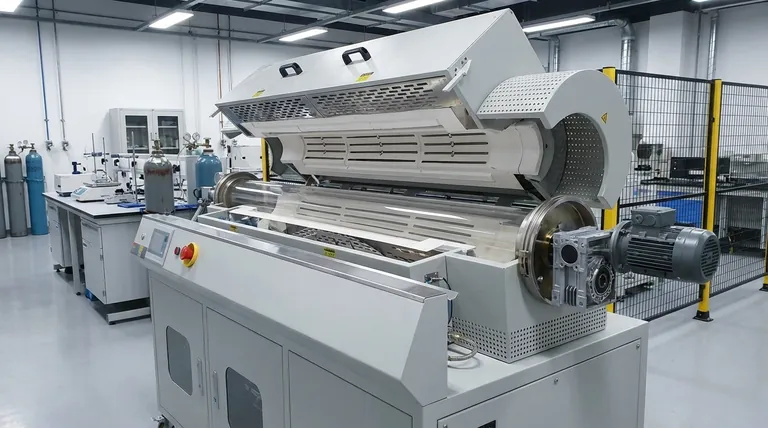
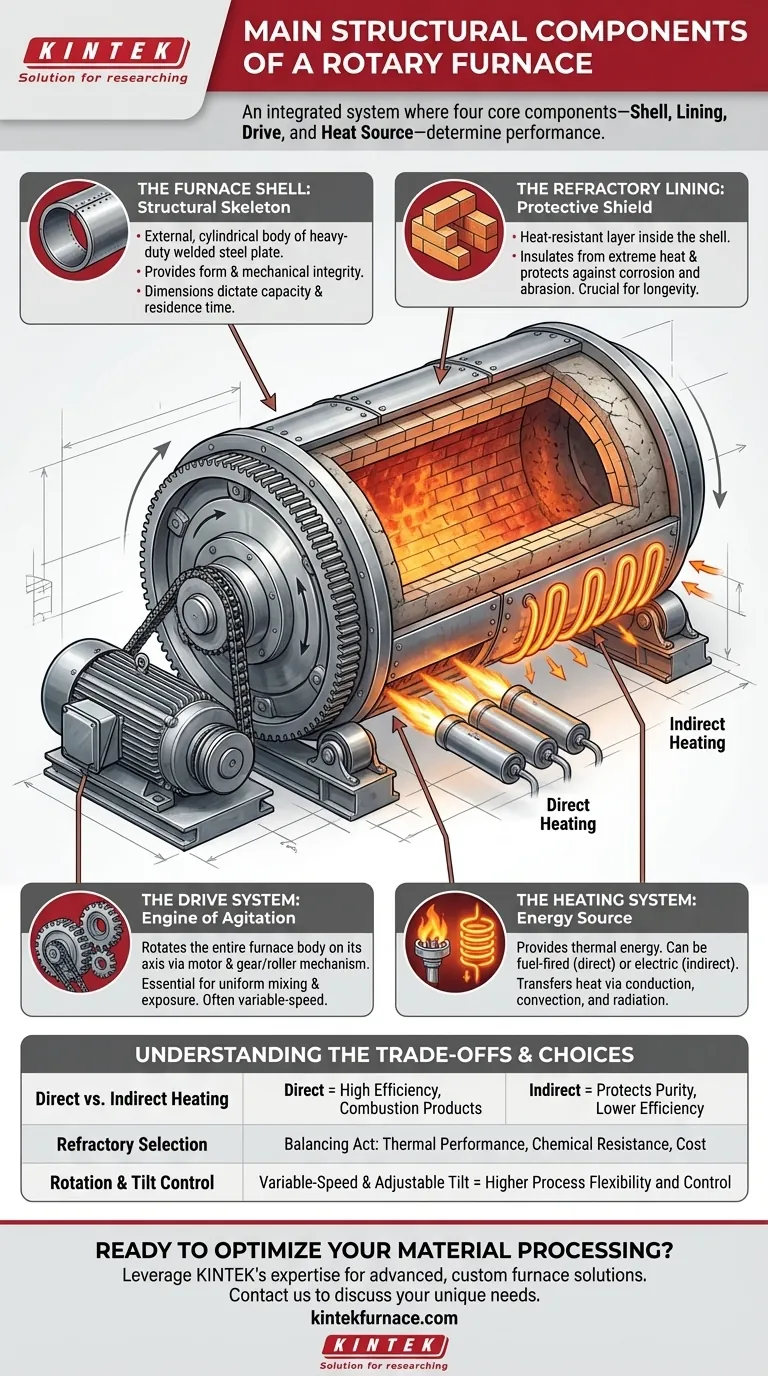
At its core, a rotary furnace is an integrated system built from four primary components. These are the outer furnace shell, the internal refractory lining, the drive mechanism that enables rotation, and the heating system that provides the necessary thermal energy. Together, these elements create a dynamic environment for continuous, high-temperature material processing.
