In short, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements are chosen for their ability to operate reliably at extremely high temperatures where traditional metallic elements would fail. They combine this high-temperature performance with excellent energy efficiency, operational cleanliness, and significant design flexibility, making them a cornerstone technology for industrial furnaces and kilns.
While many heating technologies exist, silicon carbide elements solve a specific problem: they provide clean, controllable, and efficient radiant heat at temperatures far beyond the capabilities of metal alloys. This makes them the default choice for demanding high-temperature electric heating processes.
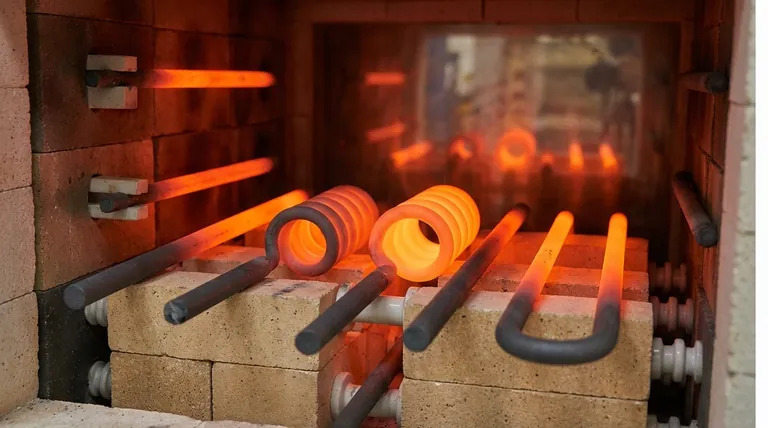

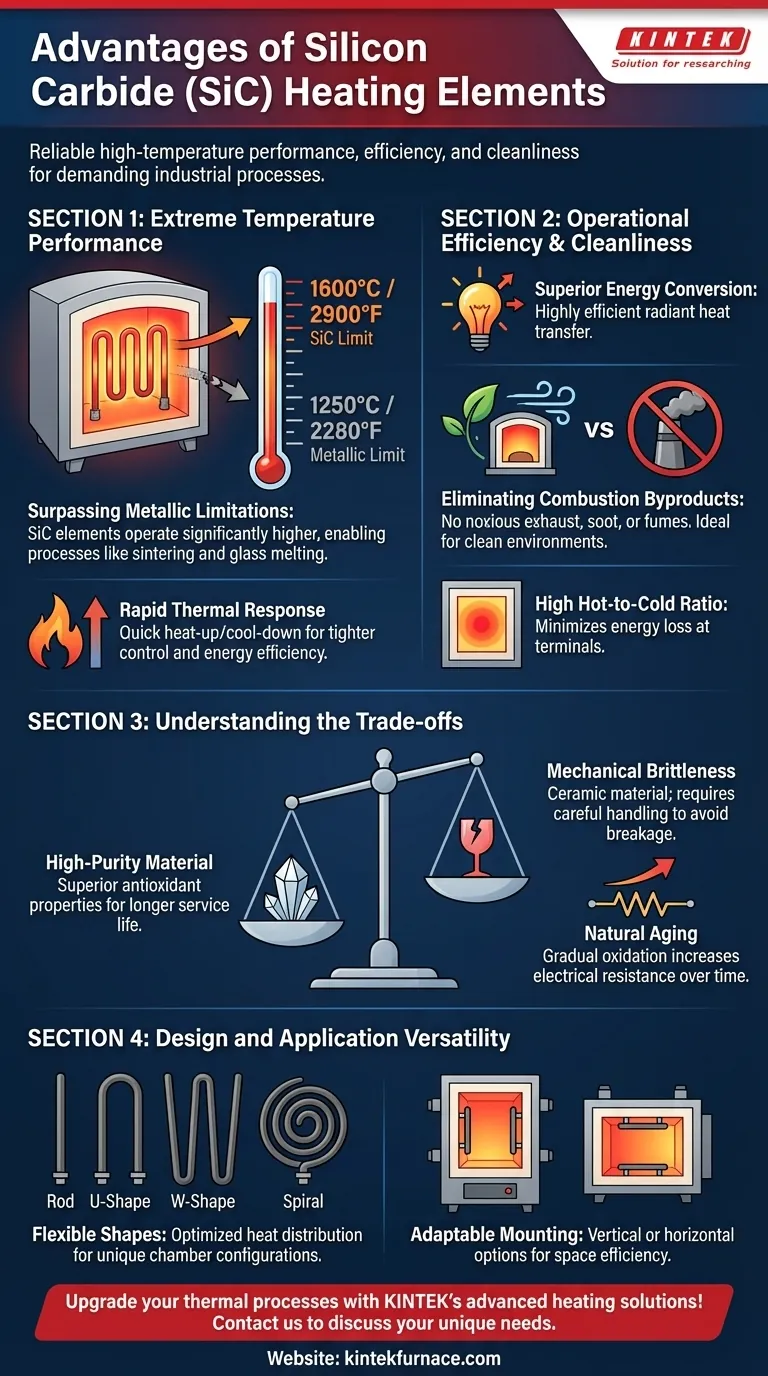
The Core Advantage: Extreme Temperature Performance
The primary reason to select silicon carbide is its ability to function in extreme heat. This capability fundamentally separates it from other common electric heating technologies.
