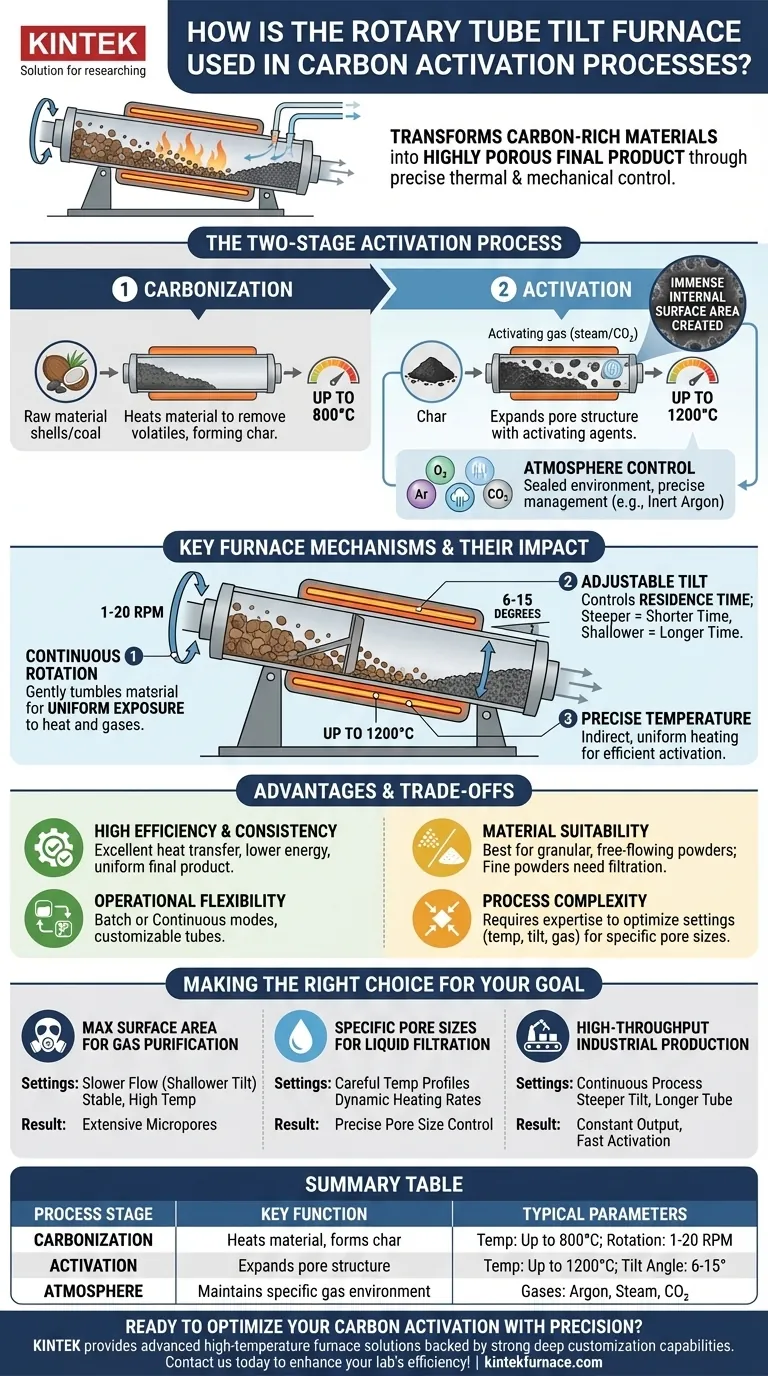
At its core, a Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace is used in carbon activation to transform raw, carbon-rich materials into a highly porous final product through precise thermal and mechanical control. It accomplishes this by tumbling the material inside a heated, rotating tube, ensuring every particle is uniformly carbonized and then activated in a controlled atmosphere. The tilting function allows for fine-tuning the material's residence time within the furnace, giving engineers exacting control over the final product's properties.
The furnace’s effectiveness comes from its unique combination of three critical actions: continuous rotation for uniform heating, adjustable tilt for controlling process duration, and a sealed environment for precise atmosphere management. This synergy guarantees the creation of high-quality activated carbon with a vast internal surface area, which is the key to its powerful adsorption capabilities.

The Two-Stage Activation Process
The transformation of a raw material like coconut shell or coal into activated carbon is not a single step. It is a carefully orchestrated two-stage thermal process, and the furnace is engineered to manage both stages with precision.
Stage 1: Carbonization
First, the raw material is heated in the rotating tube to drive off water and other volatile compounds. This initial process, known as carbonization, leaves behind a carbon-rich, porous solid called "char." The furnace's slow rotation ensures every particle is heated evenly, preventing hot spots and producing a consistent char.
