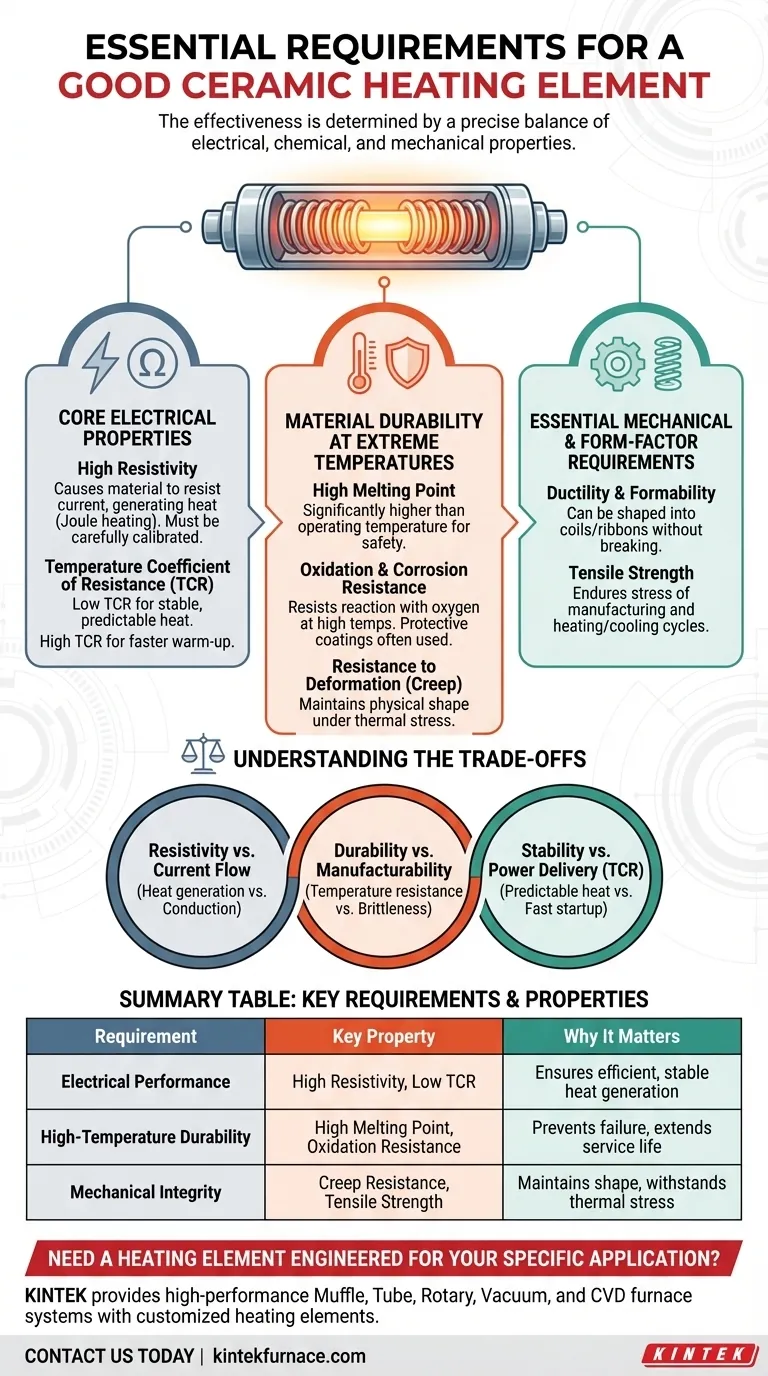
The effectiveness of a ceramic heating element is determined by a precise balance of electrical, chemical, and mechanical properties. A superior element must possess high electrical resistance to generate heat efficiently, a high melting point to withstand extreme temperatures, and excellent resistance to oxidation to ensure a long operational lifespan. Furthermore, it requires physical durability to be formed into specific shapes and to resist deformation under constant thermal stress.
The core challenge in designing a ceramic heating element is not simply making something hot, but creating a component that produces heat predictably, efficiently, and reliably over thousands of hours. This requires a material that can endure constant electrical and thermal abuse without degrading.

