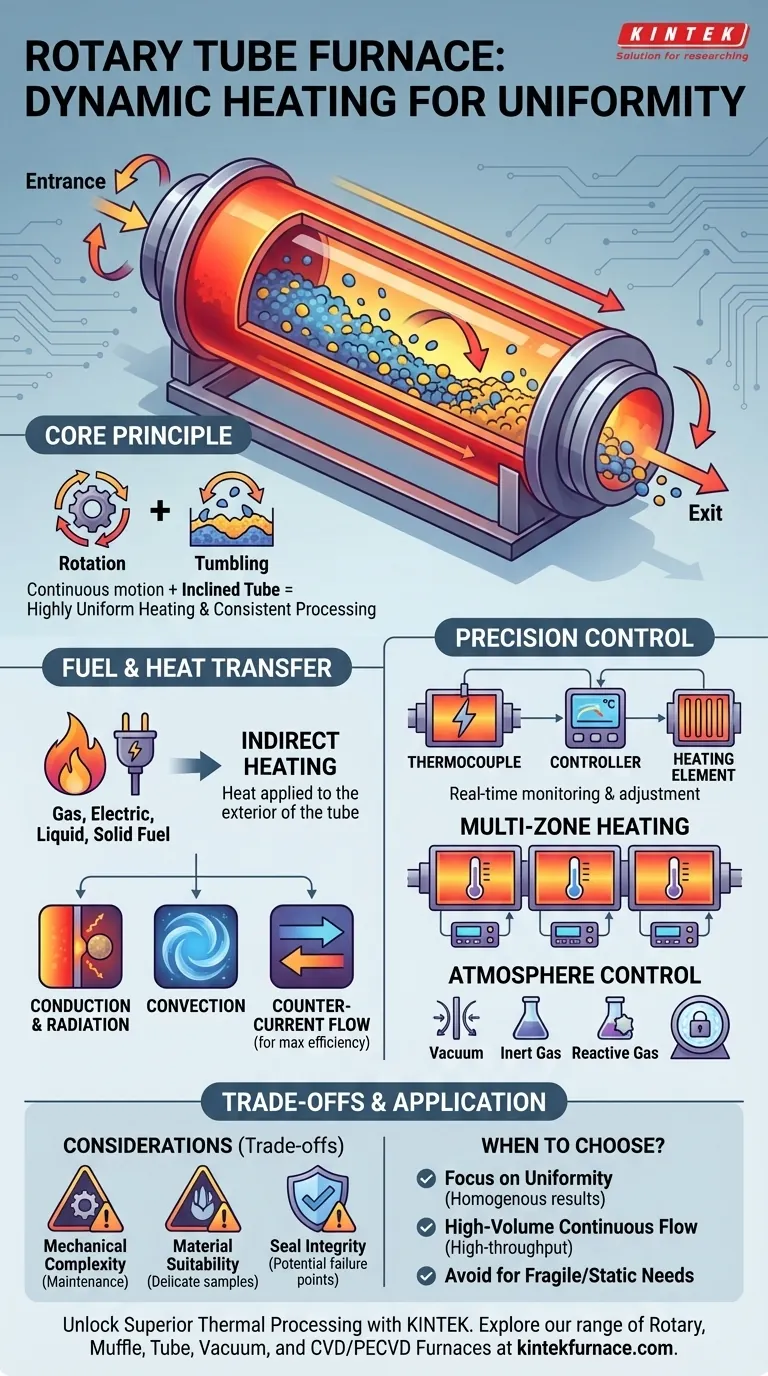
At its core, a rotary tube furnace operates by using a fuel source to heat the exterior of a rotating, inclined tube. This combination of rotation and heat transfer ensures that the material tumbling inside is heated with exceptional uniformity. The system can be fueled by a wide range of sources, including gas, electricity, liquid, or even solid pulverized fuels, making it highly versatile.
The defining characteristic of a rotary tube furnace is not simply its heat source, but its use of constant motion. By continuously rotating the material within the heated tube, it solves the fundamental challenge of uneven heating, ensuring every particle is exposed to the same thermal conditions for highly consistent processing.

The Core Principle: Dynamic Heating for Uniformity
The primary advantage of a rotary tube furnace stems from its ability to move the material during the heating cycle. This dynamic approach is fundamentally different from static furnaces and is key to its performance.
The Role of the Rotating Tube
The central component is the furnace tube, which is rotated by a motor. As the tube spins, it causes the material inside to gently tumble and mix. This constant flipping ensures that no single part of the material is overexposed or underexposed to the heat source.
