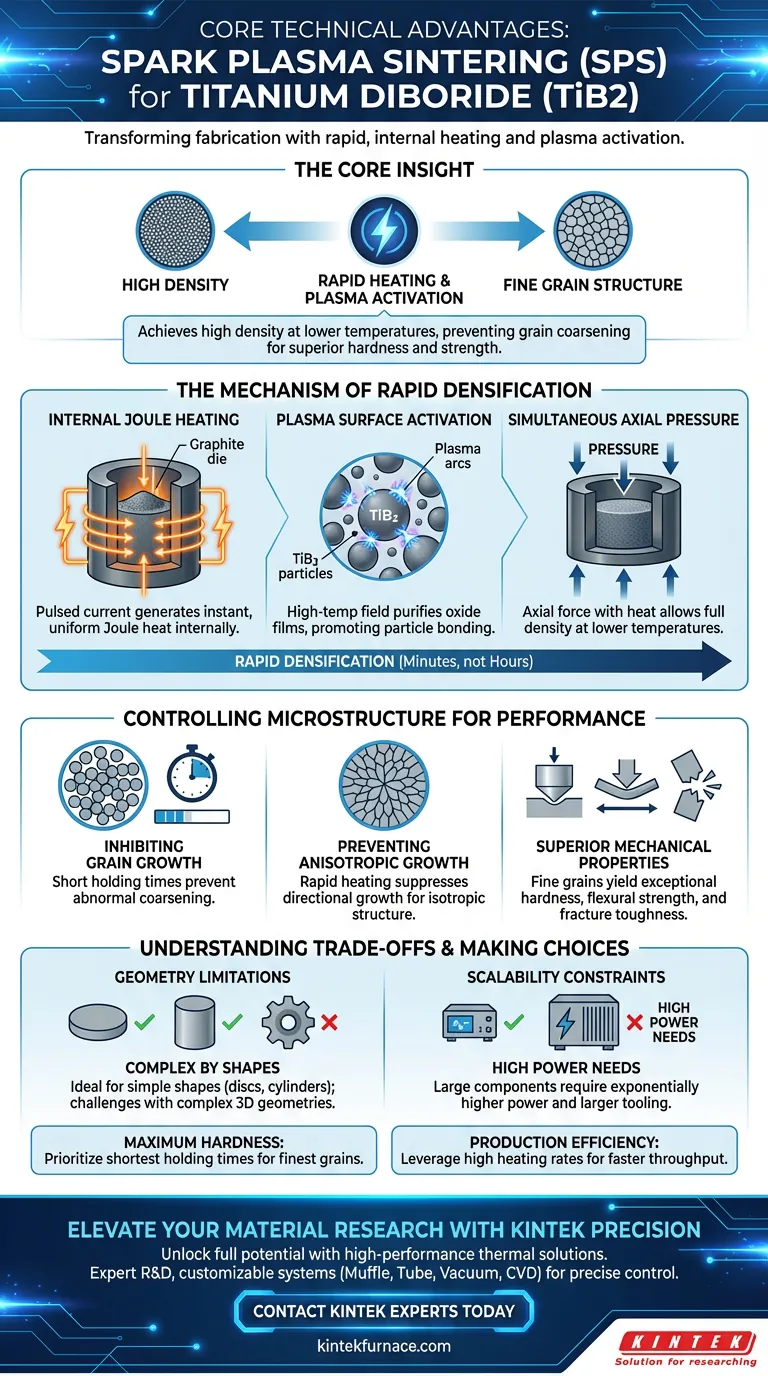
Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) fundamentally transforms the fabrication of Titanium Diboride by utilizing pulsed electric currents to generate internal heat directly within the graphite mold and the sample itself. This mechanism facilitates heating rates of several hundred degrees per minute, allowing for the purification of powder surfaces and complete densification of the material in a matter of minutes rather than hours.
The Core Insight SPS solves the primary challenge of sintering Titanium Diboride: balancing density with grain structure. By utilizing rapid heating and plasma activation, SPS achieves high density at lower temperatures without allowing the grain structure to coarsen, resulting in superior hardness and mechanical strength compared to traditional hot pressing.

The Mechanism of Rapid Densification
Internal Joule Heating
Unlike traditional furnaces that rely on external heating elements, SPS passes high-current pulses directly through the graphite mold and the ceramic powder.
