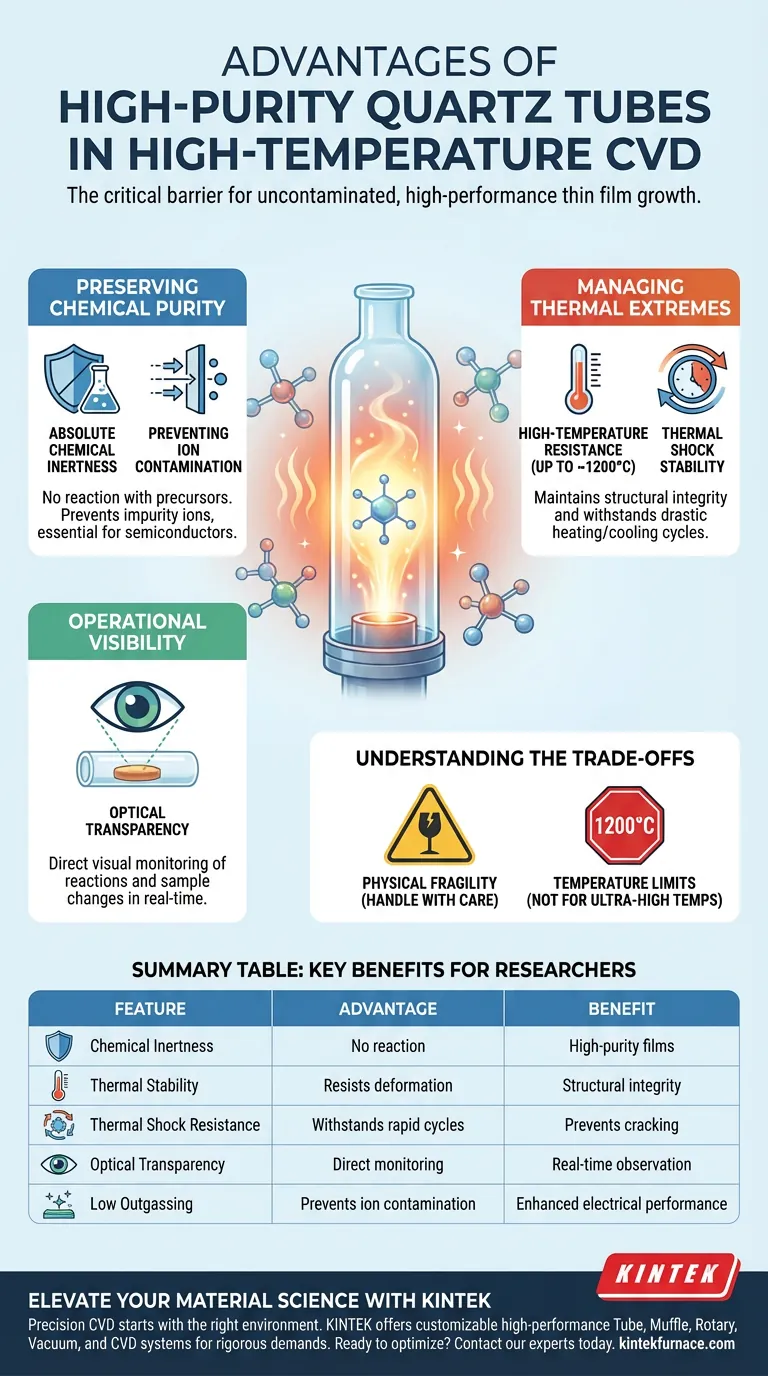
High-purity quartz tubes serve as the critical barrier between a volatile reaction environment and the external world, ensuring that delicate chemical vapor deposition (CVD) processes remain uncontaminated. They are chosen specifically because they withstand extreme thermal stress while remaining chemically invisible to the reaction occurring inside them.
Core Takeaway Success in Chemical Vapor Deposition relies on maintaining a pristine environment under high heat. High-purity quartz is the industry standard because it provides a rare combination of optical transparency, extreme thermal shock resistance, and chemical inertness, ensuring that no foreign impurities degrade the quality of the thin films being grown.

Preserving Chemical Purity
The most significant threat to a CVD reaction, particularly for semiconductors like graphene or MoS2, is contamination. If the reaction chamber degrades or interacts with the gases, the resulting film is compromised.
