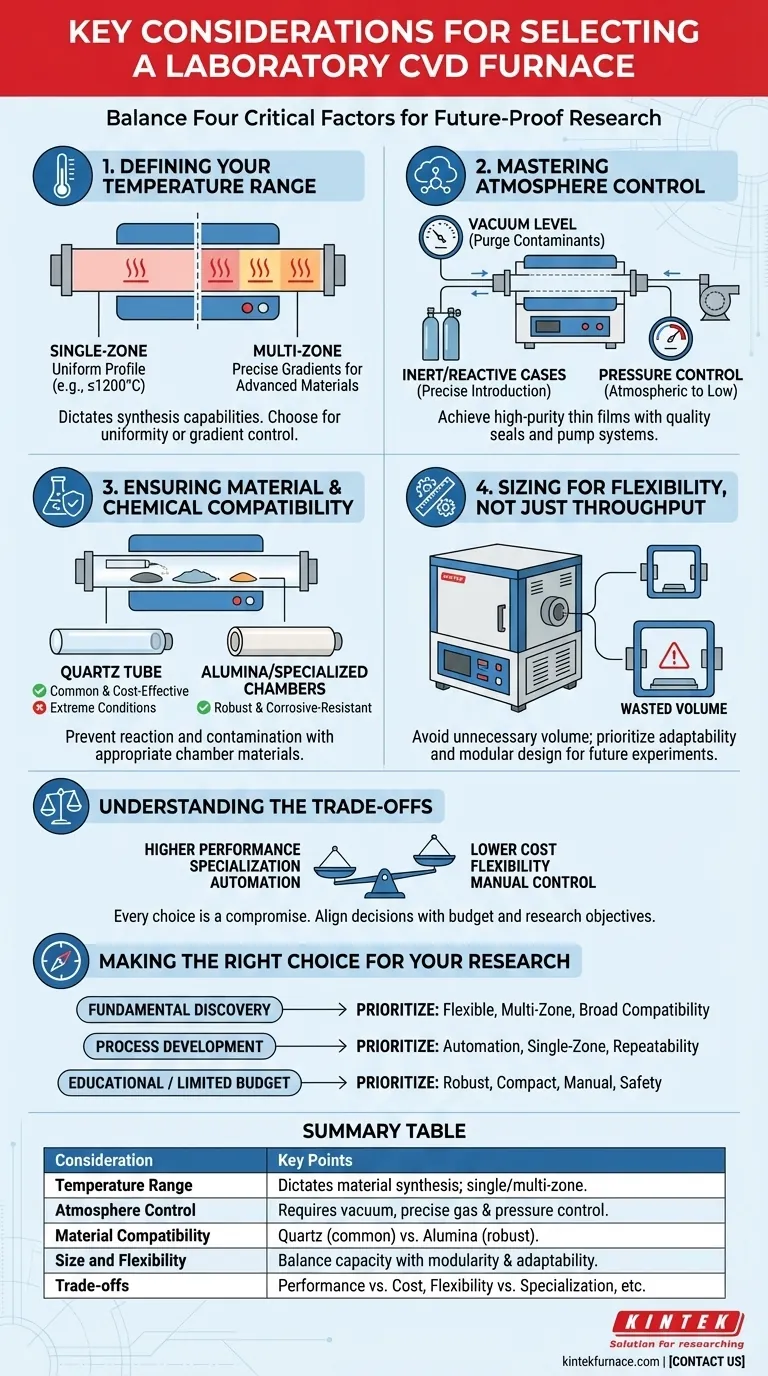
When selecting a CVD furnace for laboratory use, your decision must balance four critical factors: the required processing temperature, the necessary atmosphere control, the chemical compatibility of the furnace materials, and the physical size and flexibility of the system. Unlike industrial systems focused on throughput, a lab furnace must be an adaptable tool that can accommodate a wide range of future experiments.
The core challenge in choosing a lab-based CVD furnace is not just meeting today's experimental needs, but investing in a versatile platform that can answer tomorrow's research questions. The best choice prioritizes experimental flexibility and precise control over raw production volume.

Deconstructing Your Research Needs
The first step is to translate your research goals into specific technical requirements. A furnace is a long-term investment, so consider not only your current projects but also the potential future directions of your work.
Defining Your Temperature Range
The maximum temperature dictates the types of materials you can synthesize. Most lab-scale CVD for common materials occurs below 1200°C, but certain advanced materials may require significantly higher temperatures.
