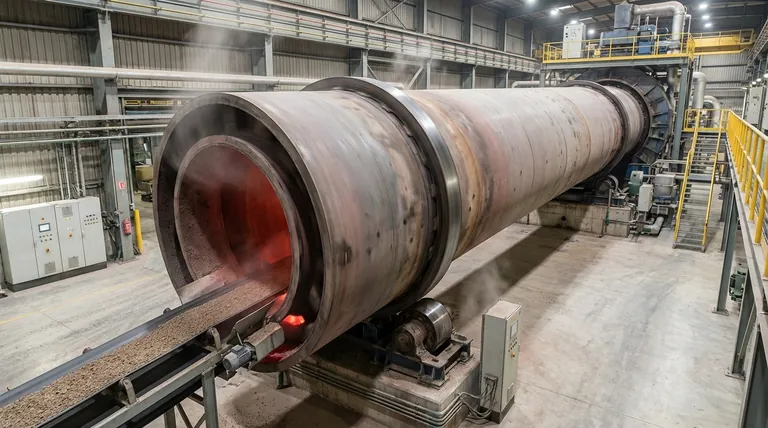
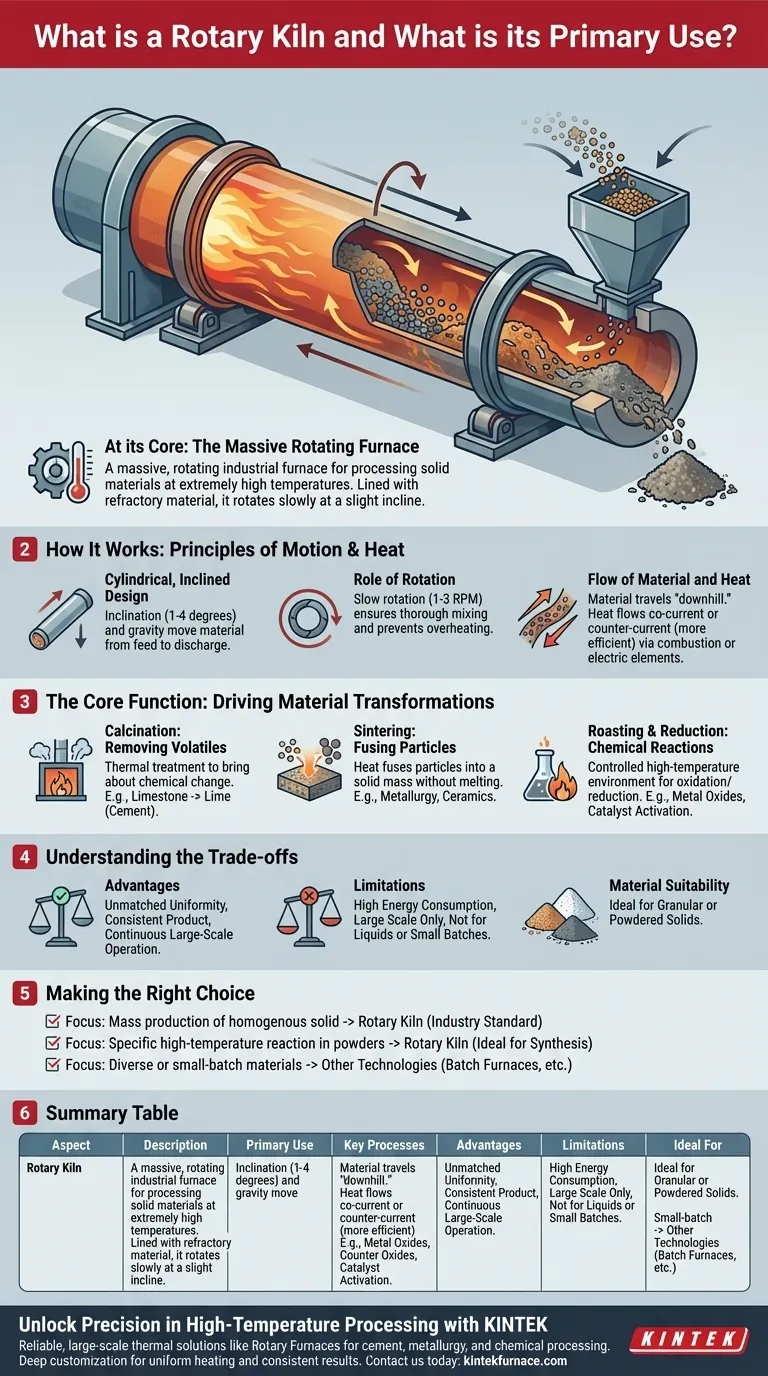
At its core, a rotary kiln is a massive, rotating industrial furnace designed to process solid materials at extremely high temperatures. It consists of a long, cylindrical steel shell lined with refractory material, which is mounted at a slight incline and rotates slowly. Its primary use is to induce specific chemical reactions or physical changes in materials, such as powders and granules, by ensuring they are heated uniformly for a precise duration.
