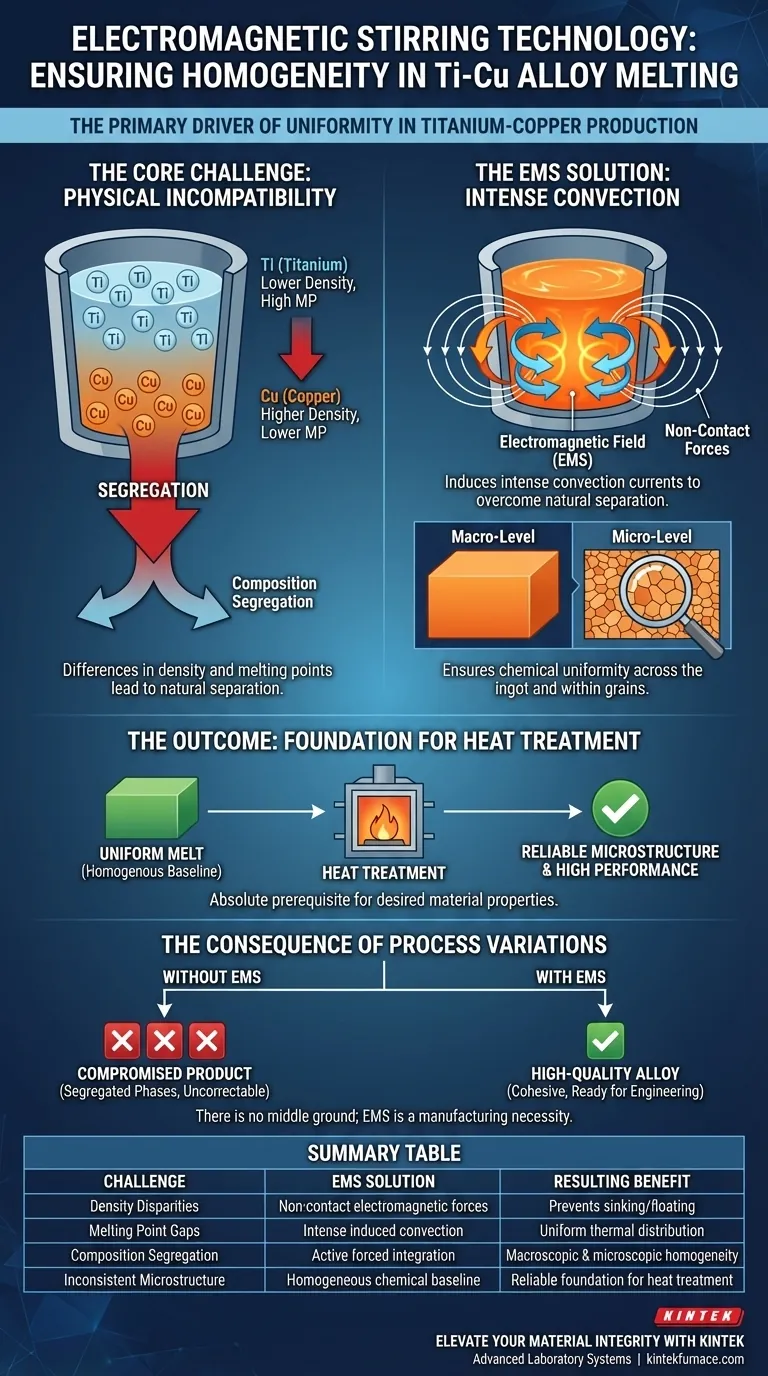
Electromagnetic stirring technology is the primary driver of homogeneity in the production of Titanium-Copper (Ti–Cu) alloys. It employs non-contact forces to generate intense convection within the melt pool, effectively neutralizing the natural segregation caused by the significant differences in density and melting points between the two metals. By ensuring chemical uniformity at both macroscopic and microscopic levels, this technology creates the essential foundation required for successful subsequent heat treatment processes.
Core Takeaway: Without electromagnetic stirring, the physical disparities between titanium and copper lead to severe composition segregation. The technology forces necessary convection to ensure a uniform chemical structure, which is the absolute prerequisite for achieving desired microstructures during later processing.

The Core Challenge: Physical Incompatibility
To understand the necessity of this technology, one must first understand the inherent difficulty in combining these specific elements.
