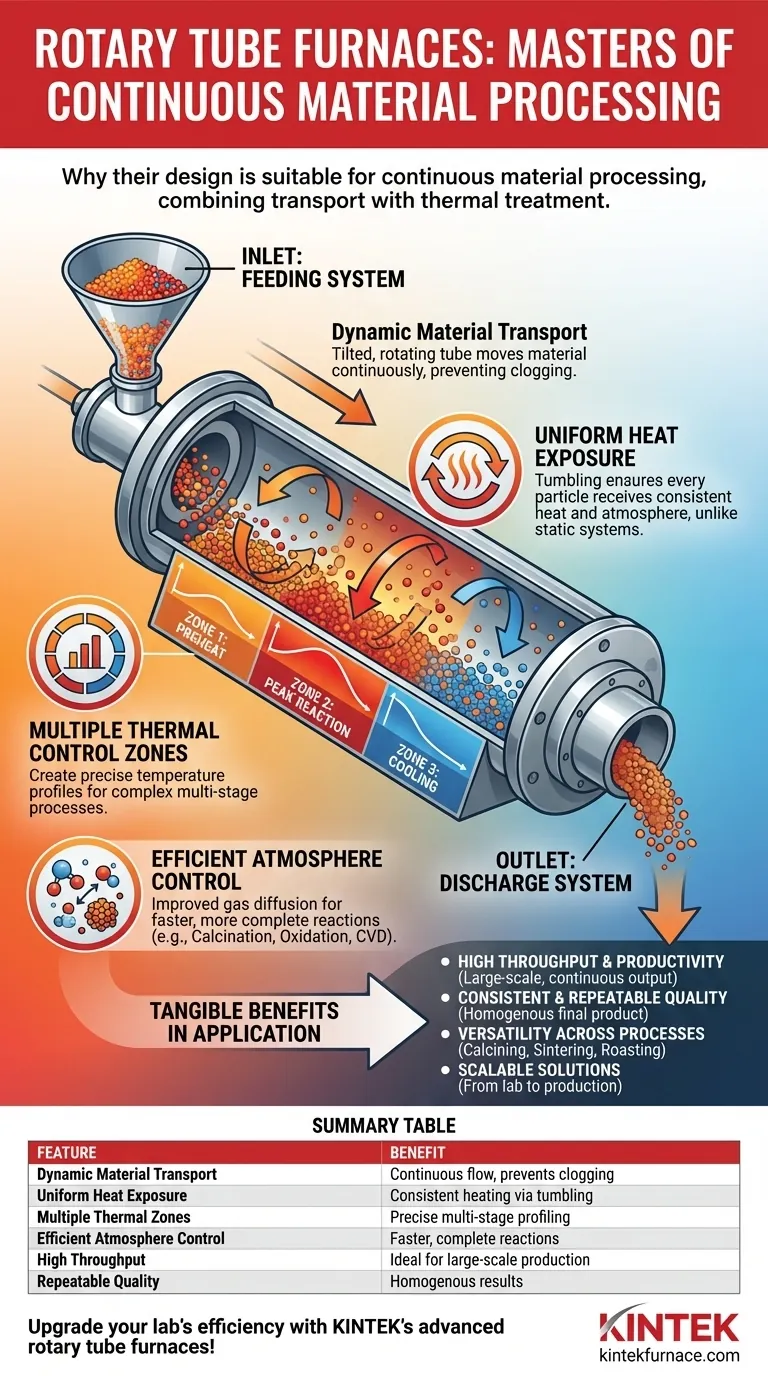
At their core, rotary tube furnaces are suitable for continuous material processing because their design intrinsically combines material transport with thermal treatment. A tilted, rotating tube simultaneously heats and moves loose materials from a feeding point to a discharge point, creating an uninterrupted and highly efficient production line within a single piece of equipment.
The fundamental advantage of a rotary tube furnace is its ability to dynamically and uniformly process materials. By constantly tumbling the sample, it ensures every particle receives consistent exposure to both heat and the controlled atmosphere, a feat unattainable in static batch systems.

The Core Mechanics of Continuous Processing
To understand why this design is so effective, we must look at the interplay of its key mechanical and thermal features. These elements work in concert to create a stable, continuous, and repeatable processing environment.