Core Electrical Properties for Efficient Heating
The primary function of a heating element is to convert electrical energy into thermal energy. This conversion hinges on a few fundamental electrical characteristics.
The Principle of High Resistivity
An effective heating element must have high electrical resistivity. This property causes the material to resist the flow of electrical current, generating heat in the process (known as Joule heating).
However, the resistivity must be carefully calibrated. If it's too high, the material becomes an electrical insulator, preventing sufficient current from flowing to generate the required heat.
Temperature Coefficient of Resistance (TCR)
The Temperature Coefficient of Resistance (TCR) describes how much a material's resistance changes as its temperature changes.
For most applications, a low TCR is ideal. This ensures that the heat output remains stable and predictable even as the element heats up to its operating temperature.
In some specific designs, a high and predictable TCR can be used to deliver more power during the initial warm-up phase.
Material Durability at Extreme Temperatures
A heating element's value is directly tied to its ability to survive its harsh operating environment. High temperatures introduce significant material science challenges that must be overcome.
High Melting Point
This is a non-negotiable requirement. The material's melting point must be significantly higher than its maximum operating temperature to provide a safe margin and prevent catastrophic failure.
Oxidation and Corrosion Resistance
At high temperatures, materials react more readily with oxygen in the air, a process called oxidation. This can degrade the element's structure, reduce its efficiency, and lead to premature failure.
Good heating elements are made from materials inherently resistant to oxidation or are treated with protective coatings, such as silicon oxide or aluminum oxide.
Resistance to Deformation (Creep Resistance)
Materials can slowly deform or "creep" over time when subjected to stress at high temperatures. A quality heating element must maintain its physical shape and structural integrity throughout its service life to function correctly and safely.
Essential Mechanical and Form-Factor Requirements
Beyond its intrinsic material properties, a heating element must be able to be manufactured into a usable form and withstand the physical stresses of its application.
Ductility and Formability
Ductility is the ability of a material to be stretched or drawn into a wire or other shape without breaking. This property is critical for manufacturing elements into common forms like coils and ribbons without compromising their efficiency or strength.
Tensile Strength
The material must possess sufficient tensile strength to endure the stresses of manufacturing and handling. It also needs to withstand the expansion and contraction that occurs during repeated heating and cooling cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a material for a heating element involves balancing competing properties. Understanding these compromises is key to choosing the right component for a specific task.
Resistivity vs. Current Flow
The central trade-off is balancing high resistivity for heat generation against the need for sufficient current flow. The perfect material is a "poor conductor," not a true insulator.
Durability vs. Manufacturability
Often, the materials with the highest temperature resistance and strength are also the most brittle. This creates a conflict between operational durability and the ease of forming the material into a complex shape.
Stability vs. Power Delivery (TCR)
While a low TCR provides predictable, stable heat, it offers a flat power curve. A controlled, high TCR element is less stable but can be engineered for specialized applications requiring a burst of heat during startup.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The "best" heating element is the one whose properties are optimized for its intended purpose. Consider the primary goal of your system to guide your selection.
- If your primary focus is stable, long-term operation: Prioritize materials with a low temperature coefficient of resistance and superior oxidation resistance.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures: The material's melting point and its ability to resist physical deformation (creep) are the most critical factors.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing complex element shapes: Emphasize high ductility and tensile strength to ensure the element can be reliably formed.
Ultimately, an effective heating element is an engineered system where material science and physical design work in concert to deliver reliable heat.
Summary Table:
| Requirement | Key Property | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Performance | High Resistivity, Low TCR | Ensures efficient, stable heat generation |
| High-Temperature Durability | High Melting Point, Oxidation Resistance | Prevents failure and extends service life |
| Mechanical Integrity | Creep Resistance, Tensile Strength | Maintains shape and withstands thermal stress |
Need a heating element engineered for your specific application?
At KINTEK, we understand that the right balance of electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties is critical. Our expert R&D and manufacturing team designs and produces high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD furnace systems, with heating elements customized for your unique temperature, stability, and durability requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how we can provide a reliable heating solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability



