This generates Joule heat internally, ensuring that energy is delivered instantly and uniformly to the material.
Plasma Surface Activation
The high-temperature field created by the pulsed current provides a critical chemical advantage: it purifies the oxide film on the powder surfaces.
This "plasma activation" cleans the grain boundaries, which promotes better particle bonding and accelerates the densification process.
Simultaneous Axial Pressure
While the current heats the material, the system applies synchronized axial pressure.
This combination of thermal and mechanical energy allows the material to reach full density at significantly lower temperatures than conventional methods require.
Controlling Microstructure for Performance
Inhibiting Grain Growth
The defining technical advantage of SPS is the speed of processing. Because the holding times are extremely short, the material is not exposed to high heat long enough for grains to merge and grow larger.
This significantly inhibits the abnormal coarsening of Titanium Diboride grains, preserving a fine microstructure.
Preventing Anisotropic Growth
Titanium Diboride has a tendency toward anisotropic growth (growing in specific directions) during long heating cycles.
The rapid heating rates of SPS suppress this behavior, ensuring a more uniform and isotropic grain structure.
Superior Mechanical Properties
The preservation of fine grains directly translates to mechanical performance.
Because the microstructure remains fine and dense, the final component exhibits exceptional hardness, improved flexural strength, and higher fracture toughness.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Geometry Limitations
SPS typically utilizes uniaxial pressure within a graphite die.
This makes the process ideal for simple shapes like discs or cylinders, but it presents significant challenges for fabricating complex, non-symmetrical 3D geometries.
Scalability Constraints
The necessity of passing high current through the mold creates size limitations.
Fabricating very large components requires exponentially higher power supplies and larger tooling, making scaling more difficult compared to pressureless sintering.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the value of Spark Plasma Sintering for your specific application, consider these strategic priorities:
- If your primary focus is Maximum Hardness: Prioritize the shortest possible holding times to maintain the finest possible grain size, as this is the primary driver of mechanical strength.
- If your primary focus is Production Efficiency: Leverage the high heating rates to reduce total cycle times to minutes, significantly increasing throughput compared to hot pressing.
SPS is not just a faster heater; it is a microstructural control tool that allows you to bypass the traditional compromise between processing speed and material quality.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Technical Advantage | Performance Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Joule Heating | Direct pulsed current through mold/sample | Rapid densification in minutes, not hours |
| Plasma Activation | Purifies oxide film on powder surfaces | Enhanced particle bonding & grain boundary purity |
| Rapid Processing | Extremely short holding times | Inhibits grain coarsening for finer microstructure |
| Combined Energy | Simultaneous thermal and axial pressure | Achieves full density at significantly lower temperatures |
| Microstructure Control | Suppresses anisotropic growth | Exceptional hardness and improved fracture toughness |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Unlock the full potential of your ceramic fabrication with high-performance thermal solutions from KINTEK. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with other specialized lab high-temp furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique research or production requirements.
Whether you are refining Titanium Diboride composites or developing next-generation materials, our equipment delivers the precise control needed to bypass traditional processing compromises.
Ready to optimize your lab’s efficiency? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and find the ideal high-temperature system for your application.
Visual Guide
References
- Xinran Lv, Gang Yu. Review on the Development of Titanium Diboride Ceramics. DOI: 10.21926/rpm.2402009
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is electromagnetic stirring technology employed during the melting process of Titanium-Copper (Ti–Cu) alloys?
- What is the role of an industrial oven in the drying stage of Rosa roxburghii biochar? Unlock Structural Integrity
- What role do high-temp furnaces play in co-firing SOFCs? Master Ceramic Densification and Sintering
- How does a displacement measurement device ensure data validity? Mastering Iron Ore Softening Shrinkage Accuracy
- What is the purpose of using an industrial oven for flax fiber pretreatment? Ensure Superior Composite Integrity
- What is the function of an industrial drying oven in EFB fiber pretreatment? Optimize Biochar Yield & Quality
- What is the role of a laboratory drying oven in catalyst precursor control? Maximize Dispersion and Stability
- What role does a laboratory blast drying oven play in metal powder preparation? Ensure Purity & Prevent Oxidation



