Surpassing Metallic Element Limitations
Traditional heating elements, typically made from nickel-chromium (NiCr) or iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl) alloys, have maximum operating temperatures that top out around 1250°C (2280°F). Silicon carbide elements can operate at significantly higher surface temperatures, often reaching 1600°C (2900°F) or more.
Enabling High-Temperature Processes
This high-temperature tolerance is not just an incremental improvement; it enables entire industrial processes that are otherwise impossible with electric heat. This includes applications like sintering technical ceramics, melting glass, and running high-temperature laboratory furnaces.
Rapid Thermal Response
Silicon carbide has a relatively low thermal mass, allowing the elements to heat up and cool down quickly. This rapid response provides tighter process control, reduces cycle times, and improves overall energy efficiency by minimizing wasted heat during furnace cooldown.
Operational Efficiency and Cleanliness
Beyond raw temperature, SiC elements offer distinct operational benefits that simplify system design and reduce long-term costs.
Superior Energy Conversion
SiC elements work by radiating heat directly when an electric current is passed through them. This method of heat transfer is highly efficient, ensuring that the majority of electrical energy is converted directly into usable thermal energy within the furnace chamber.
Eliminating Combustion Byproducts
As an electric heating source, SiC elements produce no noxious exhaust, soot, or fumes. This eliminates the need for fuel storage, fuel lines, and complex ventilation systems, creating a cleaner and safer working environment. It is ideal for processes where atmospheric purity is critical.
High Hot-to-Cold Ratio
These elements can be manufactured with a very high resistance difference between the hot zone (the heating section) and the cold ends (the terminals). This concentrates the heat precisely where it is needed inside the furnace, minimizing energy loss at the terminal connections.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. Acknowledging the properties and limitations of silicon carbide is key to successful implementation and long service life.
The Importance of High-Purity Material
The quality of a SiC element is directly tied to its raw material. High-purity green silicon carbide powder creates a denser, more uniform element. This results in superior antioxidant properties and a longer, more predictable service life.
Mechanical Brittleness
Silicon carbide is a ceramic material. While it is incredibly strong under high temperatures, it is also brittle at room temperature. Care must be taken during installation and maintenance to avoid mechanical shock, which can cause the elements to crack or break.
Natural Aging and Resistance
Over their operational life, SiC elements gradually oxidize. This process slowly increases their electrical resistance. Power supply systems must be designed to accommodate this change by providing progressively higher voltage to maintain the desired power output and temperature.
Design and Application Versatility
Silicon carbide is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It can be adapted to fit the specific geometry and requirements of a wide range of heating equipment.
Flexible Shapes and Sizes
Manufacturers can produce SiC elements in various shapes, including rods, U-shapes, W-shapes, and spirals. This allows furnace designers to optimize heat distribution and fit elements into unique chamber configurations.
Adaptable Mounting Options
Most SiC element types can be mounted either vertically or horizontally. This provides significant flexibility in furnace design, allowing for the most efficient use of space and optimal heat transfer to the product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heating element depends entirely on your process requirements.
- If your primary focus is reaching temperatures above 1250°C (2280°F): Silicon carbide is the standard and most reliable choice, as metallic elements are not suitable.
- If your primary focus is process cleanliness and atmospheric control: SiC provides precise, contaminant-free electric heat without the byproducts associated with gas combustion.
- If your primary focus is rapid cycling and process efficiency: SiC's fast thermal response can significantly reduce cycle times and lower energy costs compared to slower, higher-mass heating systems.
Ultimately, choosing silicon carbide is a decision to prioritize high-temperature capability and clean, efficient performance for your most demanding thermal processes.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Temperature Performance | Operates up to 1600°C, surpassing metal alloys | Sintering ceramics, high-temperature labs |
| Energy Efficiency | High radiant heat conversion, rapid thermal response | Reducing cycle times and energy costs |
| Operational Cleanliness | No combustion byproducts, contaminant-free | Processes requiring atmospheric purity |
| Design Flexibility | Various shapes and mounting options | Custom furnace configurations |
Upgrade your thermal processes with KINTEK's advanced heating solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for superior efficiency and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism



















