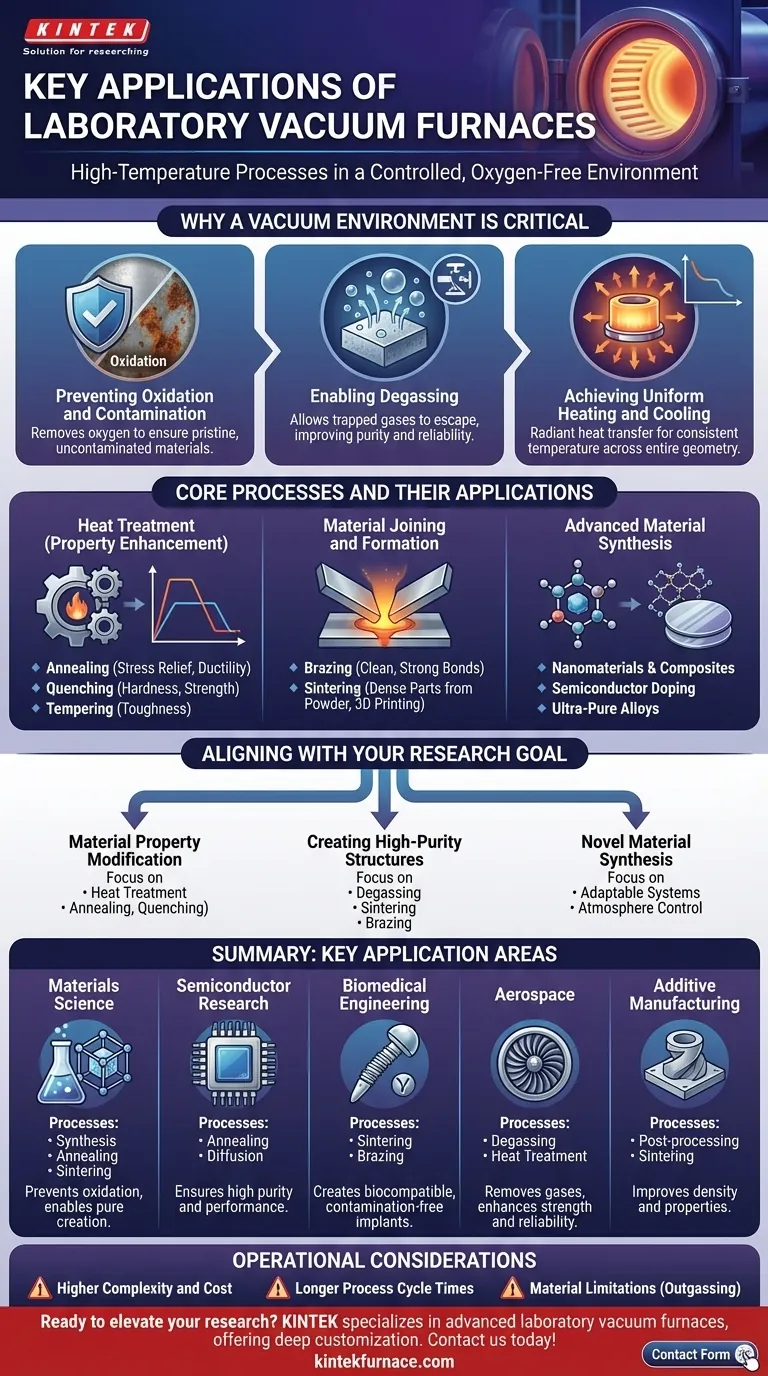
In a laboratory, vacuum furnaces are used for a wide range of high-temperature processes where atmospheric contamination must be eliminated. Their key applications span materials science for synthesizing advanced ceramics and alloys, semiconductor research for annealing wafers, biomedical engineering for creating pure medical implants, and post-processing 3D-printed metal parts for the aerospace industry.
The essential value of a laboratory vacuum furnace is not just its ability to generate heat, but its power to create a highly controlled, oxygen-free environment. This prevents unwanted chemical reactions, removes trapped impurities, and unlocks material properties that are impossible to achieve in open air.
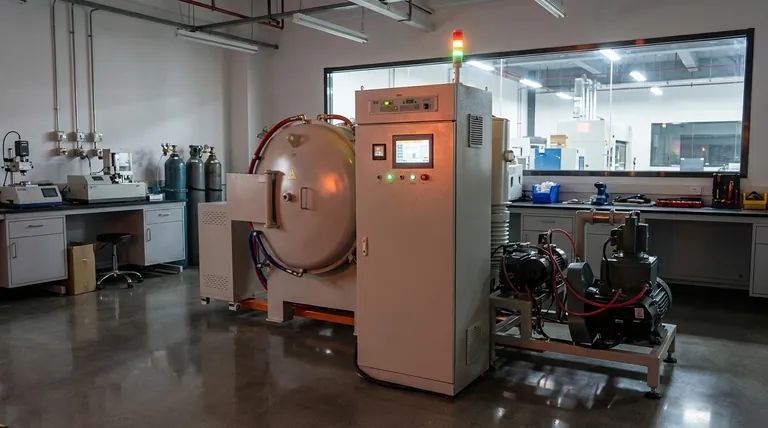

Why a Vacuum Environment is Critical
A vacuum furnace is fundamentally a tool for environmental control. By removing air and other gases, it provides a stable and pure workspace for thermally processing sensitive materials.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
The most immediate benefit of a vacuum is the removal of oxygen. At high temperatures, oxygen aggressively reacts with most materials, leading to oxidation (like rust on iron) that degrades their structural, electrical, or chemical properties.
