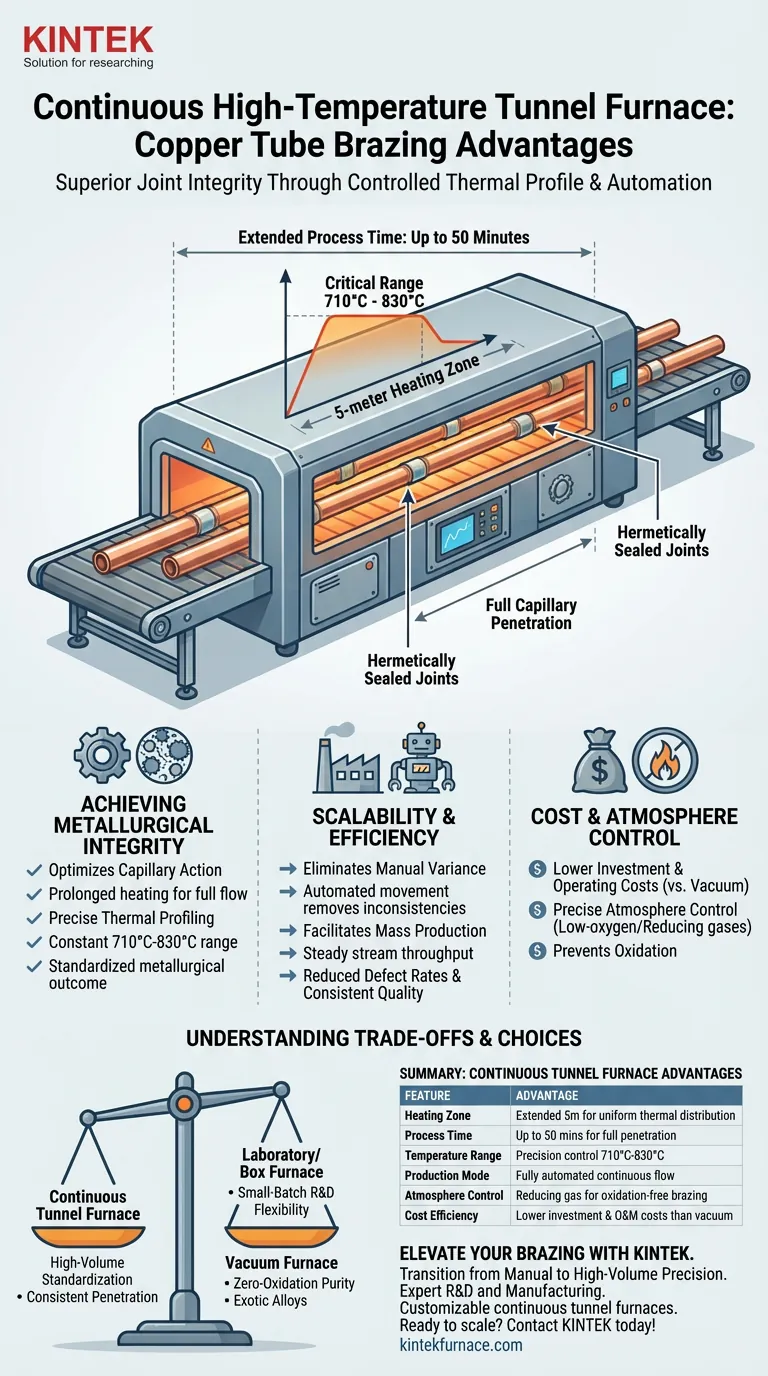
The primary process advantages of a continuous high-temperature tunnel furnace stem from its ability to maintain a strictly controlled thermal profile over a prolonged period, ensuring superior joint integrity. By utilizing a heating zone extending up to 5 meters and a process time of up to 50 minutes, this equipment guarantees full capillary penetration of filler metals within the critical 710°C to 830°C range. This continuous method eliminates the non-uniformity inherent in manual brazing, enabling high-quality, automated production for large-scale components.
By stabilizing the thermal environment and automating the workflow, continuous tunnel furnaces transform copper brazing from a variable manual task into a consistent, high-volume industrial process.

Achieving Metallurgical Integrity
Optimizing Capillary Action
The most critical factor in brazing is ensuring the filler metal flows completely into the joint gap.
A tunnel furnace provides a prolonged heating process of up to 50 minutes. This extended duration allows sufficient time for the filler metal to melt, flow, and achieve full capillary penetration, creating a hermetically sealed and mechanically strong joint.
