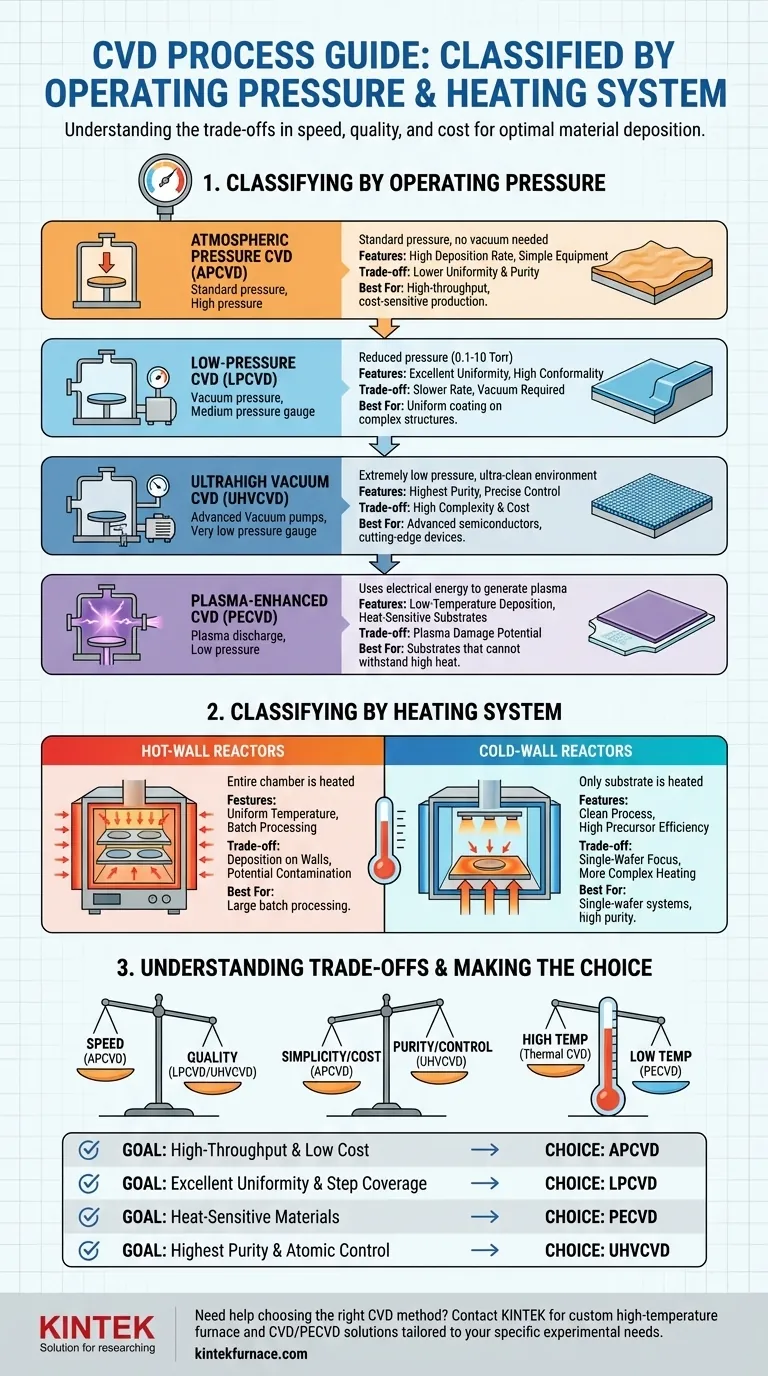
In short, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) processes are primarily categorized by their operating pressure and the method used to heat the substrate. Based on pressure, the main types are Atmospheric Pressure (APCVD), Low-Pressure (LPCVD), and Plasma-Enhanced (PECVD). Based on the heating system, they are classified as either Hot-Wall or Cold-Wall reactors.
The choice between these CVD types is not arbitrary; it represents a fundamental trade-off between deposition speed, film quality, process complexity, and cost. Understanding this balance is key to selecting the right method for a specific application.

Classifying CVD by Operating Pressure
The pressure inside the reaction chamber dictates how gas molecules travel and interact. This has a profound impact on the quality of the deposited film.
Atmospheric Pressure CVD (APCVD)
APCVD operates at standard atmospheric pressure. This makes the equipment simpler and cheaper, as no expensive vacuum systems are required.
Because of the high pressure, gas molecules collide frequently, leading to a shorter mean free path. This often results in lower film uniformity and purity, but allows for very high deposition rates.
Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD)
LPCVD operates at a reduced pressure, typically in the range of 0.1 to 10 Torr. This is one of the most common methods used in modern manufacturing.
