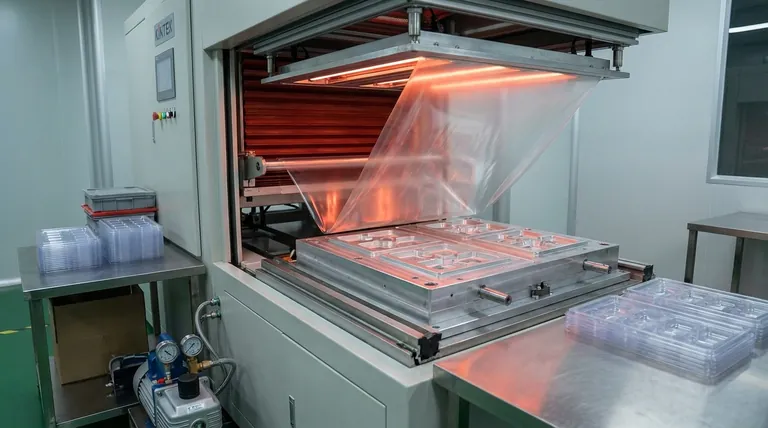
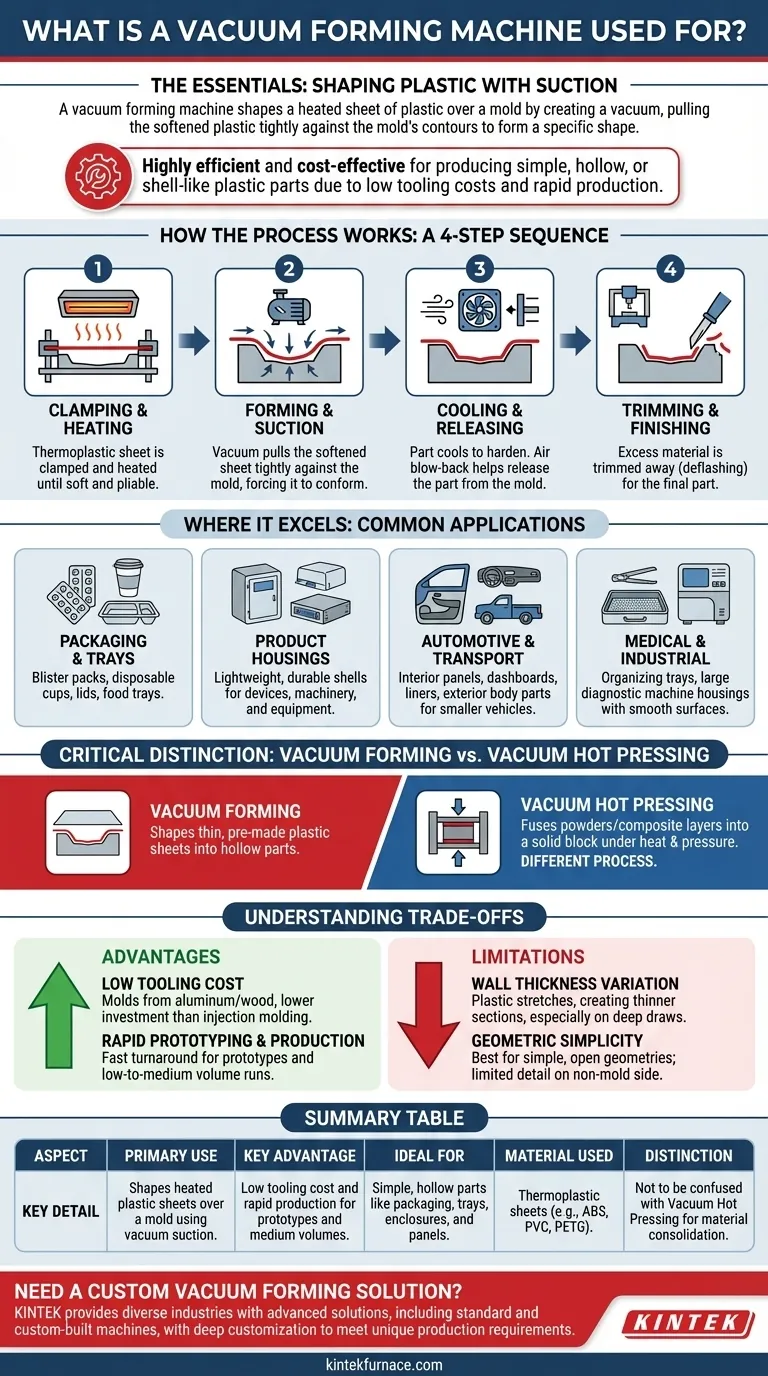
At its core, a vacuum forming machine is used to shape a heated sheet of plastic over a mold. By creating a vacuum, the machine pulls the softened plastic tightly against the mold's contours, forming a specific shape. This process is fundamental to manufacturing countless everyday items, from simple packaging to complex automotive parts.
Vacuum forming is a highly efficient and cost-effective method for producing simple, hollow, or shell-like plastic parts. Its value lies in its low tooling costs and rapid production cycle, especially when compared to more complex processes like injection molding.

How the Vacuum Forming Process Works
To understand its applications, you must first understand the core mechanics. The process is a straightforward sequence of heating, forming, and finishing.