Density and Melting Point Disparities
Titanium and copper possess fundamentally different physical characteristics. They have distinct densities and melting points that do not naturally align during the melting process.
The Risk of Composition Segregation
Left to a passive melting process, these physical differences cause the elements to separate. This phenomenon, known as composition segregation, results in an alloy where the two metals are not evenly distributed.
How Electromagnetic Stirring Solves the Problem
Electromagnetic stirring (EMS) moves beyond passive melting to actively force the integration of the alloy's components.
Generating Non-Contact Forces
The technology utilizes electromagnetic fields to apply force to the molten metal without physical contact. This eliminates the need for mechanical stirrers that could introduce contaminants or fail under high temperatures.
Inducing Intense Convection
These non-contact forces generate intense convection currents within the melt pool. This forced movement physically mixes the heavy and light elements, overcoming their natural tendency to separate.
The Outcome: Uniformity and Process Readiness
The ultimate goal of employing EMS is to prepare the material for the final stages of manufacturing.
Achieving Macroscopic and Microscopic Homogeneity
The convection ensures that the chemical composition is uniform across the entire ingot (macroscopic) and within the grain structure itself (microscopic). This eliminates weak spots or inconsistent areas within the alloy.
Foundation for Heat Treatment
A uniform melt is not the final step; it is a baseline. This chemical uniformity provides a consistent foundation for subsequent heat treatment. Without a homogenous mixture, heat treatment cannot produce the desired reliable microstructure.
The Consequence of Process Variations
While EMS is a powerful tool, it is important to understand the binary nature of its application in this context.
The Trade-off of Omission
There is no effective "middle ground" for mixing Ti–Cu alloys. Omitting intense convection results in a compromised product with segregated phases that no amount of post-processing or heat treatment can correct. The use of EMS is not merely an enhancement; it is a manufacturing necessity for this specific alloy combination.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When evaluating the production or specification of Ti–Cu alloys, understanding the role of the melting process is critical for quality assurance.
- If your primary focus is Material Integrity: Ensure the manufacturing process explicitly utilizes electromagnetic stirring to guarantee the elimination of composition segregation.
- If your primary focus is Downstream Processing: Recognize that the success of your heat treatment protocols is entirely dependent on the chemical uniformity achieved during the initial melt via induced convection.
Electromagnetic stirring transforms a physically incompatible mixture into a cohesive, high-performance alloy ready for advanced engineering applications.
Summary Table:
| Challenge in Ti–Cu Melting | EMS Solution | Resulting Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Density Disparities | Non-contact electromagnetic forces | Prevents element sinking/floating |
| Melting Point Gaps | Intense induced convection | Uniform thermal distribution |
| Composition Segregation | Active forced integration | Macroscopic & microscopic homogeneity |
| Inconsistent Microstructure | Homogeneous chemical baseline | Reliable foundation for heat treatment |
Elevate Your Material Integrity with KINTEK
Don't let composition segregation compromise your alloy performance. KINTEK’s advanced laboratory systems are designed to handle the most demanding material challenges. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, as well as specialized high-temp furnaces—all fully customizable to your unique research or production needs.
Whether you are refining Ti–Cu alloys or developing next-generation ceramics, our precision heating solutions ensure the uniformity your application demands. Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace requirements and see how we can optimize your thermal processing outcomes.
Visual Guide
References
- Daisy Rabbitt. Antimicrobial Titanium–Copper Alloys: The Role of Microstructure in Arc‐Melted Compositions. DOI: 10.1002/adem.202500347
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What role does an RTA system play in processing SiN thin films? Unlock High-Performance Quantum & Optical Materials
- What is the significance of the 200 °C calcination for Fe3O4/biochar? Enhancing Stability and Magnetic Recovery
- What hardware characteristics are required for a reactor system to support a three-step redox process in chemical looping?
- How do industrial furnaces and quenching tanks affect TiCp/Fe composites? Optimize Heat Treatment Performance
- Why is a laboratory vacuum oven utilized for ZnO-FL drying? Preserving Delicate Nanoparticle Morphologies
- What is the purpose of applying a hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN) coating to graphite? Enhance Purity & Tool Longevity
- Why is a high flow rate of synthetic air maintained during magnetite oxidation? Ensure Accurate Kinetic Modeling
- Why is high-temperature drying of NaCl particles necessary? Prevent Aluminum Foam Defects and Ensure Integrity



