A vacuum environment eliminates this threat, ensuring the material's surface and internal structure remain pristine and uncontaminated during processing.
Enabling Degassing
Many materials contain trapped or dissolved gases, such as hydrogen or water vapor, which can create voids or cause brittleness. Heating a material under vacuum allows these trapped gases to escape in a process known as degassing.
This is critical in applications like aerospace and electronics, where material purity directly impacts performance and reliability.
Achieving Uniform Heating and Cooling
Without air molecules to cause convection currents, heat transfer in a vacuum is primarily driven by radiation. This allows for exceptionally uniform heating, ensuring a component reaches the target temperature evenly across its entire geometry.
This same principle allows for highly controlled cooling rates, which is essential for processes like quenching and tempering.
Core Processes and Their Applications
The controlled environment of a vacuum furnace enables several distinct thermal processes that are foundational to modern materials research and production.
Heat Treatment for Property Enhancement
Heat treatment involves carefully controlled heating and cooling cycles to alter a material's microstructure and, therefore, its physical properties.
- Annealing: This process involves heating a material and then cooling it slowly to relieve internal stresses, soften it, and improve its ductility.
- Quenching: The opposite of slow cooling, quenching involves rapidly cooling a material from a high temperature to lock in a specific crystalline structure, typically to increase its hardness and strength.
- Tempering: Often performed after quenching, tempering is a lower-temperature heating process used to reduce brittleness and improve the toughness of hardened materials.
Material Joining and Formation
Vacuum furnaces are ideal for creating and joining high-performance components without compromising the base materials.
- Brazing: This process joins two or more metal items by melting a filler metal into the joint. Performing this in a vacuum prevents oxidation, resulting in a clean, strong, and void-free bond that is often as strong as the parent material.
- Sintering: Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat, without melting it to the point of liquefaction. It is used to create dense ceramic parts, biocompatible implants, and components from powdered metals, including those made via additive manufacturing.
Advanced Material Synthesis and Processing
The precision of laboratory vacuum furnaces makes them essential for cutting-edge research and development.
This includes the synthesis of novel nanomaterials and composites, controlled diffusion of dopants into semiconductors, and the creation of ultra-pure alloys for next-generation electronics and turbines.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces present certain operational considerations that differ from conventional atmospheric furnaces.
Higher Complexity and Cost
Vacuum systems, including pumps, seals, and control instrumentation, add significant complexity and cost to a furnace setup. They require specialized knowledge for proper operation and maintenance.
Longer Process Cycle Times
Achieving a deep vacuum takes time. The pump-down phase before heating and the potential need for slow, controlled backfilling or cooling after the cycle mean that total process times are often longer than in an atmospheric furnace.
Material Limitations
Some materials are not suitable for high-vacuum processing. Materials with high vapor pressures can outgas excessively or even sublimate (turn directly from a solid to a gas), potentially contaminating the furnace and the workpiece itself.
Aligning the Furnace with Your Research Goal
Choosing to use a vacuum furnace depends entirely on the material properties you need to achieve. The process you select must align with your end goal.
- If your primary focus is material property modification: You need precise control over temperature profiles and cooling rates for processes like vacuum annealing and quenching.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity structures: Your main concern is achieving a deep vacuum for effective degassing and contamination-free sintering or brazing.
- If your primary focus is novel material synthesis: You need an adaptable system that can handle precise temperature ramps and potentially accommodate different inert gas atmospheres for developing new alloys, composites, or ceramics.
Ultimately, a laboratory vacuum furnace is a gateway to manipulating matter at a fundamental level, enabling the creation of materials engineered for ultimate performance.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Processes | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Materials Science | Synthesis, Annealing, Sintering | Prevents oxidation, enables pure material creation |
| Semiconductor Research | Annealing, Diffusion | Ensures high purity and performance for wafers |
| Biomedical Engineering | Sintering, Brazing | Creates biocompatible, contamination-free implants |
| Aerospace | Degassing, Heat Treatment | Removes gases, enhances strength and reliability |
| Additive Manufacturing | Post-processing, Sintering | Improves density and properties of 3D-printed parts |
Ready to elevate your research with precise, high-temperature solutions? KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory vacuum furnaces, offering Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With our strong R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs—ensuring purity, performance, and innovation in materials science, semiconductors, and beyond. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?



















