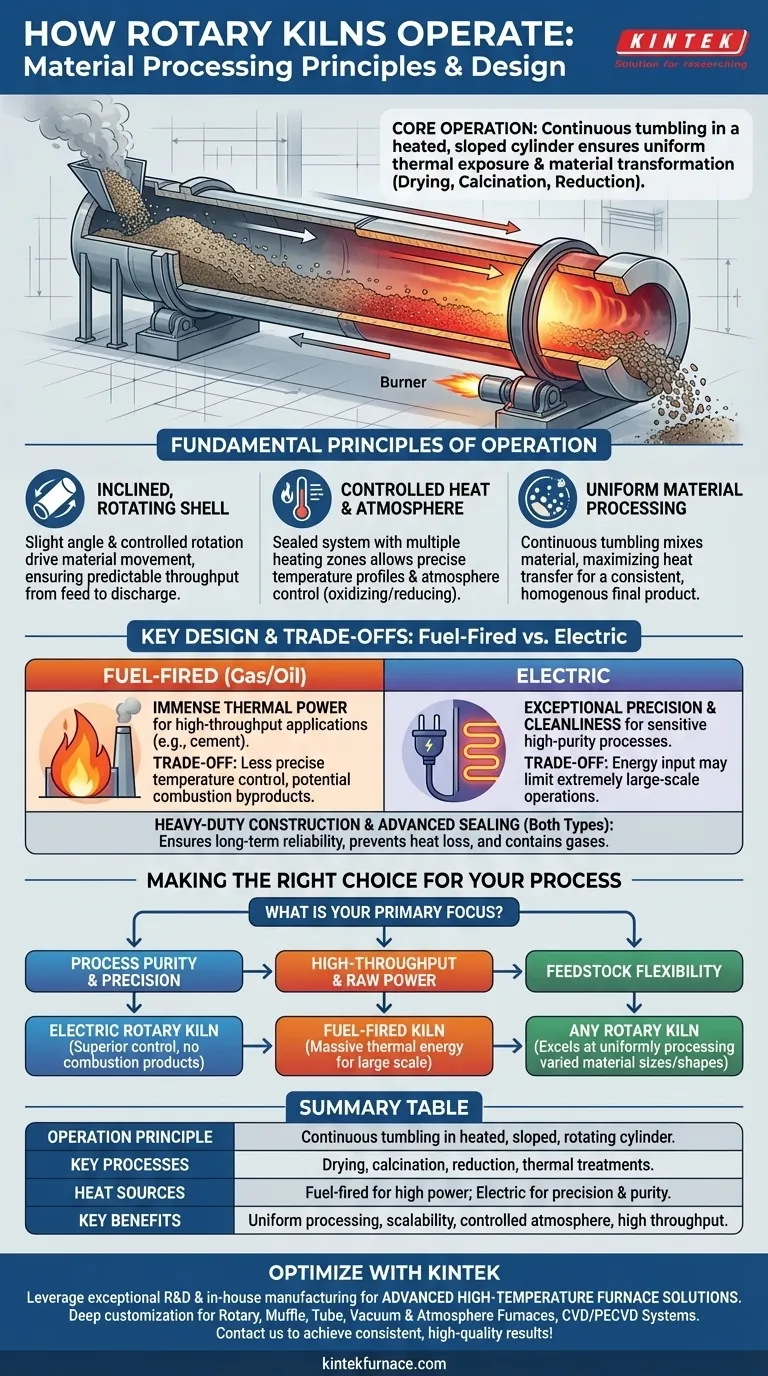
At its core, a rotary kiln processes materials by continuously tumbling them inside a large, heated, and gently sloped rotating cylinder. This movement ensures every particle is uniformly exposed to a controlled temperature and atmosphere. The purpose is to drive specific physical changes or chemical reactions, such as drying, calcination, or reduction, by precisely managing the material's journey through the heat.
The true value of a rotary kiln is not just its ability to heat materials, but its power to guarantee uniform processing at scale. By combining controlled motion with a precise thermal environment, it transforms a raw feedstock into a consistent, high-quality final product.

The Fundamental Principles of Operation
A rotary kiln's effectiveness comes from a few key interacting principles. It is a dynamic system designed for continuous, uniform material transformation.
