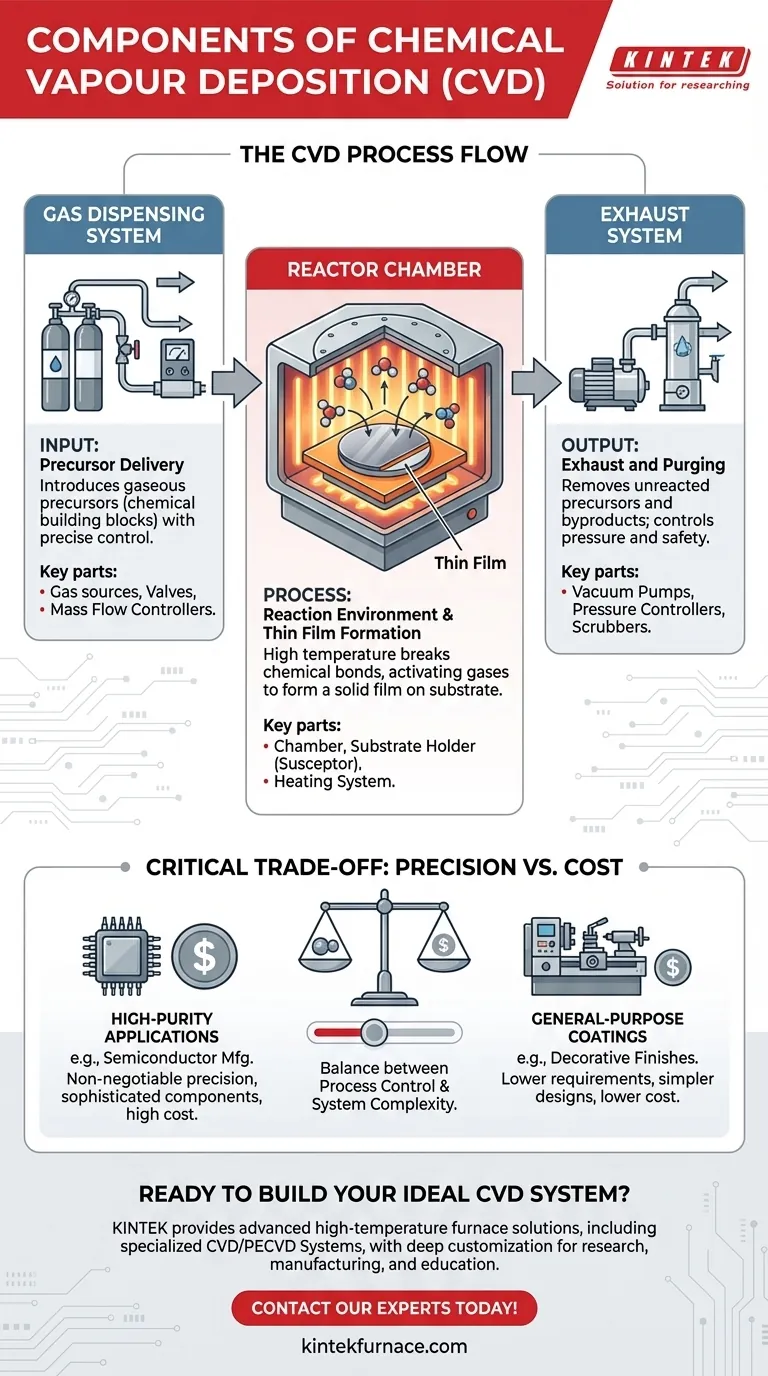
At its core, a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) system is comprised of three fundamental sections. These are a gas dispensing system to introduce reactant precursors, a reaction chamber where the film is grown on a substrate, and an exhaust system to remove byproducts and control pressure.
A CVD apparatus is best understood not as a list of parts, but as a highly controlled environment designed to manage a precise sequence of events: delivering reactive gases, inducing a chemical reaction to form a solid film, and safely exhausting the leftovers.

The CVD Process: How the Components Work Together
To truly understand the components, we must first look at the four critical steps of the CVD process. Each step is enabled by a specific part of the system.
Step 1: Precursor Delivery
The process begins with the gas dispensing system. This system introduces carefully measured amounts of gaseous precursors—the chemical building blocks of the final film—into the reaction chamber.
