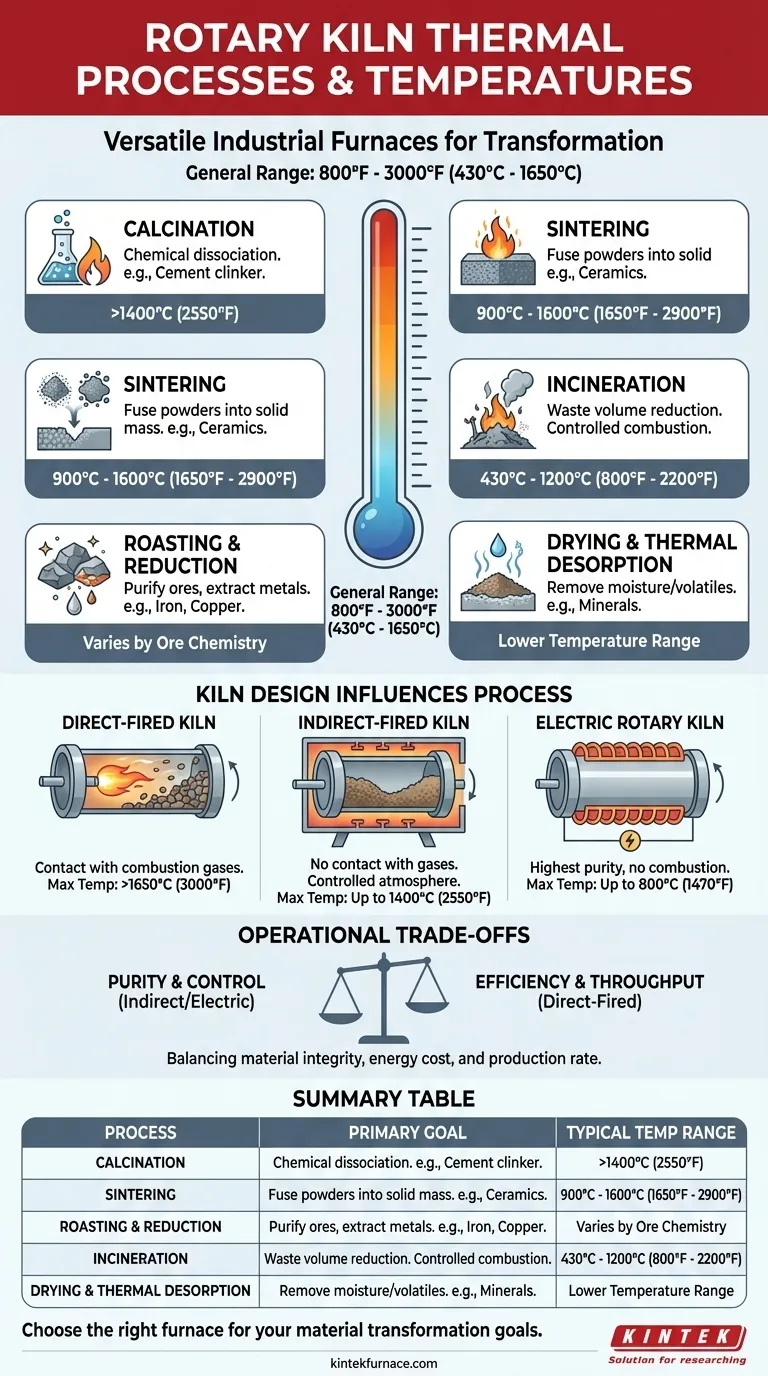
At their core, rotary kilns are versatile industrial furnaces that perform a range of thermal processes, most commonly calcination, sintering, roasting, incineration, and drying. The specific operating temperature is dictated entirely by the material and the desired chemical or physical transformation, generally falling within a wide range of 800°F to 3000°F (430°C to 1650°C).
The fundamental takeaway is that a rotary kiln is not a one-size-fits-all device. The process defines the temperature, and together they dictate the kiln's design—from its heating method to its material handling capabilities—to achieve a specific industrial outcome.

The Core Thermal Processes in a Rotary Kiln
A rotary kiln's primary function is to facilitate continuous, high-temperature reactions by tumbling material through a heated, rotating cylinder. This ensures uniform heat exposure and consistent processing.
Calcination: Driving Chemical Reactions
Calcination uses high heat to cause a material's chemical dissociation. It's about breaking down compounds, not just removing water.
The most prominent example is in the cement industry, where a mixture of limestone and clay is heated to over 1400°C to produce clinker, the primary component of Portland cement.
Sintering: Creating a Solid Mass
Sintering heats powdered materials to a point just below melting, causing the particles to fuse together into a solid, coherent mass.
This process is critical in the ceramics and refractory industries for firing bricks and activating clays, typically at temperatures between 900°C and 1600°C.