Precise Thermal Profiling
Manual operations often suffer from temperature spikes or drops that compromise the bond.
Continuous tunnel furnaces maintain a constant temperature profile typically between 710°C and 830°C. This consistency ensures that every component passing through the 5-meter heating zone experiences the exact same thermal history, effectively standardizing the metallurgical outcome.
Scalability and Operational Efficiency
Eliminating Manual Variance
Human operators introduce variables such as inconsistent heating angles or timing differences.
By automating the movement of parts through the heat zone, the furnace removes these manual inconsistencies. This results in a drastic reduction in defect rates and ensures that consistent welding quality is maintained across every shift.
Facilitating Mass Production
For manufacturers dealing with large-scale components or high volumes, batch processing can be a bottleneck.
Continuous furnaces are designed for the automated processing of large-scale components. Unlike box furnaces which require loading and unloading cycles, a tunnel furnace allows for a steady stream of production, significantly increasing throughput.
Cost and Atmosphere Control
Beyond speed, these furnaces offer economic and environmental control advantages.
They generally present lower investment and operating costs compared to vacuum furnaces. Furthermore, they allow for precise control of internal atmospheres—such as using low-oxygen or reducing gases—to prevent oxidation without the high expense of maintaining a high vacuum.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While continuous tunnel furnaces are superior for high-volume uniformity, they are not the universal solution for every brazing scenario.
Flexibility Limitations
These furnaces are optimized for steady-state operation. They are less agile than laboratory or box furnaces when it comes to frequent changes in temperature profiles or processing very small, diverse batches of experimental parts.
Startup and Shutdown Energy
Because they rely on a long, stable heated tunnel, these furnaces are best utilized in continuous shifts. Frequent startups and shutdowns can be energy-intensive and reduce overall efficiency compared to smaller batch units designed for intermittent use.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To decide if a continuous high-temperature tunnel furnace is the right fit for your copper brazing needs, evaluate your production volume and quality requirements.
- If your primary focus is High-Volume Standardization: Choose the continuous tunnel furnace to guarantee consistent capillary penetration and lower per-unit costs through automation.
- If your primary focus is Small-Batch R&D: Consider a laboratory tube or box furnace, which offers greater flexibility for changing parameters and testing distinct thermal profiles.
- If your primary focus is Zero-Oxidation Purity: Evaluate a vacuum furnace, especially if the absolute cleanest environment is required for exotic alloys, despite the higher operational cost.
For industrial-scale copper tube brazing, the continuous tunnel furnace remains the definitive standard for balancing throughput with metallurgical quality.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Continuous Tunnel Furnace Advantage |
|---|---|
| Heating Zone | Extended 5-meter zone for uniform thermal distribution |
| Process Time | Up to 50 minutes for full capillary penetration |
| Temperature Range | Precision control between 710°C and 830°C |
| Production Mode | Fully automated, continuous flow for large-scale components |
| Atmosphere Control | Reducing gas capability for oxidation-free brazing |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower investment and O&M costs than vacuum systems |
Elevate Your Brazing Production with KINTEK
Transition from inconsistent manual brazing to high-volume precision. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, alongside customizable continuous tunnel furnaces tailored to your unique industrial needs.
Whether you require high-volume standardization or specialized laboratory solutions, our engineers provide the thermal expertise to optimize your metallurgical outcomes.
Ready to scale your production? Contact us today to find your perfect furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- António B. Pereira, Ana Horovistiz. Brazing of Copper Pipes for Heat Pump and Refrigeration Applications. DOI: 10.3390/met14020171
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory furnace affect chemical bonding in hybrid composites? Unlock Superior Material Strength
- What are the advantages of Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) for TiC alloys? Preserve Precision and Microstructure
- Why is high temperature control stability required for KAS method kinetics? Ensure Accurate Activation Energy Results
- What role does the addition of NaCl as a diluent play in the SHS of Titanium Diboride? Master Nano-Powder Synthesis
- Why is Copper (Cu) introduced as a flux in AlN single crystal growth? Enhance Source Stability and Yield
- Why is a stainless steel autoclave with a Teflon liner necessary for BiVO4? Ensure Purity & High Performance
- Why is high-purity argon gas required for MTO synthesis? Ensure Stability in Rhenium Organometallic Catalysis
- What is the purpose of using a vacuum dryer for PU and AlN composite sheets? Enhance Thermal & Structural Integrity



