Think of this as the system's "supply chain." Its precision is paramount, as the ratio and flow rate of these gases directly dictate the composition and quality of the resulting thin film.
Step 2: The Reaction Environment
Next, the precursors enter the reactor chamber. This chamber houses the substrate (the material to be coated) and is heated to a specific, uniform temperature.
This high temperature provides the necessary energy to break the chemical bonds in the precursor gases, making them reactive and ready to form a solid.
Step 3: Thin Film Formation
Once activated by the heat, the precursor gases react on or near the hot substrate surface. This chemical reaction results in the formation of a solid, dense, and uniform thin film on the substrate.
The unreacted gas molecules and chemical byproducts from the reaction remain in the chamber as vapor.
Step 4: Exhaust and Purging
Finally, the exhaust system removes the unreacted precursors and gaseous byproducts from the chamber. This is a critical step for both safety and process control.
This system typically includes vacuum pumps to maintain low pressure, scrubbers to neutralize hazardous gases before they are released, and controllers to ensure the entire process occurs under stable conditions.
Understanding the Core Components
Based on the process, we can group the hardware into three essential subsystems.
The Gas Dispensing System
This is the input module of the CVD reactor. It consists of gas sources, valves, and mass flow controllers that ensure a stable and repeatable flow of reactants into the chamber.
The Reactor Chamber
This is the heart of the system where the deposition occurs. Key components include the chamber itself, the substrate holder (or susceptor), and a powerful heating system (e.g., resistive or induction heaters) to achieve the high temperatures required.
The Exhaust System
This is the output and safety module. It includes a pressure controller, vacuum pumps to create the necessary low-pressure environment, and a scrubber or abatement system to treat hazardous exhaust gases.
The Critical Trade-off: Precision vs. Cost
The primary trade-off in any CVD system is between the level of process control and the overall system cost and complexity.
High-Purity Applications
For applications like semiconductor manufacturing, absolute precision is non-negotiable. This requires highly sophisticated mass flow controllers, ultra-uniform heating systems, and advanced, multi-stage exhaust treatment. These systems are extremely expensive.
General-Purpose Coatings
For applications like coating machine tools or decorative finishes, the requirements for uniformity and purity can be less stringent. This allows for simpler and more robust system designs with lower upfront and operational costs. The choice of components directly reflects this end-goal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" CVD component configuration depends entirely on the intended application.
- If your primary focus is advanced research: Prioritize a flexible gas delivery system and a reactor that allows for easy modification to test different chemistries and conditions.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing: Emphasize component reliability, process repeatability, and a robust, automated exhaust and safety system to ensure uptime and operator safety.
- If your primary focus is fundamental material science education: A simpler system with manual controls and basic vacuum and exhaust components may be sufficient and more instructive.
Ultimately, understanding how each component serves the overall process empowers you to select or design a system that perfectly matches your technical and economic goals.
Summary Table:
| CVD Component | Primary Function | Key Parts Included |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Dispensing System | Delivers precise amounts of reactant precursors | Gas sources, valves, mass flow controllers |
| Reactor Chamber | Heats the substrate to enable the chemical reaction | Chamber, substrate holder (susceptor), heating system |
| Exhaust System | Removes byproducts and controls chamber pressure | Vacuum pumps, pressure controllers, scrubbers |
Ready to Build Your Ideal CVD System?
Understanding the components is the first step; integrating them into a reliable, high-performance system is the next. KINTEK excels at this.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and specialized CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements—whether for advanced research, high-volume manufacturing, or education.
Let's discuss your project goals and build a CVD solution tailored for your success.
Contact our experts today to get started!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of CVT equipment in growth of CrSb crystals? High-Purity Single Crystal Growth
- How does a mass flow controller (MFC) improve MoS2 quality? Achieve Precision in CVD Synthesis
- What are the characteristics of the coating film produced by CVD? Achieve Superior Thin Films for Your Applications
- What factors contribute to the high cost of CVD processes? Uncover Key Drivers and Cost-Saving Insights
- What industries commonly use PVD and CVD? Discover Key Applications in Tech and Manufacturing
- What is chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and how does it work? Discover High-Performance Film Growth for Your Lab
- What are the environmental concerns related to CVD? Managing Risks in Thin Film Coating
- Why is high-precision gas flow control essential for the CVD of graphene-palladium? Master Material Quality Control



















