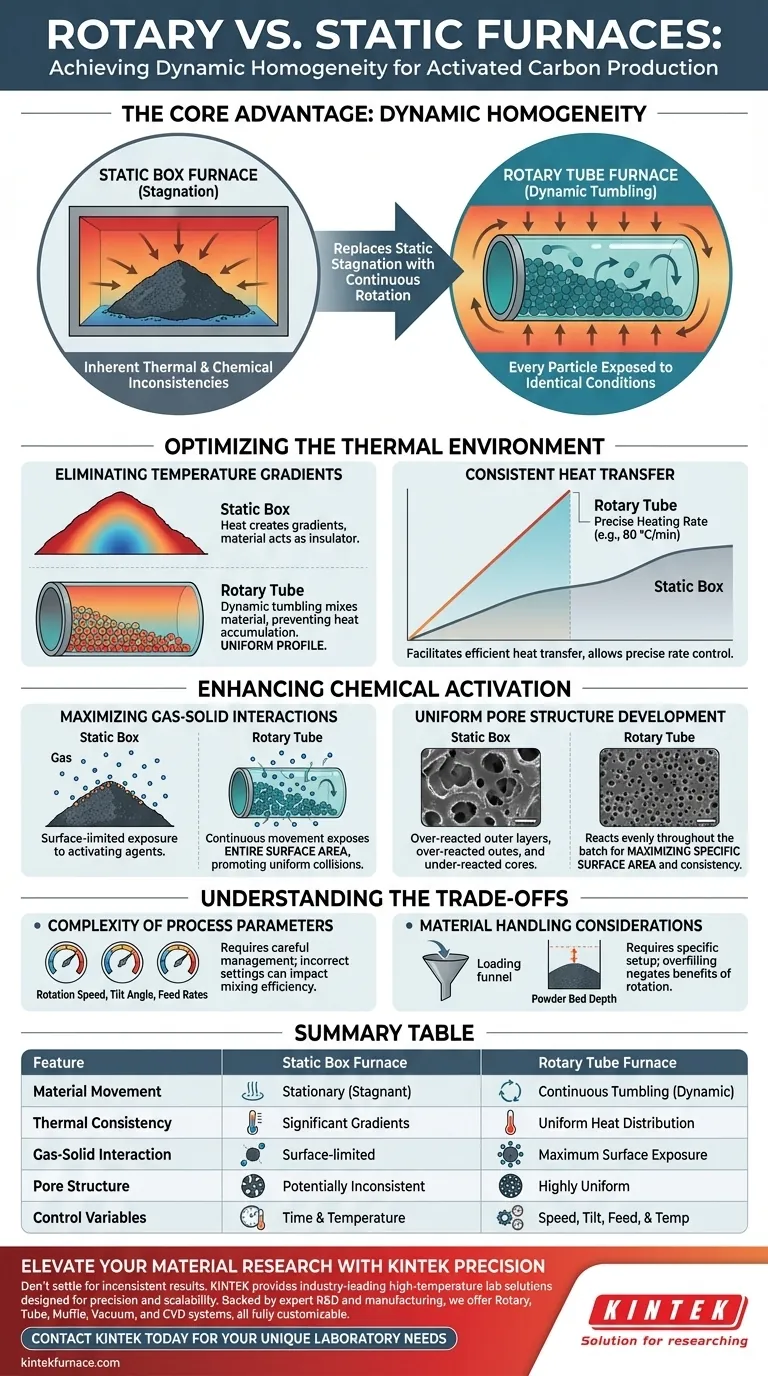
The primary process advantage of a laboratory-grade high-temperature rotary tube furnace is the achievement of dynamic homogeneity. Unlike a static box furnace where materials remain stationary, a rotary furnace continuously tumbles the precursor materials (such as waste wood or goethite powders). This mechanical action ensures every particle is exposed to identical thermal conditions and chemical interactions, effectively eliminating the inconsistencies inherent in static heating.
By replacing static stagnation with continuous rotation, the rotary tube furnace removes thermal gradients within the reaction chamber. This ensures that the chemical activation process—crucial for defining pore structure—occurs uniformly across the entire batch, resulting in activated carbon with highly consistent physical properties.