The lower pressure increases the mean free path of the reactant gases. This allows molecules to coat surfaces more evenly, resulting in excellent film uniformity and conformality (the ability to coat complex, 3D structures).
Ultrahigh Vacuum CVD (UHVCVD)
As the name implies, UHVCVD operates at even lower pressures than LPCVD, creating an extremely clean environment.
This process is used when exceptional film purity and precise control over layer thickness are required, often for advanced semiconductor devices. The trade-off is significantly increased equipment complexity and cost.
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD)
PECVD is a special case that also operates at low pressure. However, it does not rely solely on thermal energy to drive the reaction.
Instead, it uses an electric field to generate a plasma, which energizes the precursor gases. This allows deposition to occur at much lower temperatures than thermal CVD methods, making it ideal for substrates that cannot withstand high heat.
Classifying CVD by Heating System
The method for delivering thermal energy to the substrate defines the reactor's design and influences process efficiency and cleanliness.
Hot-Wall Reactors
In a hot-wall design, the entire process chamber is heated externally. This creates a very uniform temperature profile across the substrates.
This design is excellent for processing large batches of wafers simultaneously. However, deposition occurs on the chamber walls as well as the substrate, consuming precursors and creating particles that can contaminate the films.
Cold-Wall Reactors
In a cold-wall design, only the substrate holder (the "susceptor") is directly heated, while the chamber walls remain cool. Heating is typically achieved using lamps or an induction coil.
This approach minimizes unwanted deposition on the reactor walls, leading to a cleaner process and higher precursor efficiency. It is the dominant design for single-wafer processing systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a CVD method involves balancing competing technical and economic priorities.
Quality vs. Speed
There is a direct trade-off between deposition rate and film quality. High-pressure systems like APCVD are fast but produce lower-quality films. Low-pressure systems like LPCVD are slower but deliver superior uniformity and conformality.
Temperature vs. Substrate Compatibility
High temperatures are needed in thermal CVD (APCVD, LPCVD) to break down precursor molecules. If your substrate is sensitive to heat (like many plastics or pre-processed semiconductor wafers), these methods are unsuitable. PECVD overcomes this limitation by using plasma energy instead of high heat.
Simplicity vs. Purity
The simplest and least expensive systems operate at atmospheric pressure (APCVD). As you move to lower pressures (LPCVD) and ultrahigh vacuums (UHVCVD), the need for complex and costly vacuum hardware increases dramatically, but so does the purity of the resulting film.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective determines the optimal CVD process.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput production at the lowest cost: APCVD is often the most suitable choice, provided that moderate film quality is acceptable.
- If your primary focus is excellent film uniformity and step coverage: LPCVD is the industry workhorse for a wide range of critical applications.
- If your primary focus is depositing on heat-sensitive materials: PECVD is the necessary choice, as it enables high-quality film growth at low temperatures.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible film purity and atomic-level control: UHVCVD is required for developing cutting-edge electronic and photonic devices.
Ultimately, selecting the correct CVD technique is a critical engineering decision that directly impacts the performance and feasibility of the final product.
Summary Table:
| CVD Type | Operating Pressure | Heating System | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| APCVD | Atmospheric | Hot-Wall/Cold-Wall | High deposition rate, low cost, moderate quality | High-throughput, cost-sensitive applications |
| LPCVD | Low (0.1-10 Torr) | Hot-Wall | Excellent uniformity, conformality, slower rate | Uniform film deposition on complex structures |
| UHVCVD | Ultrahigh Vacuum | Hot-Wall/Cold-Wall | Highest purity, precise control, high cost | Advanced semiconductors, high-purity films |
| PECVD | Low | Hot-Wall/Cold-Wall | Low-temperature deposition, uses plasma | Heat-sensitive substrates, low-temperature processes |
| Hot-Wall | Varies | Entire chamber heated | Uniform temperature, batch processing, potential contamination | Large batch processing |
| Cold-Wall | Varies | Only substrate heated | Clean process, high precursor efficiency, single-wafer processing | Single-wafer systems, minimal contamination |
Struggling to choose the right CVD method for your lab's unique needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your experimental requirements—whether you need high throughput, superior film quality, or low-temperature compatibility. Let us help you optimize your processes and achieve better results. Contact us today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the operational benefits of using a CVD Tube Furnace? Enhance Precision and Efficiency in Your Lab
- What is the process for synthesizing transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) using CVD tube furnaces? Master High-Quality Thin Film Growth
- What future trends are expected in the development of CVD tube furnaces? Discover Smarter, More Versatile Systems
- What are 2D heterostructures and how are they created using CVD tube furnaces? Unlock Atomic-Scale Material Engineering
- What are the key design features of a CVD Tube Furnace? Optimize Your Material Synthesis with Precision



















