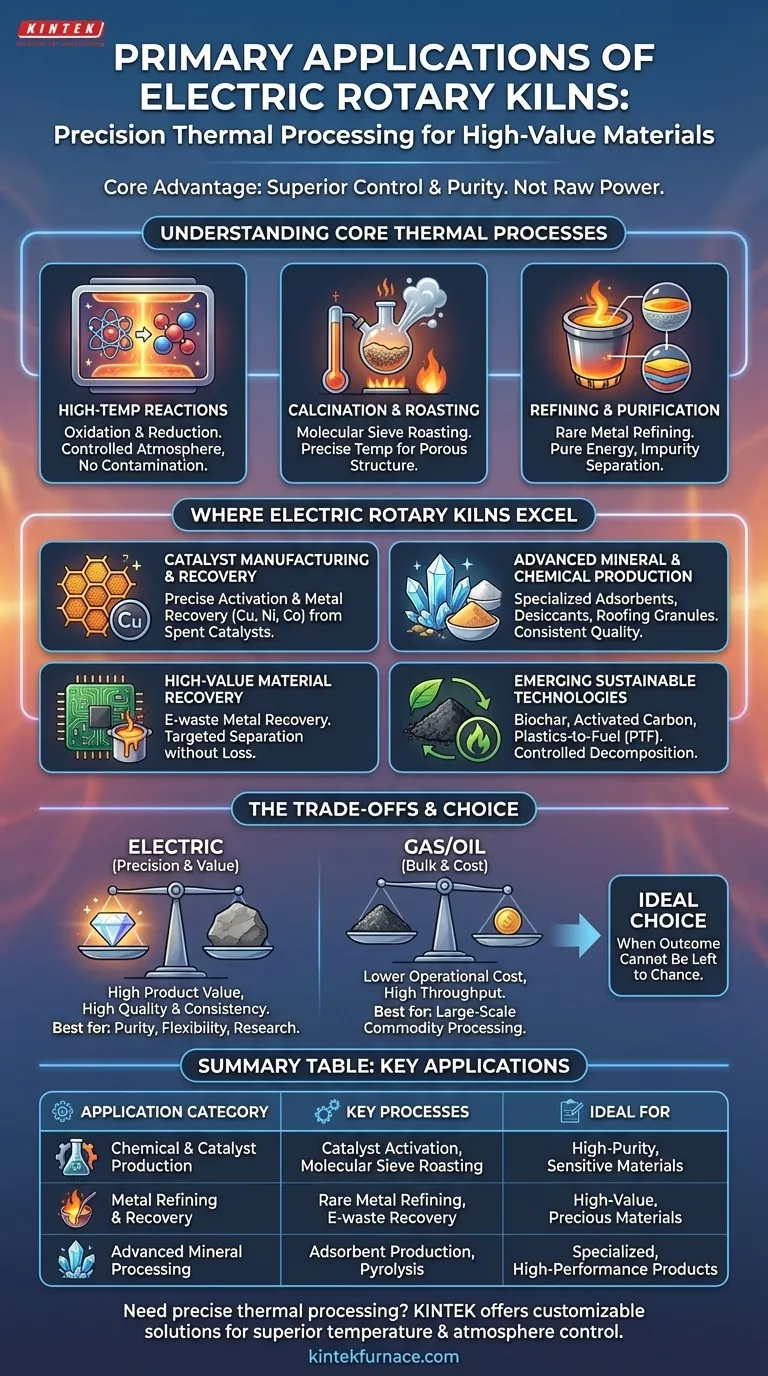
In short, electric rotary kilns are primarily used for high-precision thermal processing of specialized materials where temperature and atmosphere control are critical. Key applications include high-temperature oxidation and reduction reactions, the roasting of chemical molecular sieves, catalyst activation, advanced mineral production, and the refining of valuable or rare metals.
The core advantage of an electric rotary kiln is not raw power, but precise control. By using electricity instead of combustible fuel, these kilns offer superior temperature regulation and the ability to maintain a pure, controlled atmosphere, making them essential for creating high-value, sensitive materials.

