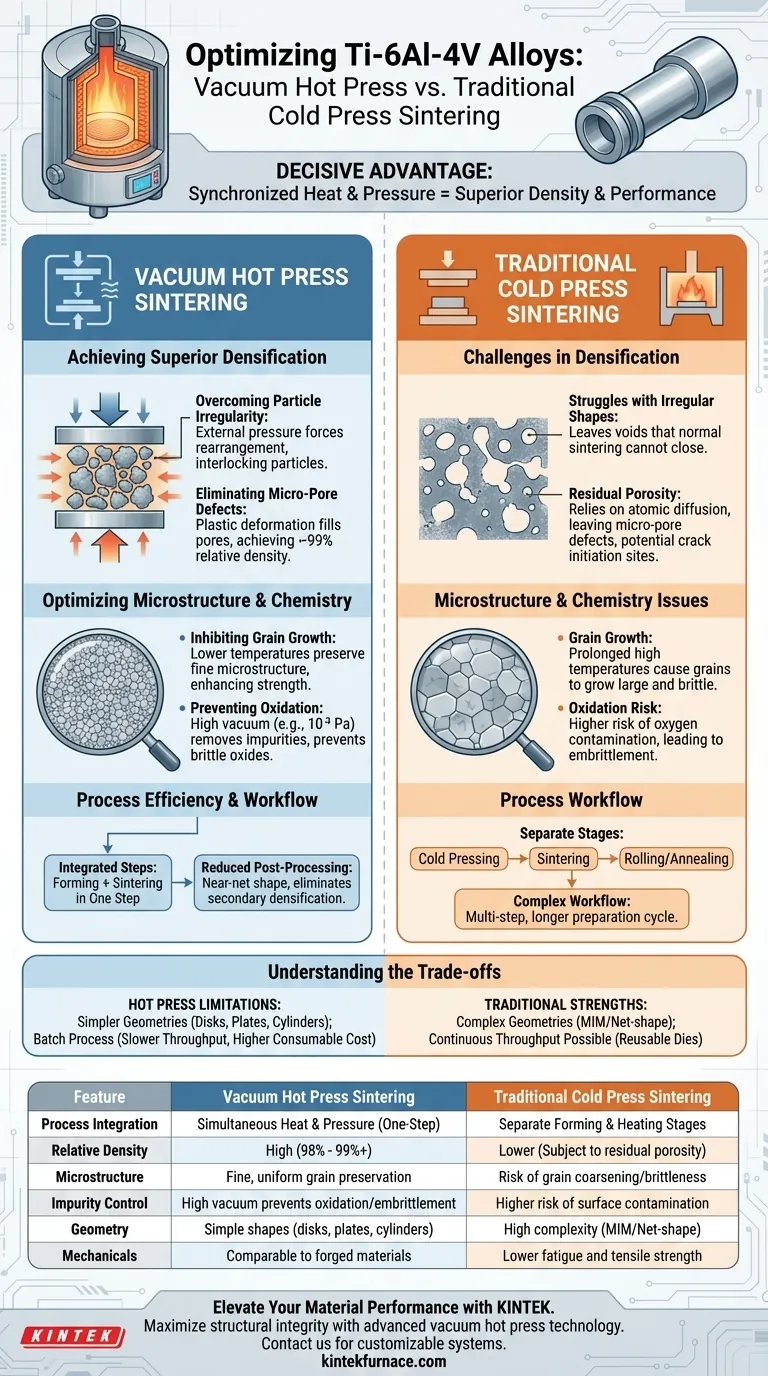
The decisive advantage of a vacuum hot press furnace is its ability to synchronize high-temperature thermal energy with mechanical pressure into a single operation. Unlike traditional cold press sintering—which separates the forming and heating stages—vacuum hot pressing applies force (e.g., 30 MPa) directly during the sintering phase. This enables the consolidation of difficult materials, such as irregular Hydrogenation-Dehydrogenation (HDH) titanium powders, achieving relative densities of 98% or higher and mechanical properties that rival forged materials.
By introducing mechanical pressure as a driving force alongside heat, vacuum hot pressing lowers the activation energy required for densification. This allows for near-perfect density at lower temperatures or shorter times, effectively preventing the grain coarsening that often degrades the strength of Ti-6Al-4V alloys in traditional processing.

Achieving Superior Densification
Overcoming Particle Irregularity
Standard cold pressing often struggles with irregular powder shapes, leaving voids that normal sintering cannot close.
The vacuum hot press overcomes this by applying external pressure that forces powder rearrangement. This effectively neutralizes surface tension issues and ensures particles physically interlock, regardless of their initial morphology.
Eliminating Micro-Pore Defects
In pressureless sintering, densification relies entirely on atomic diffusion, which can leave residual porosity.