Optimizing the Thermal Environment
Eliminating Temperature Gradients
In a static box furnace, heat must penetrate from the outside of the sample pile to the center, often creating significant temperature differences.
A rotary furnace solves this through dynamic tumbling. As the quartz tube rotates, the material is constantly mixed, preventing heat from accumulating in specific zones and ensuring the entire batch maintains a uniform temperature profile.
Consistent Heat Transfer
The rotation facilitates a more efficient transfer of heat over short periods.
Because the material is not static, it does not act as its own insulator. This allows for precise heating rates (e.g., 80 °C/min), which are essential for controlling the carbonization and activation phases accurately.
Enhancing Chemical Activation
Maximizing Gas-Solid Interactions
Activated carbon production relies on the reaction between the carbon precursor and an activating agent (often oxygen or chemical agents like KOH).
Continuous movement ensures that the entire surface area of the particles is exposed to the atmosphere. This improves gas diffusion and promotes uniform collisions between the activating agent and carbon particles, leading to more efficient chemical reactions.
Uniform Pore Structure Development
The ultimate goal of activation is to etch the carbon skeleton to create micropores and mesopores.
If the material is static, the outer layer may over-react while the inner core under-reacts. The rotary motion ensures that chemical agents, such as potassium hydroxide, react evenly throughout the batch. This uniformity is critical for maximizing the specific surface area and achieving a consistent pore structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Complexity of Process Parameters
While a rotary furnace offers superior quality control, it introduces variables that a static furnace does not require.
Operators must carefully manage tube rotation speed, tilt angle, and feed rates. Incorrect settings in these areas can impact mixing efficiency or lead to material agglomeration, requiring a more nuanced understanding of the equipment than a simple "set-and-forget" box furnace.
Material Handling Considerations
Rotary furnaces are excellent for powders and granular materials but require specific setup for loading and unloading.
Factors such as powder bed depth must be calculated to ensure proper tumbling. Overfilling the tube can negate the benefits of rotation by preventing the material from cascading properly, reverting the process to a semi-static state.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your activated carbon, align your equipment choice with your specific production metrics.
- If your primary focus is Product Consistency: Utilize the rotary furnace to eliminate "hot spots" and ensure every gram of product has identical chemical properties.
- If your primary focus is Maximizing Surface Area: Rely on the rotary action to ensure the activating agent (KOH) etches the carbon skeleton evenly, preventing under-activation in the material core.
The rotary tube furnace transforms activated carbon production from a passive heating process into a dynamic, controlled reaction, serving as the core equipment for determining the final quality of your material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Static Box Furnace | Rotary Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Material Movement | Stationary (Stagnant) | Continuous Tumbling (Dynamic) |
| Thermal Consistency | Significant Gradients | Uniform Heat Distribution |
| Gas-Solid Interaction | Surface-limited | Maximum Surface Exposure |
| Pore Structure | Potentially Inconsistent | Highly Uniform |
| Control Variables | Time & Temperature | Speed, Tilt, Feed, & Temp |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Don't settle for inconsistent results in your activated carbon or powder processing. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-temperature lab solutions designed for precision and scalability. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer Rotary, Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your specific research parameters.
Whether you need to eliminate thermal gradients or optimize chemical activation, our engineering team is ready to assist. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique laboratory needs and discover how our advanced heating technology can transform your production quality.
Visual Guide
References
- W. F. Spencer, Aleksandar N. Nikoloski. Sustainable Production of Activated Carbon from Waste Wood Using Goethite Iron Ore. DOI: 10.3390/su17020681
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
People Also Ask
- How do rotary kilns operate in terms of material processing? Unlock Efficient Material Transformation
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- How does a rotary tube furnace operate in terms of fuel and heating? Discover Dynamic Heating for Uniform Results
- How is the Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace used in carbon activation processes? Achieve Precise Control for High-Quality Activated Carbon
- Why are rotary tube furnaces suitable for continuous material processing? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput
- What is a rotary kiln and what is its primary use? Achieve Uniform High-Temperature Processing for Solids
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- How do vibrational feeder specifications impact rotary kiln efficiency? Optimize Your Lab's Material Flow & Stability



