Understanding the Core Thermal Processes
Electric rotary kilns are versatile tools capable of executing several fundamental thermal processes with high fidelity. The choice of an electric heat source is deliberate, enabling a level of control that direct-fired kilns cannot match.
High-Temperature Reactions
Electric kilns provide the stable, uniform heat necessary for driving specific chemical reactions like oxidation and reduction. Because there are no combustion byproducts, operators can introduce specific gases to create a controlled atmosphere, ensuring the desired reaction occurs without contamination.
Calcination and Roasting
Calcination is a process that uses heat to cause thermal decomposition, often to remove a volatile component from a solid. A key application is the roasting of chemical molecular sieves, where precise temperature control is vital to creating the material's porous structure without destroying it.
Refining and Purification
These kilns are used for refining rare metals and purifying mixtures. The clean energy source prevents the introduction of impurities from fuel, while precise temperature ramps can be used to volatilize and separate different materials effectively.
Where Electric Rotary Kilns Excel
While gas-fired kilns dominate bulk material processing like cement, electric kilns have carved out a crucial niche in industries that produce specialized, high-performance materials.
Catalyst Manufacturing and Recovery
Creating and activating industrial catalysts requires exact temperatures to achieve the desired surface properties. Electric kilns provide this precision. They are also used to recover valuable metals like copper, nickel, and cobalt from spent catalysts.
Advanced Mineral and Chemical Production
Electric kilns are ideal for manufacturing products like specialized adsorbents, desiccants, and roofing granules. These materials require consistent quality and performance, which is a direct result of the highly controlled processing environment.
High-Value Material Recovery
The controlled atmosphere is perfect for recovering valuable metals from e-waste or other industrial byproducts. The process can be tailored to target specific metals without losing them to unwanted side reactions.
Emerging Sustainable Technologies
Newer applications include producing biochar and activated carbon, where the final product's properties are heavily dependent on the heating profile. They are also used in pyrolysis for plastics-to-fuel (PTF) technologies, which require controlled thermal decomposition in an oxygen-free environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an electric rotary kiln involves weighing its unique benefits against practical limitations. Its strengths in one area create trade-offs in others.
The Precision vs. Cost Equation
The primary trade-off is operational cost. Electricity is typically more expensive than natural gas or other fossil fuels. This makes electric kilns less economical for processing massive volumes of low-cost bulk materials like cement or lime, where raw heat per dollar is the key metric.
Throughput and Scale
While rotary kilns in general are known for high throughput, electric models are often engineered for applications where product value is more important than sheer volume. The investment in precise electrical heating systems is justified by the high quality and consistency of the final product, not by its tonnage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the right heating technology depends entirely on your material, your budget, and your quality requirements.
- If your primary focus is precision and product purity: The superior temperature and atmosphere control of an electric kiln is the definitive choice for sensitive, high-value materials.
- If your primary focus is processing bulk materials at the lowest cost: A direct-fired gas or oil kiln is almost always the more economical solution for large-scale industrial applications like minerals and cement.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility and handling varied feedstock: An electric kiln's ability to precisely manage different heating profiles makes it highly adaptable for research, development, or multi-product manufacturing lines.
Ultimately, an electric rotary kiln is a specialized instrument for when the outcome cannot be left to chance.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical & Catalyst Production | Catalyst activation, molecular sieve roasting | High-purity, sensitive materials |
| Metal Refining & Recovery | Rare metal refining, e-waste metal recovery | High-value, precious materials |
| Advanced Mineral Processing | Adsorbent/desiccant production, pyrolysis | Specialized, high-performance products |
Need precise thermal processing for your high-value materials?
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers customizable electric rotary kilns, tube furnaces, and other lab high-temperature systems. Our solutions deliver the superior temperature and atmosphere control essential for catalyst manufacturing, metal recovery, and advanced material production.
Contact us today to discuss how our precision heating technology can enhance your process and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency



