Stage 2: Activation
Next, the char is heated to a higher temperature, often up to 800°C, in the presence of an activating agent. This is the activation step, where the internal pore structure is dramatically expanded. This process carves out a network of microscopic pores, creating the immense internal surface area that gives activated carbon its adsorptive power.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere Control
The furnace’s ability to maintain a controlled atmosphere is essential. The references cite an argon atmosphere, which is an inert gas used for physical activation, preventing the carbon from burning away (oxidizing). The furnace's gas purging and vacuum capabilities allow operators to introduce specific activating gases (like steam or carbon dioxide in other processes) and remove byproducts, directly influencing the final pore structure.
Key Furnace Mechanisms and Their Impact
The unique design features of the Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace are what enable such precise control over the activation process. Each mechanism serves a distinct and vital purpose.
Continuous Rotation for Uniform Exposure
The tube's slow rotation, typically between 1-20 RPM, gently tumbles the material. This constant, delicate mixing guarantees that every particle receives uniform exposure to both the heat from the furnace walls and the activating gases in the atmosphere. This is the primary mechanism for achieving a consistent, high-quality product.
Tilt Angle for Material Flow Control
The ability to tilt the furnace, usually between 6-15 degrees, is a powerful tool for process control. The tilt angle dictates the speed at which material travels through the tube, thereby controlling its residence time in the hot zone. A steeper angle results in a shorter residence time for continuous production, while a shallower angle increases it, allowing for deeper activation.
Precise Temperature and Mixing
The furnace can reach temperatures up to 1200°C, providing more than enough thermal energy for activation. More importantly, this heat is applied indirectly and uniformly. To aid this, internal scraper bars can be fitted inside the tube to prevent material from sticking to the walls and to ensure it is constantly being folded and mixed.
Understanding the Advantages and Trade-offs
While highly effective, it's important to view the Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace as a specialized tool with a specific set of strengths and operational considerations.
Advantage: High Efficiency and Consistency
The combination of indirect heating and constant material tumbling results in excellent heat transfer efficiency and significantly lower energy consumption compared to static furnaces. The primary advantage remains the production of an exceptionally uniform and consistent final product batch after batch.
Advantage: Operational Flexibility
These furnaces can be run in batch mode (for smaller, developmental quantities) or continuous mode (for large-scale production). The ability to change tube materials (e.g., quartz for purity, alumina for high temperatures) and customize furnace length adds another layer of adaptability for different raw materials and process goals.
Consideration: Material Suitability
This design excels with granular, free-flowing powders and small particles. Extremely fine powders may become entrained in the exhaust gas flow, requiring filtration systems. Large, irregular chunks of material may not tumble effectively, leading to non-uniform treatment.
Consideration: Process Complexity
This is not a simple "set and forget" device. Optimizing the final product requires a sophisticated understanding of how temperature, rotation speed, tilt angle, gas composition, and flow rate interact. Achieving specific pore sizes or surface area targets requires significant process development and expertise.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The furnace's settings must be tuned to engineer the specific properties required for the activated carbon's intended application.
- If your primary focus is maximizing surface area for gas purification: You will likely use a slower material flow (shallower tilt) and a stable, high activation temperature to allow for the extensive development of micropores.
- If your primary focus is creating specific pore sizes for liquid filtration: You will need to carefully control both the carbonization and activation temperature profiles, using the furnace's dynamic controls to manage heating rates and residence time precisely.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput industrial production: You will optimize for a continuous process, likely using a steeper tilt angle and a longer furnace tube to achieve the required activation time while maintaining a constant output.
Mastering the interplay of these variables allows you to engineer activated carbon with performance characteristics tailored to your exact needs.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Function | Typical Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Carbonization | Heats material to remove volatiles, forming char | Temperature: Up to 800°C; Rotation: 1-20 RPM |
| Activation | Expands pore structure with activating agents | Temperature: Up to 1200°C; Tilt Angle: 6-15° |
| Atmosphere Control | Maintains inert or specific gas environments | Common gases: Argon, steam, CO₂ |
Ready to optimize your carbon activation with precision? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Tube Tilt Furnaces. Our product line—featuring Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- In what environments are rotary tube furnaces considered indispensable? Essential for Uniform Thermal Processing
- What are the advantages of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Material Processing
- How is the Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace used in the carbon activation process? Achieve Uniform, High-Porosity Activated Carbon
- What makes rotary tube furnaces user-friendly? Achieve Superior Process Uniformity and Efficiency
- How do rotary tube furnaces enhance efficiency in materials processing? Boost Throughput and Quality



