A critical decision is the number of heating zones. A single-zone furnace is simpler and more cost-effective, providing one uniform temperature profile. A multi-zone furnace offers independent control over several sections, allowing you to create precise temperature gradients along the tube, which is essential for certain advanced deposition processes.
Mastering Atmosphere Control
CVD processes are defined by their atmosphere. Your furnace must be able to create and maintain the specific environment your chemistry requires.
This includes the ability to achieve a certain vacuum level to purge contaminants, introduce various inert or reactive gases with precision, and operate at atmospheric or low pressure. The quality of the seals and the vacuum pump system are paramount for achieving high-purity thin films.
Ensuring Material & Chemical Compatibility
The furnace chamber, typically a quartz tube, will be exposed to high temperatures and corrosive chemical precursors. You must ensure the furnace materials will not react with your chemicals or contaminate your process.
Quartz tubes are common and cost-effective for many processes but can be unsuitable for certain chemistries or extreme temperatures. In those cases, more robust materials like alumina or even specialized chambers may be necessary.
Sizing for Flexibility, Not Just Throughput
In a research environment, adaptability is more valuable than scale. The furnace's physical design should support, not hinder, the experimental process.
Chamber Size and Substrate Capacity
The furnace's tube diameter and heated length determine the maximum size of your substrate. However, bigger is not always better in a lab.
A larger chamber requires more gas flow to achieve the same process conditions and takes longer to heat and cool. Choose a size that accommodates your largest planned substrate but avoids unnecessary volume that wastes energy and precursor materials.
The Value of Modular and Compact Design
Laboratory space is always at a premium. A compact furnace is easier to integrate into a crowded lab.
Furthermore, a modular design allows for greater flexibility. The ability to easily swap process tubes, reconfigure gas lines, or integrate new analytical tools makes the system far more powerful as a research platform.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Every design choice involves a compromise. Being aware of these trade-offs is key to making an informed decision that aligns with your budget and research objectives.
Performance vs. Cost
Higher performance specifications directly translate to higher costs. A furnace capable of reaching 1700°C will be substantially more expensive than a 1200°C model. Likewise, multi-zone control, high-vacuum capabilities, and advanced gas handling systems all add to the price.
Flexibility vs. Specialization
A highly flexible, modular system can be adapted for a wide variety of experiments. However, a furnace designed for a very specific process may offer superior performance and repeatability for that single task. You must decide if your lab needs a versatile workhorse or a specialized thoroughbred.
Automation vs. Manual Control
Fully automated systems with programmable recipes offer excellent repeatability, which is crucial for process development. However, they can be less intuitive for rapid, exploratory experiments where parameters are changed on the fly. Manual controls often provide more direct and immediate feedback for fundamental research.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
Ultimately, the ideal furnace is the one that best empowers your specific research goals. Use your primary objective as a guide to prioritize features.
- If your primary focus is fundamental materials discovery: Prioritize a flexible, multi-zone furnace with broad material compatibility and excellent atmosphere control to explore new chemistries.
- If your primary focus is process development for a specific material: Prioritize automation for repeatability, uniform single-zone heating, and precise gas flow and pressure control.
- If you are working with a limited budget in an educational setting: Focus on a robust, compact, single-zone furnace with reliable safety features and clear manual controls to teach core CVD principles effectively.
Choosing the right furnace is a strategic decision that will define the capabilities of your lab for years to come.
Summary Table:
| Consideration | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Dictates material synthesis; single-zone for uniform heating, multi-zone for gradients |
| Atmosphere Control | Requires vacuum levels, inert/reactive gases, and precise seals for purity |
| Material Compatibility | Quartz tubes for cost-effectiveness, alumina for robustness against corrosion |
| Size and Flexibility | Chamber size affects substrate capacity; modular designs enhance adaptability |
| Trade-offs | Balance performance vs. cost, flexibility vs. specialization, automation vs. manual control |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with a tailored CVD furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, empowering your research with flexibility, precision, and reliability. Don't settle for a one-size-fits-all solution—contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific goals and drive innovation in your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis
- Which industries and research fields benefit from CVD tube furnace sintering systems for 2D materials? Unlock Next-Gen Tech Innovations
- Why are CVD tube furnace sintering systems indispensable for 2D material research and production? Unlock Atomic-Scale Precision
- Where is a CVD Tube Furnace commonly used? Essential for High-Tech Materials and Electronics



