Hot pressing utilizes plastic deformation to physically fill the pores between grains. This mechanism pushes the relative density to nearly 99%, eliminating the micro-pore defects that typically act as crack initiation sites in finished components.
Optimizing Microstructure and Chemistry
Inhibiting Grain Growth
Traditional sintering often requires prolonged exposure to peak temperatures to maximize density, which inadvertently causes grains to grow large and brittle.
Because hot pressing utilizes pressure to assist densification, the process requires significantly lower temperatures or shorter durations. This preserves a fine, uniform microstructure—and potentially nano-crystalline structures—which is critical for maintaining high ductility and strength in Ti-6Al-4V.
Preventing Oxidation and Embrittlement
Titanium and aluminum have an extremely high affinity for oxygen at elevated temperatures.
The high vacuum environment (e.g., 10⁻³ Pa) significantly reduces oxygen partial pressure. This facilitates the removal of adsorbed gases and volatile impurities from the powder surface, preventing the formation of brittle oxides and ensuring clean, metallic bonding at the grain boundaries.
Process Efficiency and Workflow
Integration of Steps
Traditional powder metallurgy often involves a complex sequence: cold pressing, sintering, rolling, and multi-step annealing.
Vacuum hot pressing integrates forming and sintering into one step. This consolidation significantly shortens the preparation cycle and simplifies the overall manufacturing workflow.
Reducing Post-Processing
By achieving near-net shape with high density immediately, the need for secondary densification processes (like Hot Isostatic Pressing or heavy rolling) is often reduced or eliminated.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Geometric Limitations
While hot pressing offers superior material properties, it is generally limited to simpler geometries (disks, plates, cylinders) compared to cold press/sinter or metal injection molding. The uniaxial pressure makes creating complex undercuts or internal features difficult without expensive, complex die designs.
Throughput and Cost
This is a batch process, often slower than the continuous throughput possible with belt furnaces used in traditional sintering. Additionally, the graphite dies used in hot pressing are consumables that degrade over time, adding to the operational cost compared to reusable steel dies used in cold pressing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if vacuum hot pressing is the correct solution for your Ti-6Al-4V application, evaluate your specific requirements:
- If your primary focus is Maximum Mechanical Performance: Choose vacuum hot pressing to achieve near-forged strength, high density (98%+), and fine grain structures that resist fatigue.
- If your primary focus is Complex Geometry: Stick to traditional cold press and sinter (or MIM), as hot pressing is constrained by the limitations of uniaxial die compaction.
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Rely on vacuum hot pressing to actively remove volatile impurities and prevent oxidation during the critical high-heat phases.
Vacuum hot pressing is not just a method of heating; it is a mechanical forcing function that guarantees structural integrity where traditional thermal diffusion fails.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Hot Press Sintering | Traditional Cold Press Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Process Integration | Simultaneous Heat & Pressure (One-Step) | Separate Forming & Heating Stages |
| Relative Density | High (98% - 99%+) | Lower (Subject to residual porosity) |
| Microstructure | Fine, uniform grain preservation | Risk of grain coarsening/brittleness |
| Impurity Control | High vacuum prevents oxidation/embrittlement | Higher risk of surface contamination |
| Geometry | Simple shapes (disks, plates, cylinders) | High complexity (MIM/Net-shape) |
| Mechanicals | Comparable to forged materials | Lower fatigue and tensile strength |
Elevate Your Material Performance with KINTEK
Maximize the structural integrity of your Ti-6Al-4V components by leveraging KINTEK’s advanced vacuum hot press technology. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-performance Vacuum, CVD, Muffle, Tube, and Rotary systems—all fully customizable to your specific metallurgical requirements.
Whether you need to eliminate micro-pore defects or preserve nano-crystalline structures, our engineering team is ready to deliver the precision you demand. Contact KINTEK today to optimize your lab's high-temperature processing.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the primary components of a vacuum hot press furnace? Master the Core Systems for Precise Material Processing
- How does the programmable pressure function of a vacuum hot press furnace influence the quality of IZO targets?
- How do temperature, pressure and holding time affect hot pressed product density? Optimize Your Process for Maximum Efficiency
- What is a vacuum forming machine used for? A Guide to Cost-Effective Plastic Shaping
- What are the available pressing force and temperature ranges for vacuum hot pressing? Optimize Your Material Processing
- What are the advantages of Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) systems? Superior High-Entropy Carbide Ceramic Fabrication
- How do pressure parameters in a vacuum hot press influence stainless steel? Master High-Performance Densification
- What are the advantages of benchtop SPS/FAST for titanium R&D? Accelerate Your Microstructural Engineering



