A rotary furnace is not merely a rotating, heated cylinder. It is a carefully engineered system where the design and interplay of its core components—the shell, lining, drive, and heat source—directly determine its performance, lifespan, and suitability for a specific industrial process.

Deconstructing the Rotary Furnace
To truly understand a rotary furnace, you must look at each major component and its specific function within the larger system. Each part solves a distinct engineering challenge.
The Furnace Shell: The Structural Skeleton
The furnace shell, or body, is the external, cylindrical structure that provides the furnace's form and mechanical integrity.
It is almost always constructed from heavy-duty, welded steel plate. The dimensions, particularly the length and diameter, are dictated by the required processing capacity and residence time for the material inside. Some large-scale industrial furnaces can be over 200 meters long.
The Refractory Lining: The Protective Shield
The refractory lining is arguably the most critical component for furnace longevity and performance. It is a layer of heat-resistant material installed inside the steel shell.
This lining serves two primary purposes: insulating the steel shell from extreme internal temperatures and protecting it from chemical corrosion or physical abrasion from the material being processed.
Lining materials vary based on the application and include refractory bricks, castable or moldable cements, and other specialized composites. The choice of refractory directly impacts the furnace's maximum operating temperature and resistance to specific chemical agents.
The Drive System: The Engine of Agitation
The drive system is what makes the furnace "rotary." It consists of a powerful motor and a gear or roller mechanism that rotates the entire furnace body on its axis.
This rotation is essential for the process. It constantly tumbles and mixes the material, ensuring uniform exposure to the heat source and promoting consistent chemical reactions or phase changes throughout the batch.
Most modern furnaces feature a variable-speed drive. This allows operators to precisely control the rotation speed to optimize the mixing intensity and the material's residence time inside the furnace.
The Heating System: The Energy Source
The heating system provides the thermal energy required for the process. This is typically achieved in one of two ways: fuel-fired burners or electric heating elements.
Fuel-fired burners (using gas or oil) can be positioned to fire directly into the furnace chamber, offering high thermal efficiency. Electric elements are often arranged outside the furnace shell for indirect heating, which is ideal for processes requiring a controlled atmosphere or preventing product contamination from combustion byproducts.
Heat is transferred to the material through a combination of conduction, convection, and radiation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The design of a rotary furnace involves several critical trade-offs that determine its operational capabilities and cost. Understanding these is key to selecting or specifying the right equipment.
Direct vs. Indirect Heating
A furnace with burners firing directly into the chamber (direct heating) is more energy-efficient but introduces combustion gases that can react with the product. Indirect heating protects product purity but suffers from lower thermal efficiency as heat must transfer through the furnace shell.
Refractory Material Selection
Choosing a refractory lining is a balancing act between thermal performance, chemical resistance, and cost. An inexpensive lining might fail quickly when exposed to corrosive materials, leading to costly downtime and repairs. A high-performance lining, while more expensive upfront, ensures reliability and process integrity.
Rotation and Tilt Control
A simple, fixed-speed drive is less expensive but offers limited process control. A variable-speed drive, often combined with an adjustable tilt mechanism, provides the flexibility to fine-tune material residence time and mixing dynamics, making the furnace adaptable to a wider range of materials and process requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific application dictates which component features are most critical.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput for bulk materials: Prioritize a large-diameter furnace body, a robust and reliable drive system, and an efficient direct-fired heating system.
- If your primary focus is ensuring high product purity: Select an indirect heating design and a non-reactive refractory lining that will not contaminate your material.
- If your primary focus is processing abrasive or corrosive materials: The selection of a specialized, highly durable refractory lining becomes the most critical decision to ensure furnace longevity.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility: Invest in a system with a variable-speed drive and adjustable tilt to adapt to different feedstocks and desired outcomes.
Understanding how these core components function and interact is the first step toward mastering rotary furnace operation and design.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace Shell | Provides structural integrity and form | Made of heavy-duty steel, dimensions vary by capacity |
| Refractory Lining | Insulates and protects from heat and corrosion | Uses bricks or cements, affects temperature and durability |
| Drive System | Rotates the furnace for mixing and agitation | Includes motor and gears, often variable-speed for control |
| Heating System | Supplies thermal energy for processing | Direct or indirect methods using burners or electric elements |
Ready to optimize your material processing with a custom rotary furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization capabilities to meet unique experimental and industrial requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes



















