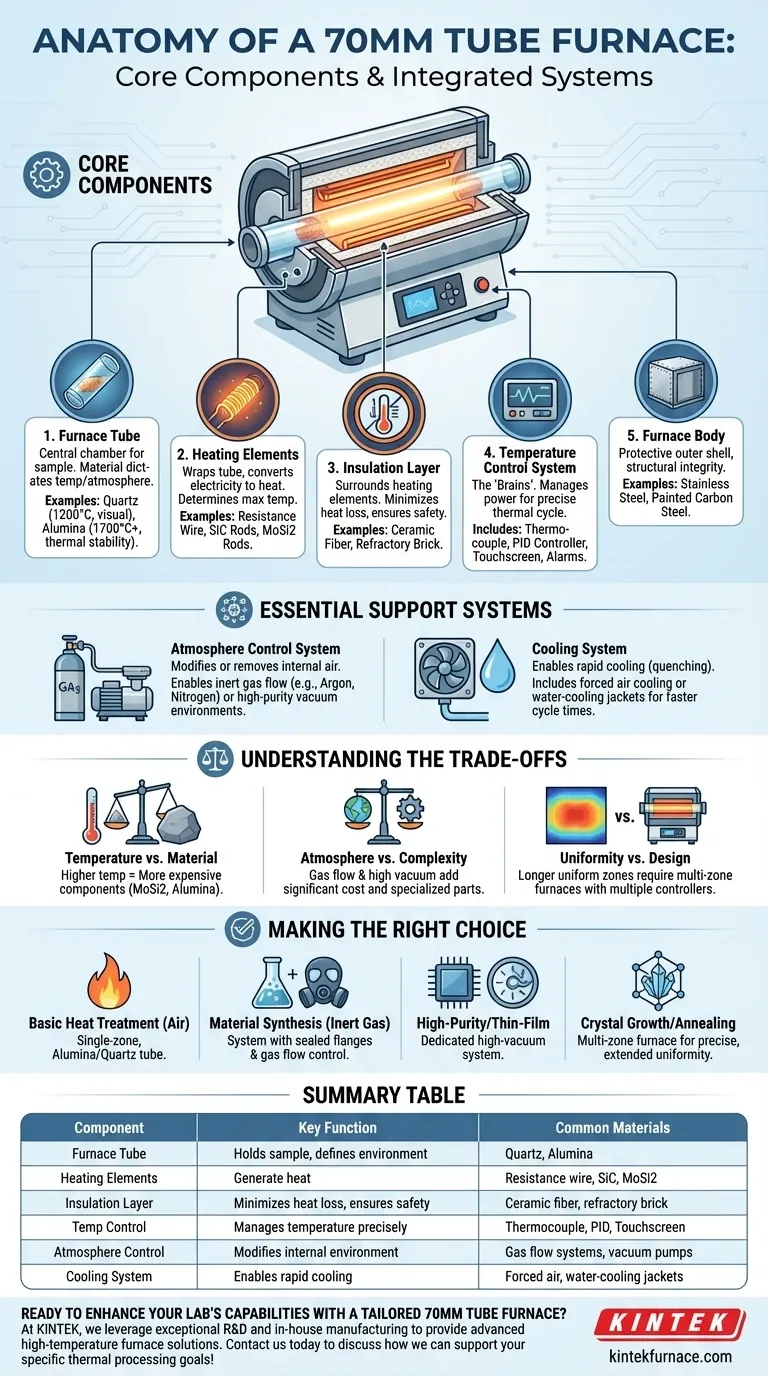
At its core, a 70mm tube furnace is a precision instrument built from several key interacting systems. The primary components are the furnace tube where the sample is placed, the heating elements that generate thermal energy, the insulation that contains the heat, and a sophisticated temperature control system that manages the entire process.
A tube furnace is more than a simple oven; it is an integrated system designed to create a highly uniform and controllable thermal environment. The specific components selected for each system dictate the furnace's ultimate capabilities, from its maximum temperature to the type of atmospheric conditions it can achieve.

The Anatomy of a Tube Furnace: Core Components
Understanding how a tube furnace works begins with its fundamental building blocks. Each component has a specific role in achieving a stable and precise thermal cycle.
The Furnace Tube: The Heart of the Operation
This is the central cylindrical chamber that holds the material being processed. The tube's material is critical and is chosen based on the required temperature and chemical environment.
Common materials include quartz, which is suitable for temperatures up to around 1200°C and allows for visual observation, and high-purity alumina, which is necessary for higher temperatures (up to 1700°C or more) and offers excellent thermal stability.
