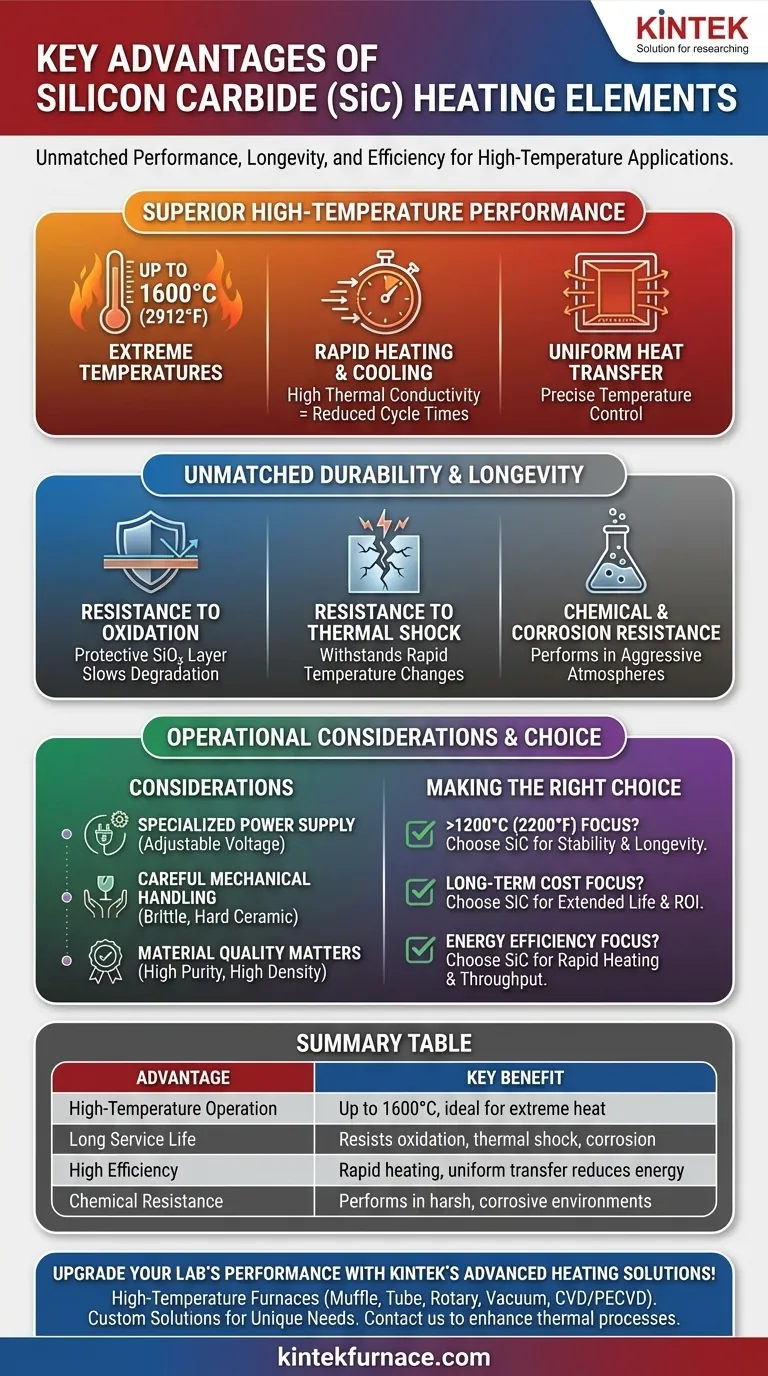
In short, the primary advantages of Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements are their ability to operate at extremely high temperatures, their long service life, and their high efficiency. Compared to traditional metallic elements, they offer superior resistance to oxidation, thermal shock, and chemical corrosion, making them the standard for demanding industrial heating applications.
The core reason to choose Silicon Carbide is for its unmatched performance in harsh, high-temperature environments. While other elements may suffice for lower temperatures, SiC delivers reliability, longevity, and efficiency where metallic elements would quickly fail.

Superior High-Temperature Performance
Silicon Carbide elements are engineered specifically for environments where extreme heat is a constant requirement. This capability fundamentally separates them from conventional heating solutions.
Reaching Extreme Temperatures
SiC elements can operate reliably at furnace temperatures up to 1600°C (2912°F). This is significantly higher than the operational ceiling of most traditional metal heating elements, opening up a range of high-temperature industrial processes.
Rapid Heating and Cooling
A key property of SiC is its high thermal conductivity. This allows the elements to transfer heat efficiently and heat up very quickly, which reduces cycle times and improves overall energy efficiency. This is critical in industries where energy costs are a major operational factor.
Uniform Heat Transfer
The excellent thermal conductivity also ensures that heat is distributed evenly throughout the furnace chamber. This uniformity is essential for processes requiring precise temperature control, such as in heat treatment, ceramics firing, and semiconductor manufacturing.
Unmatched Durability and Longevity
The material properties of Silicon Carbide directly contribute to a longer and more reliable operational life, even under constant stress.
Resistance to Oxidation
When heated in an oxygen-containing atmosphere, SiC develops a protective surface layer of silicon dioxide (SiO₂). This film effectively shields the underlying material from further oxidation, dramatically slowing degradation and extending the element's service life.
Resistance to Thermal Shock
SiC's physical structure gives it excellent resistance to thermal shock. It can withstand rapid heating and cooling cycles without cracking or failing, a crucial advantage in batch processing or cyclical furnace operations.
Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
The inherent stability of Silicon Carbide makes it highly resistant to chemical attack and corrosion. This allows it to perform reliably in processes involving aggressive chemical atmospheres where other elements would quickly degrade.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Requirements
While highly advantageous, SiC elements are not a universal drop-in replacement. Their unique properties necessitate specific operational considerations.
Specialized Power Supply
The electrical resistance of SiC elements increases gradually over their service life due to aging. To maintain consistent power output and temperature, they require a properly designed power supply (often using thyristors or transformers) that can adjust the voltage accordingly.
Mechanical Handling
SiC is a hard ceramic material with a MOH'S hardness over 9. While this contributes to its durability, it also means the elements are more brittle than ductile metallic alloys. Careful handling during installation and maintenance is required to prevent fracture.
Material Quality Matters
The performance of an SiC element is directly tied to its manufacturing quality. Elements made from high-purity green silicon carbide powder and extruded to a high density exhibit the best uniformity, strength, and antioxidant properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating element requires balancing performance needs with operational realities.
- If your primary focus is operating above 1200°C (2200°F): Silicon Carbide is the superior choice for its thermal stability and longevity in extreme heat.
- If your primary focus is long-term cost of ownership in a harsh environment: The extended service life and lower replacement frequency of SiC elements often provide a better return on investment despite a higher initial cost.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and process throughput: SiC's rapid heating capabilities can significantly reduce energy consumption and shorten cycle times.
Ultimately, choosing Silicon Carbide is an investment in reliability and performance for your most demanding thermal processes.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| High-Temperature Operation | Up to 1600°C, ideal for extreme heat processes |
| Long Service Life | Resists oxidation, thermal shock, and corrosion for durability |
| High Efficiency | Rapid heating and uniform heat transfer reduce energy use |
| Chemical Resistance | Performs well in harsh, corrosive environments |
Upgrade your lab's performance with KINTEK's advanced heating solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, delivering reliability, efficiency, and longevity in demanding environments. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your thermal processes and reduce operational costs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance



