The unique power of a rotary kiln lies in its rotation. This constant tumbling action ensures every particle of material is evenly exposed to heat, resulting in a highly consistent and uniform final product, a feat difficult to achieve in static furnaces.

How a Rotary Kiln Works: The Principles of Motion and Heat
A rotary kiln’s effectiveness comes from the elegant interplay of its physical design, rotational movement, and controlled heat application.
The Cylindrical, Inclined Design
A kiln is fundamentally a long, hollow tube. It is installed at a slight angle to the horizontal, typically between 1 and 4 degrees.
This inclination is critical, as it uses gravity to move material through the kiln from the higher feed end to the lower discharge end. The speed of this movement is controlled by the angle of inclination and the rotation speed.
The Role of Rotation
The kiln rotates slowly on its axis, generally between 1 to 3 revolutions per minute. This slow, constant tumbling is the kiln's defining feature.
This rotation lifts the material up the side of the kiln before it cascades back down, ensuring thorough mixing and preventing any single part of the material bed from overheating or being left untreated.
The Flow of Material and Heat
Material is fed into the high end and travels "downhill" to the discharge end. Heat is simultaneously introduced, either flowing in the same direction as the material (co-current flow) or in the opposite direction (counter-current flow).
Counter-current flow is most common, as it is more thermally efficient. The hottest gases encounter the most processed material, and the coolest gases encounter the fresh, cool feed, maximizing heat transfer throughout the length of the kiln. Heating can be achieved via fuel combustion or, in some designs, with electric heating elements for precise temperature control.
The Core Function: Driving Material Transformations
The combination of high temperature and uniform exposure allows rotary kilns to facilitate several key industrial processes.
Calcination: Removing Volatiles
Calcination is a thermal treatment process that brings about a chemical change, often by driving off a volatile component.
The most prominent example is in cement manufacturing, where limestone (calcium carbonate) is heated in a kiln to produce lime (calcium oxide) by driving off carbon dioxide.
Sintering: Fusing Particles
Sintering is a process where heat is used to fuse particles together into a solid, coherent mass without melting them completely.
This is essential in metallurgy for processing ores and in the production of high-strength ceramics and refractory materials.
Roasting and Reduction: Chemical Reactions
Kilns provide the controlled, high-temperature environment needed for specific chemical reactions like oxidation and reduction.
For example, they are used to create specific metal oxides (like magnetic iron oxide) or to reduce ores to recover metals. They can also be used for roasting materials like chemical molecular sieves to activate them.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the rotary kiln is a specific tool with distinct advantages and inherent limitations.
The Advantage: Unmatched Uniformity
The primary benefit of a rotary kiln is its ability to produce a highly homogenous and consistent product. The tumbling action ensures that every particle undergoes nearly identical thermal processing.
The Challenge: Energy and Scale
Rotary kilns are enormous pieces of equipment and are highly energy-intensive. Their sheer size and heat requirements make them best suited for continuous, large-scale industrial operations, not for small-batch or lab-scale work.
Material Suitability
This technology is designed specifically for granular or powdered solids. It is not suitable for processing liquids or materials that would melt into a single liquid mass, which would defeat the purpose of the tumbling action.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a rotary kiln depends entirely on the material you are processing and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is mass production of a homogenous solid: The rotary kiln is the industry standard for processes like cement manufacturing, mineral calcination, and large-scale soil remediation.
- If your primary focus is a specific high-temperature reaction in powders: The kiln's controlled environment and uniform heating make it ideal for specialized chemical synthesis, such as producing metal oxides or activating catalysts.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse or small-batch materials: Other technologies like batch furnaces, muffle furnaces, or fluidized bed reactors may offer greater flexibility and efficiency.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln is a cornerstone of modern industry, valued for its unique ability to transform raw solids into precisely engineered materials on a massive scale.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Induces chemical reactions or physical changes in solid materials via high-temperature processing. |
| Key Processes | Calcination (e.g., cement production), sintering (e.g., ceramics), roasting/reduction (e.g., metal oxides). |
| Advantages | Unmatched product uniformity, continuous large-scale operation, thorough material mixing. |
| Limitations | High energy consumption, not suitable for liquids or small batches, requires large-scale setup. |
| Ideal For | Granular or powdered solids in industries like cement, metallurgy, and chemical synthesis. |
Unlock Precision in High-Temperature Processing with KINTEK
Are you working with granular or powdered solids and need reliable, large-scale thermal solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace systems, including Rotary Furnaces, tailored for industries like cement, metallurgy, and chemical processing. Our deep customization capabilities ensure we meet your unique experimental and production requirements, delivering uniform heating and consistent results.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your processes and drive efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control



