Heating Elements: The Engine of Thermal Energy
Wrapped around the exterior of the furnace tube, these elements convert electrical energy into heat. The material used for the heating elements directly determines the furnace's maximum operating temperature.
Common types include resistance wire (like Kanthal) for lower temperatures, silicon carbide (SiC) rods for mid-range temperatures, and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) rods for the highest temperature applications.
The Insulation Layer: Maximizing Efficiency and Safety
High-quality ceramic fiber or refractory brick insulation surrounds the heating elements. This layer serves two crucial functions.
First, it minimizes heat loss, ensuring energy efficiency and promoting a uniform temperature zone inside the tube. Second, it keeps the outer casing of the furnace at a safe, cool-to-the-touch temperature, protecting both the operator and surrounding equipment.
The Temperature Control System: The Brains of the Furnace
This is the nerve center of the entire apparatus. It typically consists of a thermocouple to measure the temperature accurately and a PID controller (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) to intelligently manage power to the heating elements.
Modern systems often feature touchscreen interfaces, programmable heating and cooling rates, and critical safety alarms for over-temperature protection, ensuring both precision and operational security.
The Furnace Body: The Protective Shell
The outer casing, usually made of stainless steel or painted carbon steel, provides structural integrity. It houses all the internal components, protects them from the external environment, and provides a stable platform for the entire system.
Beyond the Basics: Essential Support Systems
For most scientific and industrial applications, controlling the environment inside the tube is just as important as controlling the temperature. This requires additional integrated systems.
The Atmosphere Control System: Defining the Environment
Many processes cannot be performed in ambient air. An atmosphere control system allows you to modify or remove the air inside the furnace tube.
This can range from a simple gas management system that flows an inert gas like argon or nitrogen to prevent oxidation, to a complex vacuum system with pumps that remove air entirely, creating a high-purity environment essential for semiconductor or nanotechnology research.
The Cooling System: Enabling Rapid Cycling
While insulation is designed to hold heat, some processes require rapid cooling (quenching) to lock in a specific material phase.
Some furnaces incorporate forced air cooling or water-cooling jackets around the furnace body to dissipate heat quickly once the heating cycle is complete, significantly reducing the time between experimental runs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing or specifying a tube furnace involves balancing capability, complexity, and cost. No single configuration is best for all tasks.
Temperature vs. Tube and Element Material
The single biggest factor is the maximum required temperature. A furnace designed for 1700°C requires expensive MoSi2 elements and a high-purity alumina tube, whereas a 1100°C application can use more affordable components.
Atmosphere Control vs. Complexity
A simple furnace for heat treating in air is straightforward. Introducing gas flow requires sealed flanges, flow meters, and gas lines. A high-vacuum system adds significant cost and complexity, demanding specialized pumps, gauges, and vacuum-compatible components.
Temperature Uniformity vs. Furnace Design
A standard furnace has a "uniform hot zone" in the center of its heated length. For applications requiring a longer, more precise uniform zone, you may need a furnace with a longer heated section or a multi-zone furnace with multiple independent controllers, which increases cost and complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application dictates the necessary components. By defining your primary objective, you can identify the right configuration.
- If your primary focus is basic heat treatment or calcination in air: A simple, single-zone furnace with a suitable alumina or quartz tube will be effective and economical.
- If your primary focus is material synthesis under an inert gas: You must select a system that includes vacuum-sealed flanges and a gas flow control package.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing or thin-film growth: A dedicated high-vacuum system with the appropriate pumps and compatible tube materials is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is growing crystals or annealing long parts: A multi-zone furnace is essential for creating the precise and extended temperature uniformity your process requires.
Ultimately, understanding these core components empowers you to select an instrument that is not just a furnace, but a precise tool tailored to your specific scientific or industrial goal.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function | Common Materials/Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace Tube | Holds sample, defines thermal environment | Quartz (up to 1200°C), Alumina (up to 1700°C+) |
| Heating Elements | Generate heat via electrical energy | Resistance wire (Kanthal), SiC rods, MoSi2 rods |
| Insulation Layer | Minimizes heat loss, ensures safety | Ceramic fiber, refractory brick |
| Temperature Control System | Manages temperature precisely | Thermocouple, PID controller, touchscreen interface |
| Atmosphere Control System | Modifies internal environment | Gas flow systems, vacuum pumps |
| Cooling System | Enables rapid cooling | Forced air, water-cooling jackets |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a tailored 70mm tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering superior performance and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific thermal processing goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