Dynamic Material Transport
The furnace is built around a tube that is both tilted and rotating. This simple mechanical action provides the force to move material from the inlet to the outlet at a controlled rate.
Specialized feeding and receiving systems ensure a steady, uninterrupted flow. This design often includes anti-clogging features to handle fine powders or granules without interruption.
Unparalleled Heat Exposure
In a static furnace, the material at the bottom of the crucible is heated differently than the material on top. A rotary furnace solves this by constantly tumbling the material.
This continuous movement ensures the entire surface area of every particle is exposed to the heat source. The result is exceptionally uniform heating, which is critical for consistent product quality.
Precise Thermal Profiling
Industrial processes rarely require a single temperature. Rotary tube furnaces are often designed with multiple, independent thermal control zones along the length of the tube.
This allows you to create a precise temperature profile. For example, a material can be gently preheated in the first zone, brought to a peak reaction temperature in the middle zones, and then cooled in the final zone, all within one continuous process.
Efficient Atmosphere Control
The tumbling action also dramatically improves the efficiency of gas-based processes like calcination, oxidation, or Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
By constantly disturbing the material bed, it improves gas diffusion into and out of the particles. This leads to more complete reactions, faster processing times, and often, a significant reduction in the consumption of expensive process gases.
The Practical Advantages in Application
The mechanics of a rotary tube furnace translate directly into tangible benefits for industrial and research settings, making it the preferred choice for specific, demanding applications.
Enhanced Throughput and Productivity
The ability to operate continuously eliminates the downtime associated with loading and unloading batches. This makes rotary furnaces ideal for large-scale industrial processes where maximizing output is a primary goal.
Consistent and Repeatable Quality
Because every parameter—from feed rate and rotation speed to the temperature profile and atmosphere—is precisely controlled, the process is highly repeatable. The uniform heating and gas exposure lead to a more homogenous final product with fewer defects.
Versatility Across Processes
This design is not limited to one type of thermal treatment. It is highly effective for a range of applications involving loose materials, including:
- Calcining: Removing water or volatile compounds.
- Roasting & Oxidation: Reacting materials with a specific gas.
- Sintering: Fusing particles together at high temperatures.
- CVD: Coating powders with new materials.
Understanding the Design Considerations
While powerful, a rotary tube furnace is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is tied to specific material properties and process requirements.
Material Suitability
The design is optimized for loose, free-flowing materials like powders, granules, and small particulates. It is generally not suitable for large single objects, liquids, or materials that can become sticky and clog the tube.
Mechanical Complexity
The rotating seals, drive motor, and support system add mechanical complexity compared to a simple, static tube furnace. These components require diligent maintenance to ensure a long operational life, especially the seals needed to maintain a vacuum or controlled atmosphere.
Process Scalability
Many rotary tube furnaces feature a modular design, allowing them to be adapted to different project requirements. However, scaling a process from a small lab-scale unit to a large production model requires careful engineering to ensure the thermal and mechanical dynamics remain consistent.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace technology depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, high-volume production: The continuous throughput and reduced downtime of a rotary tube furnace offer a clear advantage over batch processing.
- If your primary focus is ultimate process uniformity: The dynamic tumbling action provides superior heat and atmosphere exposure compared to any static furnace.
- If your primary focus is a complex, multi-stage thermal profile: The ability to use multiple, independent heating zones in a single pass makes the rotary furnace exceptionally efficient.
- If your primary focus is research and material development: The precise control, adaptability, and features like viewports for real-time monitoring make it a powerful tool for developing new processes.
Ultimately, a rotary tube furnace is the definitive choice when your process demands uniform, continuous, and scalable thermal treatment of loose materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Dynamic Material Transport | Ensures continuous flow and prevents clogging for loose materials |
| Uniform Heat Exposure | Provides consistent heating to all particles via tumbling action |
| Multiple Thermal Zones | Allows precise temperature profiling for multi-stage processes |
| Efficient Atmosphere Control | Enhances gas diffusion for faster, more complete reactions |
| High Throughput | Eliminates downtime, ideal for large-scale production |
| Repeatable Quality | Delivers homogenous results with fewer defects |
Upgrade your lab's efficiency with KINTEK's advanced rotary tube furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature solutions. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your continuous material processing with uniform heating and superior performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency
- What are some applications of rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Continuous High-Temperature Material Processing



