The Inclined, Rotating Cylinder
The kiln is a long steel cylinder, or "shell," lined with refractory material to withstand extreme heat. It is mounted at a slight angle to the horizontal.
This inclination, combined with a slow and controlled rotation speed, causes material fed into the higher end to gently tumble and flow toward the lower, discharge end. This ensures a consistent and predictable throughput.
Controlled Heat and Atmosphere
The kiln is sealed at both ends to maintain precise control over the internal environment. Heat can be applied either directly, where exhaust gases from a burner contact the material, or indirectly, where the shell is heated from the outside.
This design allows for multiple heating zones along the kiln's length, enabling complex temperature profiles. It also allows operators to control the atmosphere, for example, by creating an oxygen-rich (oxidizing) or oxygen-poor (reducing) environment to facilitate specific chemical reactions.
Uniform Material Processing
The tumbling action, often compared to that of a clothes dryer, is critical. It constantly mixes the bed of material, ensuring that no particles are left unprocessed.
This continuous movement maximizes heat transfer, exposing all surfaces of the material to the controlled temperature and atmosphere. The result is a highly consistent and homogenous final product, which is difficult to achieve in static batch furnaces.
Key Design Considerations
The robust and adaptable nature of rotary kilns stems from their core design components, each serving a specific function.
Heating System: Fuel-Fired vs. Electric
Traditional kilns are fuel-fired (gas or oil), providing immense thermal energy for large-scale processes like cement production. They are powerful and effective for high-throughput applications.
Electric rotary kilns use electrical energy for heat. This provides exceptionally precise temperature control, which is critical for sensitive materials or processes with narrow operating windows, such as producing specialty chemicals or roasting molecular sieves.
Heavy-Duty Construction and Sealing
Rotary kilns are built for demanding industrial environments. Their heavy-duty construction ensures long-term reliability and safe operation under continuous high-temperature stress.
Advanced sealing devices at the feed and discharge ends are crucial. They prevent heat loss, stop unwanted air from entering the system, and contain process gases, enhancing both efficiency and operational safety.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, choosing a rotary kiln involves understanding the inherent trade-offs between different configurations and compared to other thermal processing technologies.
Precision vs. Raw Power
Electric kilns offer unparalleled precision and cleanliness. With no combustion byproducts, they are ideal for high-purity applications. However, their energy input may be a limiting factor for extremely large-scale mineral processing.
Fuel-fired kilns deliver massive amounts of raw thermal power, making them the default choice for high-volume industries. The trade-off is less precise temperature control and the potential for product contamination from fuel combustion.
Capital Investment and Scale
Rotary kilns represent a significant capital investment. Their "simple operation" refers to the streamlined continuous process once running, not a lack of complexity in the equipment itself.
Their strength is in continuous, high-throughput processing. For very small batch production or laboratory work, other furnace types might be more economical and practical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific processing goal is the most important factor in selecting the right type of rotary kiln technology.
- If your primary focus is process purity and precision: An electric rotary kiln offers superior temperature control and eliminates contamination from combustion byproducts.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput and raw power: A traditional fuel-fired kiln provides the massive thermal energy needed for large-scale operations like mineral processing or cement production.
- If your primary focus is feedstock flexibility: The inherent tumbling action of any rotary kiln excels at uniformly processing a wide variety of material sizes, shapes, and densities.
Understanding these core principles empowers you to leverage a rotary kiln not just as a heater, but as a precision instrument for material transformation.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Operation Principle | Continuous tumbling in a heated, sloped, rotating cylinder for uniform exposure |
| Key Processes | Drying, calcination, reduction, and other thermal treatments |
| Heat Sources | Fuel-fired (gas/oil) for high power, electric for precision and purity |
| Key Benefits | Uniform processing, scalability, controlled atmosphere, high throughput |
| Design Features | Inclined cylinder, refractory lining, sealing systems, multiple heating zones |
Ready to optimize your material processing with a custom rotary kiln? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production needs. Whether you require high-throughput power or precise temperature control, we can help you achieve consistent, high-quality results. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can transform your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems



















