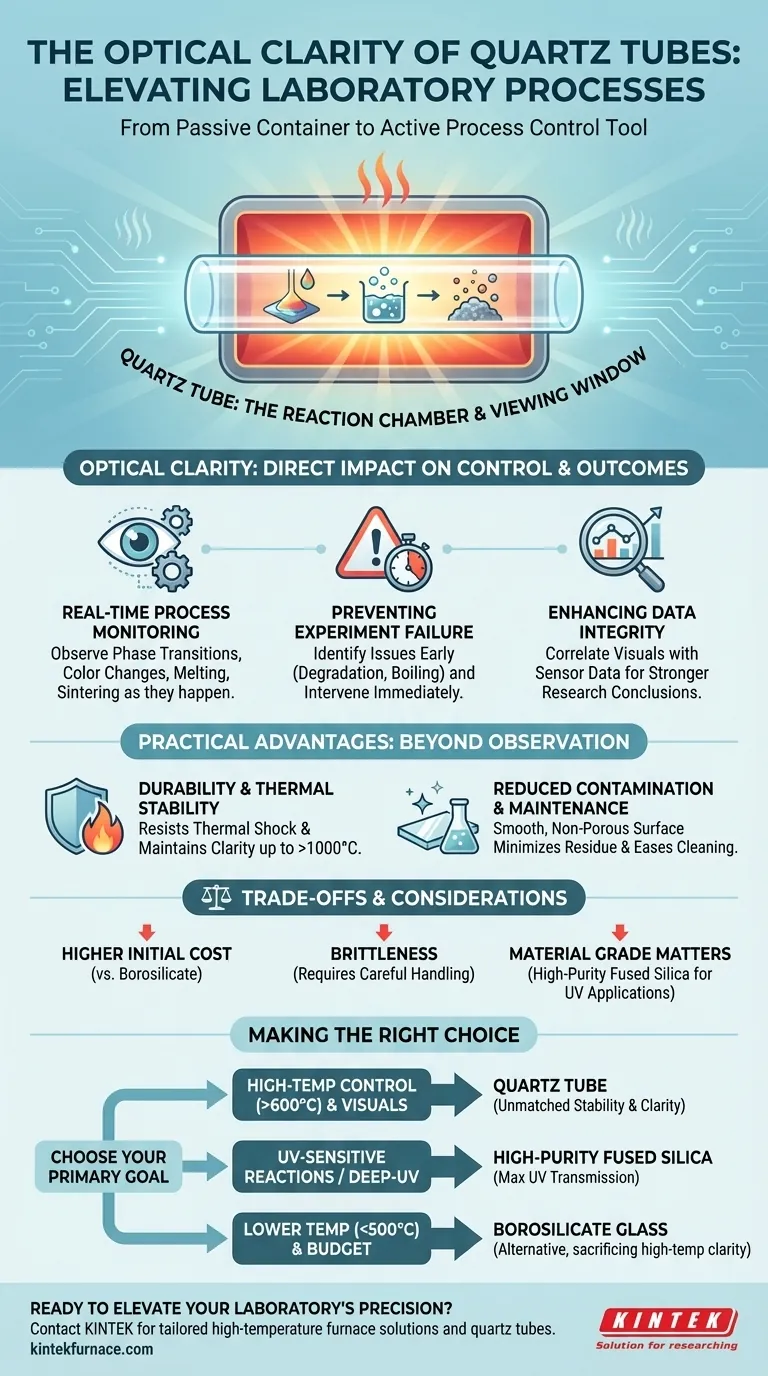
In a laboratory setting, what you can see directly impacts what you can control. The exceptional optical clarity of quartz tubes is a primary reason for their widespread use, as it allows for direct, real-time visual observation of samples during experiments. This transparency is especially critical during high-temperature processes inside a furnace, where visual monitoring is the most effective way to track reactions, prevent failures, and ensure the integrity of your results.
The optical clarity of quartz is not just a passive quality; it is an active tool for process control. It transforms the tube from a simple container into a high-performance window, enabling researchers to observe, validate, and react to chemical and physical changes as they happen.
The Quartz Tube as a Reaction Chamber
Quartz tubes are the standard for creating controlled environments in laboratory furnaces. Their unique combination of properties makes them indispensable for a range of sensitive applications.
Creating a Controlled Atmosphere
In many experiments, the tube is fitted with flanges to seal the environment. This allows researchers to conduct heat treatment processes like annealing, sintering, calcination, and thermal decomposition under a vacuum or in a specific inert gas atmosphere.