The Importance of Inclination
These furnaces are typically mounted at a slight angle. This tilt uses gravity to help the material flow continuously from the entrance to the exit, making the system ideal for continuous processing rather than just single-batch jobs. The angle can often be adjusted to control how long the material stays in the furnace.
Eliminating Hot and Cold Spots
The combination of rotation and tumbling actively prevents the formation of hot or cold spots within the material batch. In a static furnace, material at the bottom and center heats slower than material at the edges. A rotary furnace completely eliminates this problem, leading to superior product consistency.
A Closer Look at the Heat Transfer Process
The furnace's design is optimized to transfer thermal energy into the material as efficiently as possible using multiple methods.
Fuel Sources and Heat Generation
Rotary tube furnaces are flexible, using either electric heating elements or the combustion of gas, oil, or solid fuels. In many designs, the heating is indirect, meaning the flames or elements heat the outside of the process tube, which then radiates heat inward. This protects the sample from direct contact with combustion byproducts.
Conduction, Convection, and Radiation
Heat is transferred to the material through three modes simultaneously. The hot tube wall applies heat via radiation and conduction when particles touch it. The controlled atmosphere inside the tube transfers heat via convection. This multi-modal transfer is highly efficient.
Counter-Current Flow for Maximum Efficiency
For optimal performance, many systems are designed for counter-current flow. In this setup, the hot gases from the heat source flow in the opposite direction of the material. This ensures that the coldest material meets the hottest gases, maximizing the temperature difference and the rate of heat exchange along the entire length of the tube.
Precision Control: The Brains of the Operation
A rotary tube furnace is more than just a hot, spinning tube. It relies on a sophisticated control system to execute precise thermal profiles.
The Thermocouple and Controller Loop
A thermocouple is a sensor placed within the furnace chamber to measure the real-time temperature. It converts this reading into an electrical signal that is sent to a temperature controller. The controller compares this signal to the desired setpoint and adjusts the power to the heating elements or fuel burner to maintain the target temperature with high accuracy.
The Power of Multi-Zone Heating
More advanced furnaces feature multiple thermal control zones along the length of the tube. Each zone has its own thermocouple and independent controller. This allows you to create a precise temperature profile, such as heating the material up slowly, holding it at a peak temperature, and then cooling it down in a controlled manner, all within a single pass.
Controlling the Atmosphere
The heating process is often dependent on the atmosphere surrounding the material. The sealed design of a rotary tube furnace allows for precise control of this environment. It can operate under a vacuum, be filled with an inert gas like nitrogen or argon to prevent oxidation, or use a reactive gas for specific chemical processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the design of a rotary tube furnace presents specific considerations that may make it unsuitable for certain applications.
Mechanical Complexity
The rotating mechanism, motor, and seals add mechanical complexity compared to a static box furnace. These moving parts require regular maintenance to ensure reliability and preserve the integrity of the atmospheric seal.
Material Suitability
The tumbling action is a key benefit, but it can be a drawback for certain materials. Delicate or friable samples may break apart, and processes that require the material to remain completely still (like crystal growth) are not compatible with this design.
Seal Integrity
Maintaining a perfect atmospheric seal on a component that is constantly rotating is more challenging than on a static furnace. While modern seals are highly effective, they are a critical point of potential failure and require careful monitoring, especially for high-purity vacuum or inert gas applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
To decide if this technology fits your needs, evaluate your primary processing goal.
- If your primary focus is process uniformity and consistency: A rotary tube furnace is an excellent choice, as its dynamic heating method is specifically designed to produce homogenous results.
- If you are processing large volumes in a continuous flow: The inclined, rotating design is ideal for high-throughput, continuous manufacturing environments.
- If your material is fragile or requires a completely static environment: You should consider a static box or a non-rotating tube furnace, as the tumbling action may be detrimental.
By understanding its dynamic heating principles and control capabilities, you can confidently determine if a rotary tube furnace is the optimal tool for achieving your thermal processing goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Fuel Sources | Gas, electricity, liquid, or solid pulverized fuels |
| Heating Method | Indirect heating via conduction, convection, and radiation |
| Key Advantage | Uniform heating through rotation and tumbling |
| Control Systems | Multi-zone temperature control and atmosphere management |
| Applications | Continuous processing for consistent, high-throughput results |
Unlock Superior Thermal Processing with KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Whether you need uniform heating for continuous processes or tailored solutions for specific materials, KINTEK delivers reliable performance and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your lab's productivity and achieve consistent results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity



