Absolute Chemical Inertness
A high-purity quartz tube does not react chemically with the precursors used in the deposition process. Even in aggressive environments containing corrosive sulfur vapor or oxygen, the quartz remains neutral.
Preventing Ion Contamination
At high temperatures, standard materials often "outgas" or release ions into the chamber. High-purity quartz prevents the introduction of impurity ions, which is vital for maintaining the electrical performance of semiconductor interfaces.
Managing Thermal Extremes
CVD requires bringing substrates to high temperatures to facilitate molecular-level nucleation. The reaction chamber must facilitate this without failing structurally.
High-Temperature Resistance
Quartz tubes maintain structural integrity in deposition environments capable of reaching temperatures well above 600–700 °C. Unlike standard glass, which would deform or melt, quartz remains rigid and stable.
Thermal Shock Stability
CVD processes often involve rapid heating and cooling cycles. High-purity quartz possesses excellent thermal shock stability, meaning it can withstand these drastic temperature fluctuations without cracking or shattering.
Operational Visibility
Unlike metal or ceramic reaction chambers, quartz offers a distinct advantage for research and process monitoring.
Optical Transparency
The transparency of the quartz tube allows researchers to directly observe the internal environment. This is critical for monitoring the position of internal reactors and identifying color changes in samples, which serve as real-time indicators of reaction progress.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While high-purity quartz is the superior choice for many CVD applications, it is essential to recognize its limitations to ensure safe operation.
Physical Fragility
Despite its thermal robustness, quartz is a brittle material. It requires careful handling during loading and unloading of samples, as mechanical impact can easily cause fractures that compromise the vacuum seal.
Temperature Limits
While quartz excels at temperatures up to roughly 1100-1200°C (depending on the specific grade), processes requiring ultra-high temperatures (above this range) may require alternative ceramic materials like alumina, albeit at the cost of transparency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When designing your CVD setup, the choice of the reaction chamber material dictates the quality of your output.
- If your primary focus is Semiconductor Quality: Prioritize high-purity quartz to ensure zero ion contamination and chemical stability against corrosive vapors like sulfur.
- If your primary focus is R&D and Process Optimization: Leverage the transparency of quartz to visually monitor sample placement and reaction stages in real-time.
By selecting high-purity quartz, you secure a reaction environment that is as stable as it is clean, providing the perfect foundation for high-performance thin film growth.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Advantage in CVD Processes | Benefit for Researchers |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | No reaction with precursors or corrosive vapors | Ensures high-purity thin films |
| Thermal Stability | Resists deformation up to 1200°C | Maintains structural integrity |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Withstands rapid heating/cooling cycles | Prevents chamber cracking during cycles |
| Optical Transparency | Allows direct visual monitoring | Real-time observation of reaction progress |
| Low Outgassing | Prevents ion contamination | Enhances semiconductor electrical performance |
Elevate Your Material Science with KINTEK
Precision in Chemical Vapor Deposition starts with the right environment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern laboratories.
Whether you require high-purity quartz for optical clarity or specialized ceramic chambers for ultra-high temperatures, our systems are fully customizable to your unique research needs. Ensure the integrity of your thin films and the reliability of your data with industry-leading thermal technology.
Ready to optimize your deposition process? Contact our experts today to find the perfect laboratory furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Mitigating Silicon Amorphization in Si–Gr Anodes: A Pathway to Stable, High‐Energy Density Anodes for Li‐Ion Batteries. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202504704
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the technical advantages of using an LPCVD system for WS2-MoS2? Achieve Atomic Seamless Precision
- How does the ALD process ensure effective passivation on WS2 surfaces? Achieve Superior Dielectric Integrity
- Why is precise temperature control of the precursor delivery system essential in CVD for hollow silica particles?
- What are the different types of CVD based on operating pressure and heating system? Explore Key Methods for Superior Film Deposition
- What role do high-purity quartz boats play during the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) of MoS2? Optimize Thin-Film Growth
- What types of heterostructures have been successfully synthesized using these CVD systems? Discover Advanced 2D Material Architectures
- What is a CVD furnace? A Precision Tool for Building Advanced Materials
- How does a CVD reactor work? Master Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials



