A Window into High-Temperature Processes
The primary role of a quartz tube is to serve as both a reaction chamber and a sample holder. Its transparency allows it to function as a viewing window into the extreme environment of a tube furnace, where temperatures can exceed 1000°C.
How Optical Clarity Translates to Better Science
The ability to see inside the furnace is not a minor convenience; it is a fundamental advantage that directly improves experimental outcomes.
Real-Time Process Monitoring
Optical clarity allows you to witness crucial events. You can observe phase transitions, color changes, melting, or sintering progression in real time. This visual feedback is often more intuitive and immediate than sensor data alone.
Preventing Experiment Failure
Direct observation helps you identify problems before they ruin an experiment. If a sample is degrading, boiling unexpectedly, or reacting incorrectly, you can intervene immediately, saving valuable materials, time, and energy.
Enhancing Data Integrity
Visual confirmation serves as a powerful validation tool. By correlating what you see with data from thermocouples and pressure sensors, you can build a more complete and reliable picture of the process, strengthening the conclusions of your research.
Understanding the Practical Advantages
Beyond pure observation, the material properties of quartz reinforce its role as a superior choice for lab work, ensuring its clarity is maintained over time.
Durability and Thermal Stability
Quartz is exceptionally durable and resistant to thermal shock. Unlike other transparent materials, it will not easily deform, cloud, or degrade at the high temperatures required for many advanced material processes, ensuring a clear view run after run.
Reduced Contamination and Maintenance
The incredibly smooth, non-porous surface of a quartz tube minimizes residue buildup from chemical reactions. This not only prevents cross-contamination between experiments but also makes the tubes easier to clean, reducing downtime and operational costs. A clean tube is a clear tube.
Common Trade-offs and Considerations
While quartz is a superior material, no choice is without trade-offs. Objectivity requires acknowledging its limitations.
Higher Initial Cost
Quartz and fused silica are significantly more expensive than alternatives like borosilicate glass. The initial investment is higher, though it is often justified by superior performance and longer service life in high-temperature applications.
Brittleness
Despite its thermal durability, quartz is a brittle material. It is susceptible to failure from mechanical shock. Careful handling is required to prevent cracking or chipping, especially when attaching flanges or inserting samples.
Material Grade Matters
For applications involving ultraviolet (UV) light, such as photochemical reactions or UV curing, the grade of quartz is critical. Standard quartz can block some UV wavelengths, so high-purity fused silica is necessary for its excellent UV transmission properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct tube material is foundational to the success of your experiment. Use your primary objective to guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature process control (>600°C) and visual observation: Quartz is the definitive choice for its unmatched combination of thermal stability and optical clarity.
- If your work involves UV-sensitive reactions or deep-UV spectroscopy: You must use high-purity fused silica to ensure maximum transmission of ultraviolet light.
- If you are working with lower temperatures (<500°C) and budget is the main constraint: Borosilicate glass can be a sufficient alternative, but you sacrifice significant thermal performance and high-temperature clarity.
Ultimately, choosing quartz is an investment in the quality, control, and reliability of your experimental results.

Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Real-Time Monitoring | Allows visual observation of phase transitions, color changes, and reactions during high-temperature processes. |
| Failure Prevention | Enables immediate intervention to avoid sample degradation or incorrect reactions, saving time and resources. |
| Data Integrity Enhancement | Provides visual validation to complement sensor data, strengthening research conclusions. |
| Durability and Stability | Resists thermal shock and maintains clarity at temperatures over 1000°C, ensuring reliable performance. |
| Reduced Contamination | Smooth, non-porous surface minimizes residue buildup, easing cleaning and preventing cross-contamination. |
Ready to elevate your laboratory's precision and efficiency? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're conducting annealing, sintering, or UV-sensitive reactions, our quartz tubes and furnaces ensure superior optical clarity and control. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your research goals and deliver reliable, high-performance equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What technical requirements affect the external thermal strength of furnace tubes? Optimize for High-Temp Performance
- What factors should be considered when purchasing a quartz tube furnace? Ensure Reliable High-Temperature Processing
- How should a quartz tube furnace be cleaned? Essential Steps for Safe, Contamination-Free Maintenance
- What is a quartz tube furnace and what is its primary use? Essential for Controlled High-Temp Processing
- What is the difference between an alumina tube furnace and a quartz tube furnace? Choose the Right Tube Furnace for Your Lab



