Step 1: Clamping and Heating
A sheet of thermoplastic material is clamped into a frame. This sheet is then moved to a heating station where radiant heaters warm it until it becomes soft and pliable, reaching its specific forming temperature.
Step 2: Forming and Suction
The softened plastic sheet is lowered over or raised into a mold. A powerful vacuum pump is then activated, rapidly evacuating the air between the sheet and the mold. Atmospheric pressure pushes the pliable plastic down, forcing it to conform to the precise shape of the mold.
Step 3: Cooling and Releasing
Once the plastic has taken the mold's shape, it must be cooled to harden and become rigid. This is often accelerated with cooling fans or mist sprays. After cooling, air is blown back into the space to help release the part from the mold.
Step 4: Trimming and Finishing
The newly formed part is still attached to the original sheet of plastic. The final step involves trimming away this excess material, a process known as "deflashing." This can be done manually or with automated CNC routing for higher precision.
Where Vacuum Forming Excels: Common Applications
The unique characteristics of this process make it the ideal choice for a wide range of products, particularly those that function as covers, containers, or panels.
Packaging and Trays
This is the most visible application. Blister packs for electronics and pharmaceuticals, disposable cups and lids, and plastic trays for food are all classic examples of vacuum-formed products.
Product Housings and Enclosures
Vacuum forming is excellent for creating lightweight and durable shells. This includes enclosures for medical devices, covers for industrial machinery, and housings for electronic equipment where internal components are mounted separately.
Automotive and Transport Components
Many parts inside and outside a vehicle are vacuum formed. This includes interior door panels, dashboards, truck bed liners, and exterior body panels for smaller vehicles like golf carts or ATVs.
Medical and Industrial Equipment
The process is used to create trays for sterilizing and organizing surgical tools, as well as housings for large diagnostic machines. Its ability to produce smooth, easy-to-clean surfaces is a key advantage.
Critical Distinction: Vacuum Forming vs. Vacuum Hot Pressing
It is crucial not to confuse vacuum forming with other industrial processes that use vacuum, such as vacuum hot pressing. The reference materials mention this, and the distinction is significant.
- Vacuum Forming shapes thin, pre-made plastic sheets into hollow parts.
- Vacuum Hot Pressing fuses powders or composite layers into a solid, dense block under heat, pressure, and vacuum. It is used for making advanced materials like high-performance ceramics or composite billets, not for shaping thin sheets.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any manufacturing process, vacuum forming has clear advantages and limitations that define its ideal use cases.
Advantage: Low Tooling Cost
Molds for vacuum forming are typically made from aluminum or even wood and do not need to withstand high pressures. This makes the initial tooling investment significantly lower than for processes like injection molding, which require hardened steel molds.
Advantage: Rapid Prototyping and Production
The simplicity of the process and tooling allows for very fast turnaround times. This makes it an excellent choice for producing prototypes, testing designs, and fulfilling low-to-medium volume production runs.
Limitation: Wall Thickness Variation
As the plastic sheet stretches over the mold, it becomes thinner, especially on deep draws and sharp corners. The final part will not have a perfectly uniform wall thickness, which can be a constraint for structural applications.
Limitation: Geometric Simplicity
Vacuum forming is best suited for creating parts with open, simple geometries without undercuts or complex internal features. Only one side of the part makes contact with the mold, limiting the detail on the non-mold side.
Is Vacuum Forming Right for Your Project?
Your choice of manufacturing process should always align with your product's requirements and your business goals.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective prototyping or low-to-mid volume production: Vacuum forming is an ideal choice due to its low initial tooling costs and fast turnaround.
- If your project requires simple, hollow shapes like covers, trays, or enclosures: This technology is the industry standard and excels at producing these types of parts efficiently.
- If you need complex parts with uniform wall thickness or intricate internal features: You should investigate other processes, such as injection molding or rotational molding.
- If you are working with advanced raw materials like ceramic powders or carbon fiber layers: You are likely looking for vacuum hot pressing, a fundamentally different process for material consolidation.
Understanding these core principles allows you to select the right manufacturing process for your specific goal.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Shapes heated plastic sheets over a mold using vacuum suction. |
| Key Advantage | Low tooling cost and rapid production for prototypes and medium volumes. |
| Ideal For | Simple, hollow parts like packaging, trays, enclosures, and panels. |
| Material Used | Thermoplastic sheets (e.g., ABS, PVC, PETG). |
| Distinction | Not to be confused with Vacuum Hot Pressing for material consolidation. |
Need a Custom Vacuum Forming Solution?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse industries with advanced vacuum forming solutions. Our product line, including standard and custom-built machines, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique production requirements—whether for rapid prototyping or efficient medium-volume runs.
Let's shape your ideas into reality. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your plastic part manufacturing!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum press and why is it important in modern manufacturing? Unlock Flawless Bonding and Precision
- In which fields is hot pressing technology applied? Essential for Aerospace, Defense, and Advanced Manufacturing
- How does automation enhance the hot pressing process? Boost Precision, Efficiency, and Quality
- How does hot pressing work? Achieve Maximum Density and Strength for Advanced Materials
- What other types of furnaces are related to hot pressing? Explore Key Thermal Processing Technologies



