Roasting & Reduction: Purifying Ores
In mining and metallurgy, roasting is used to heat ores to remove impurities or prepare them for further processing.
Reduction is a specific pyrometallurgical process used to extract metals like iron, nickel, and copper from their ores at high temperatures.
Incineration: Managing Waste
Incineration is the controlled combustion of materials, primarily used in waste management to reduce the volume of urban, industrial, or medical waste.
This process transforms solid waste into ash, flue gas, and heat, typically operating in the 800°F to 2,200°F range.
Drying & Thermal Desorption: Removing Volatiles
This is one of the lower-temperature applications for rotary kilns. Its goal is simply to remove moisture or other volatile compounds from a material.
It's common in mineral processing for materials like gypsum, bauxite, and silica sand before they undergo higher-temperature treatments.
How Kiln Design Influences Temperature and Process
The way a kiln generates and applies heat is a critical design choice that depends entirely on the process requirements, especially the need for a controlled atmosphere.
Direct-Fired Kilns
In a direct-fired kiln, hot combustion gases flow directly over and through the material being processed.
This is highly efficient for bulk processes like cement and lime production, where the material is not sensitive to contamination from flue gas. These kilns can achieve the highest temperatures needed for calcination.
Indirect-Fired Kilns
Here, the rotating drum is heated externally. The material inside never comes into contact with the combustion flame or gases.
This design is essential for processes requiring a controlled atmosphere or where material purity is paramount, such as pyrolysis, catalyst surface treatment, and specialty chemical production. They typically operate up to 1400°C.
Electric Rotary Kilns
Electric kilns offer the highest level of control and purity, as there is no combustion at all. They are extremely efficient, with thermal efficiency often exceeding 95%.
Their precise temperature control makes them ideal for high-value or sensitive materials, though they are often limited to operating temperatures up to around 800°C.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Choosing the right thermal process involves balancing efficiency, material integrity, and cost. Temperature is just one variable in a complex equation.
Purity vs. Efficiency
Direct firing is the most thermally efficient method for heating bulk solids, but it risks contaminating the product with combustion byproducts. Indirect firing preserves purity at the cost of some thermal efficiency and mechanical complexity.
Temperature vs. Residence Time
Achieving the desired reaction is a function of both temperature and the time the material spends in the kiln (residence time). A higher temperature may shorten the required residence time, but it also increases energy costs and risks overheating or melting the material.
Process Control vs. Throughput
Simpler, direct-fired kilns are workhorses built for maximum throughput of a single product. More complex indirect or electric kilns offer superior control over atmosphere and temperature profiles but may have lower throughput rates.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal process is the one that achieves the necessary material transformation reliably and economically.
- If your primary focus is bulk material transformation (like cement or lime): Direct-fired kilns are the industry standard for high-temperature calcination, operating above 1400°C for maximum efficiency.
- If your primary focus is material purity (like catalysts or specialty chemicals): Indirect-fired or electric kilns provide the necessary atmospheric control and precise heating required for sensitive reactions.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction: Incineration in a direct-fired kiln is the most common method for controlled combustion and waste destruction.
- If your primary focus is ore purification or metal extraction: Roasting and reduction processes are used in metallurgy, with temperatures tailored specifically to the chemistry of the ore.
Ultimately, successful thermal processing relies on matching the unique properties of your material to the specific capabilities of the kiln and its heating method.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Typical Operating Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Calcination | Chemical dissociation (e.g., cement clinker production) | >1400°C (2550°F) |
| Sintering | Fuse powdered materials into a solid mass (e.g., ceramics) | 900°C - 1600°C (1650°F - 2900°F) |
| Roasting/Reduction | Purify ores or extract metals (e.g., iron, copper) | Varies by ore chemistry |
| Incineration | Reduce waste volume via controlled combustion | 430°C - 1200°C (800°F - 2200°F) |
| Drying/Thermal Desorption | Remove moisture or volatiles (e.g., minerals) | Lower temperature range |
| Kiln Type | Atmosphere Control | Max Typical Temperature |
| Direct-Fired | Material contacts combustion gases | >1650°C (3000°F) |
| Indirect-Fired | No contact with combustion gases | Up to 1400°C (2550°F) |
| Electric | Highest purity, no combustion | Up to 800°C (1470°F) |
Ready to Optimize Your Thermal Process?
Choosing the right furnace is critical to achieving your material transformation goals, whether you need the high-throughput efficiency of a direct-fired system or the precise atmospheric control of an indirect or electric kiln.
KINTEK is your trusted partner in advanced thermal processing solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of lab and industrial furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Our high-temperature furnaces are all customizable to meet your unique process requirements, ensuring optimal performance for calcination, sintering, roasting, and more.
Let's discuss your application. Contact our experts today to find the perfect kiln or furnace solution for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource



















